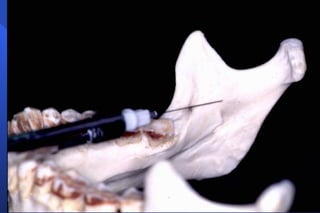
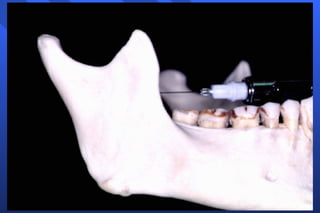
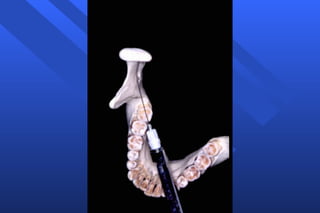
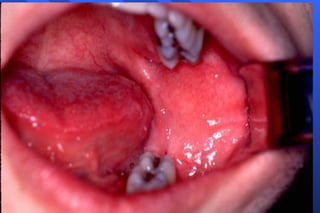
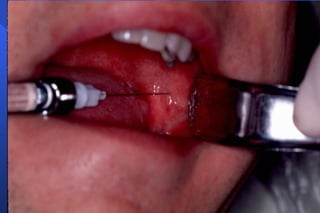
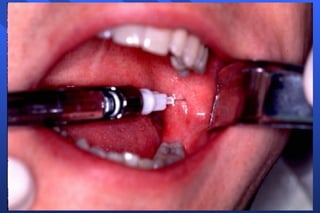
This document discusses techniques for mandibular anesthesia. It focuses on the inferior alveolar nerve block, which anesthetizes the inferior alveolar nerve, mental nerve, and incisive nerve. The technique involves locating anatomical landmarks like the coronoid notch and pterygomandibular raphe, then inserting the needle 1 cm above the occlusal plane of the mandibular posteriors and advancing it to the bone near the mandibular foramen to deposit the solution within 1 mm of the inferior alveolar nerve. Precautions are taken to avoid forceful bone contact. Failure can occur if the injection is too low or anterior, or due to accessory innervation. Complications include hematoma, tr