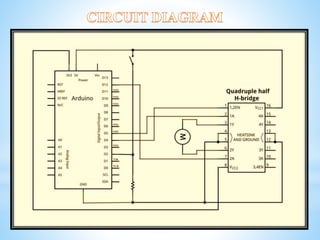
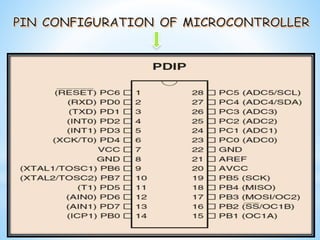
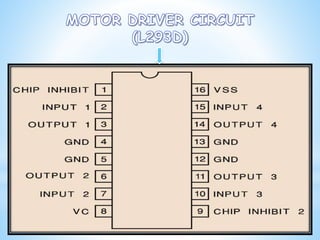
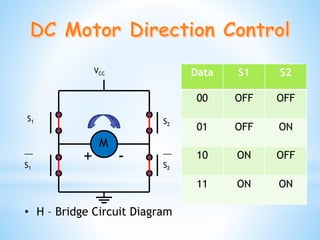
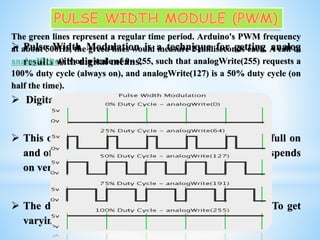
This document discusses a project to control the speed of a DC motor using a microcontroller and pulse width modulation. Specifically, it aims to vary the speed-torque relationship of a DC motor electronically using a microcontroller to generate high and low pulses that control motor speed. Pulse width modulation is identified as a technique that can be used to simulate variable voltages through variations in pulse width to achieve variable analog speed control. The document outlines the components used, including an H-bridge circuit and microcontroller, and discusses some limitations such as susceptibility to electromagnetic interference.