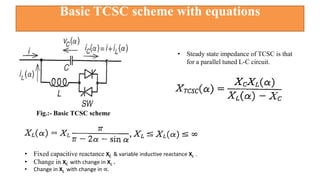
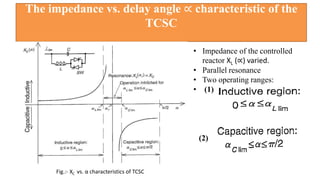
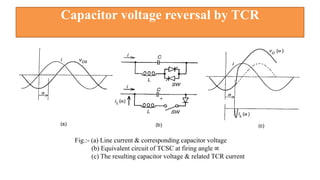
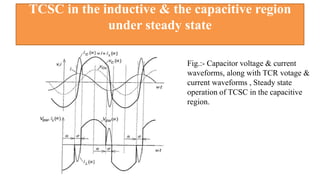
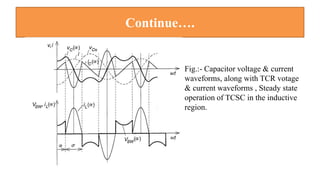
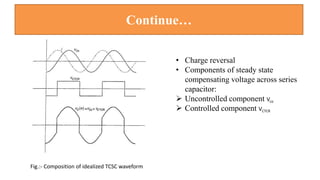
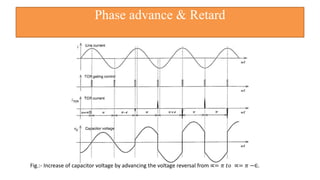
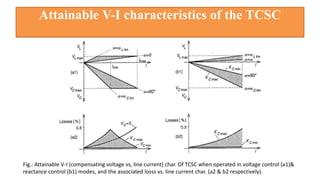
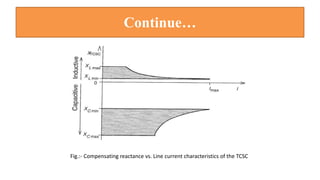
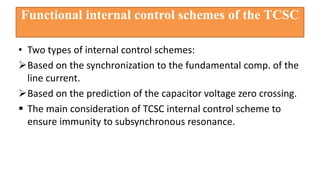
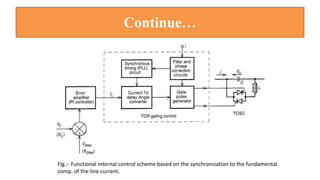
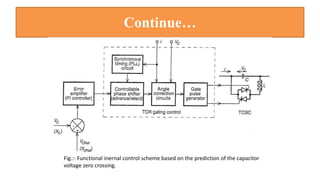
This document provides an overview of the thyristor controlled series capacitor (TCSC). It begins with the basic TCSC scheme and equations showing how the variable inductive reactance XL can change the capacitive reactance XC. It then discusses the impedance characteristics of the TCSC and how the capacitor voltage is reversed by the thyristor controlled reactor (TCR). Next, it examines the TCSC operating in the capacitive and inductive regions and how it can provide phase advance or retard. The document also covers the attainable voltage-current characteristics and harmonic voltage generation in the TCSC. It describes the functional internal control schemes and concludes with notes on design considerations.