1) The document discusses various theories of third molar impaction including orthodontic, phylogenic, Mendelian, and pathological theories.
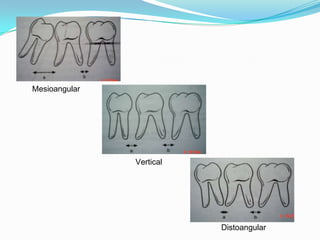
2) It also covers classifications of third molar impaction based on angulation, position, eruption state, and root morphology. Historical classifications including Winter's and Pell & Gregory are summarized.
3) Surgical considerations for impacted third molar removal are outlined, including pre-operative assessment, radiographic evaluation, difficulty indices, surgical anatomy, and mucoperiosteal flap design. Complications of retained impacted teeth are also briefly mentioned.



![Theories of impaction
2) Phylogenic theory: Nature tries to eliminate the disused organs
i.e., use makes the organ develop better, disuse causes slow
regression of organ.
[More-functional masticatory force – better the development of
the jaw]
Due to changing nutritional habits of our civilization, use of
large powerful jaws have been practically eliminated.
Thus, over centuries the mandible and maxilla decreased in size
leaving insufficient room for third molars.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mandibular3rdmolarimpactions-130421031302-phpapp02/85/Mandibular-3rd-molar-impactions-4-320.jpg)