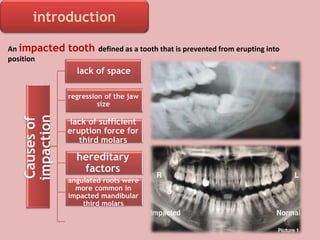
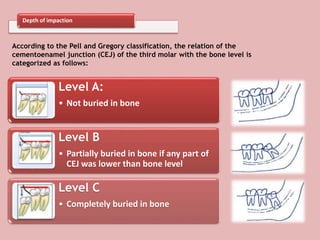
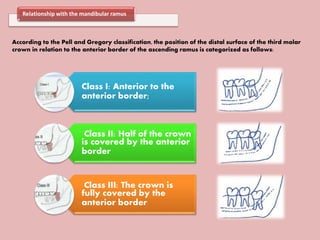
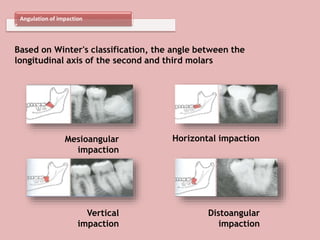
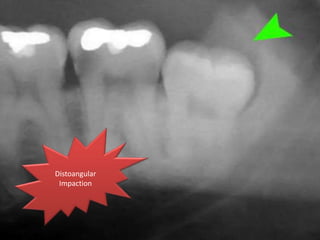
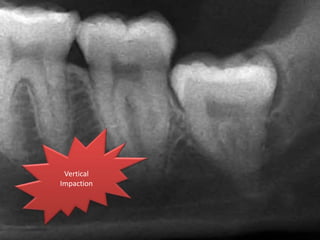
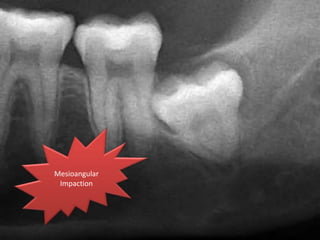
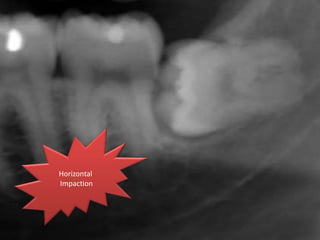
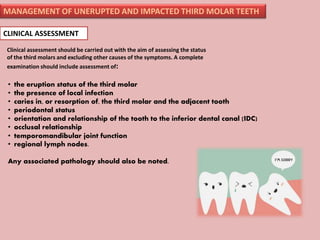
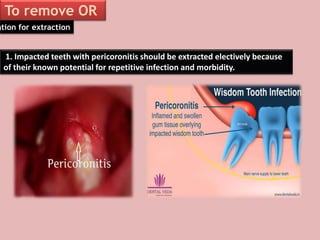
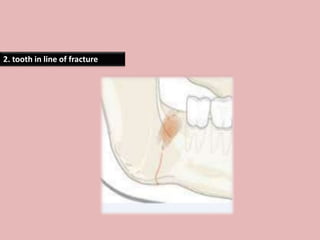
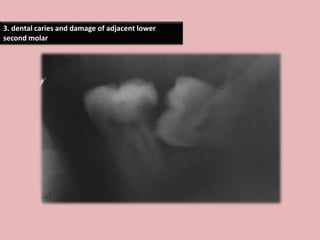
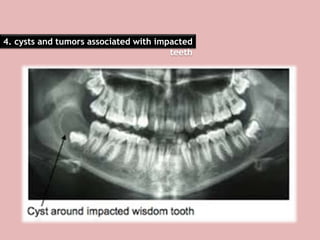
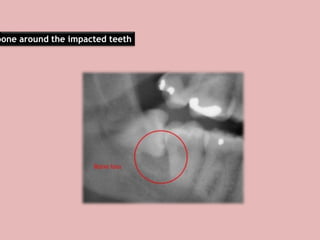
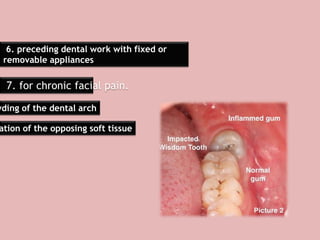
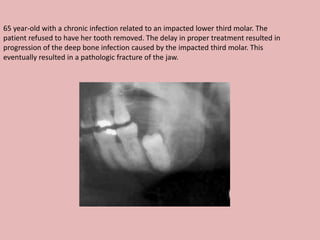
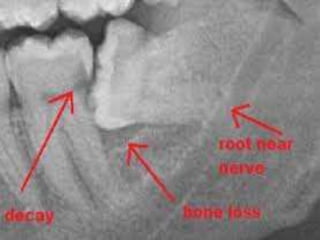
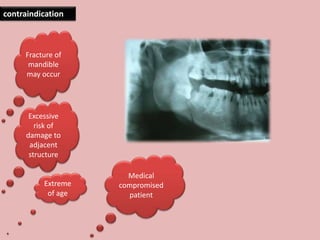
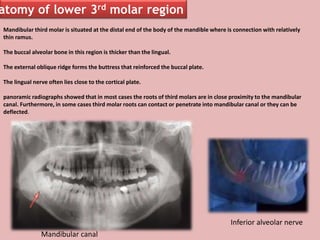
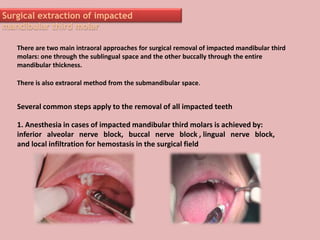
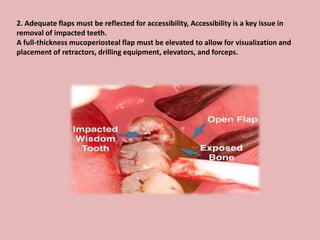
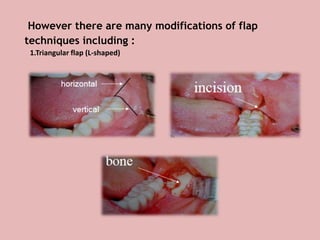
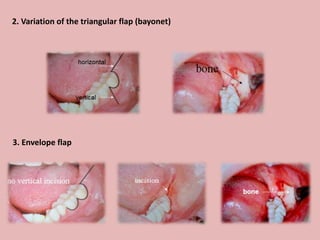
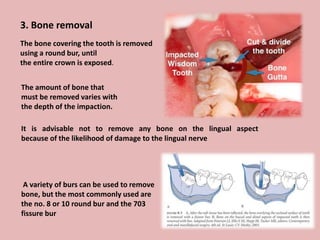
