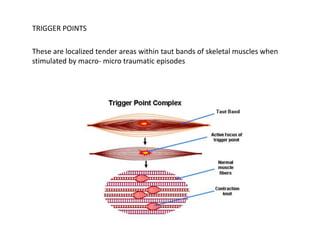
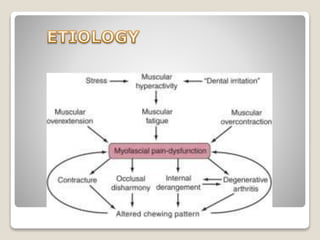
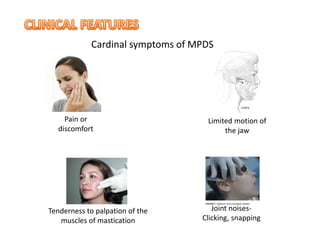
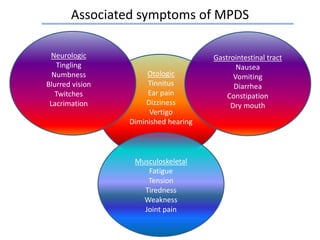
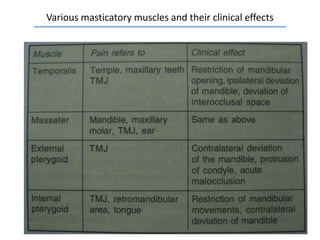
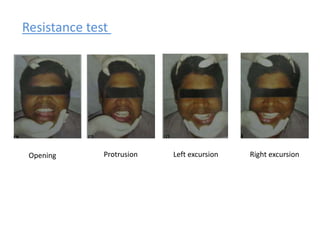
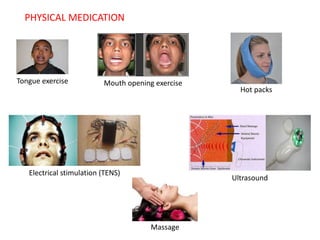
MPDS, or myofascial pain disorder syndrome, is a pain disorder characterized by unilateral pain referred from trigger points in muscles of the head and neck. These trigger points are localized tender areas within taut muscle bands caused by micro- or macro-trauma to the musculoskeletal system. Accumulation of chemicals like lactic acid and prostaglandins in the muscles lowers the pain threshold, leading to MPDS symptoms like pain, limited jaw motion, and joint noises. Diagnosis involves assessing range of motion, palpating muscles for tenderness, and grading joint clicks. Treatment aims to inactivate trigger points, prevent recurrence, and correct perpetuating factors through therapies like physical modalities, anesthesia, pharmacotherapy, and occasionally