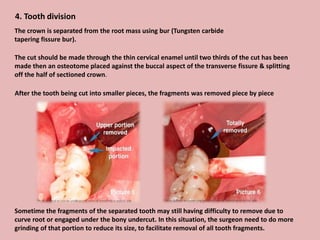
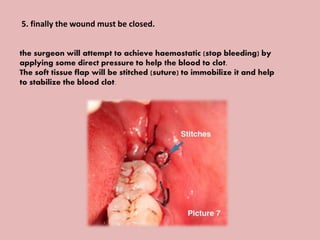
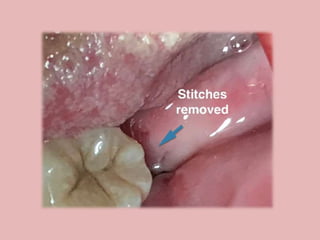
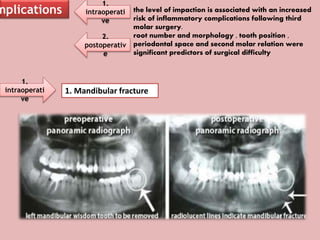
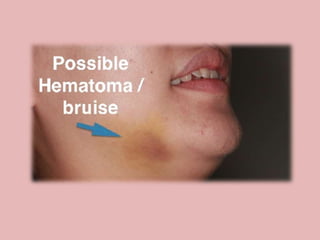
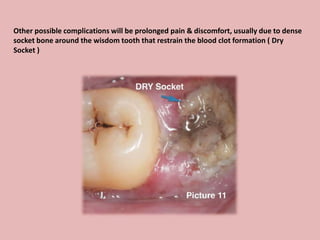
A 65-year-old patient presented with a chronic infection related to an impacted lower third molar. Despite recommendations for removal, the patient refused treatment, resulting in progression of the deep bone infection and a pathologic fracture of the jaw. Factors such as age, medical comorbidities, proximity to adjacent structures, and risk of damage during surgery are considered when determining if an impacted third molar should be removed. Surgical extraction involves raising flaps, removing bone, dividing and extracting the tooth, and closing the wound. Postoperative care may include antibiotics, analgesics, and steroids. Complications can be intraoperative such as nerve injury, fracture, or bleeding, or postoperative like pain, swelling, and infection.