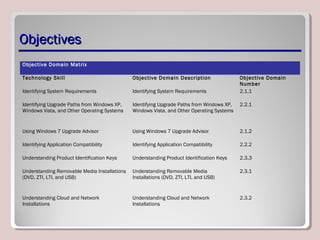
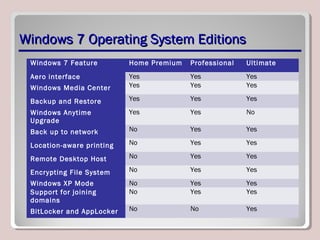
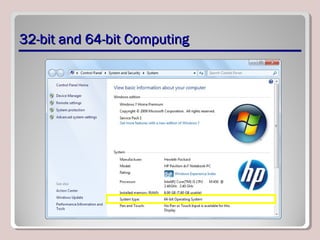
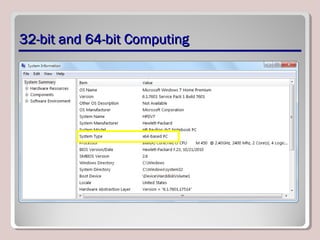
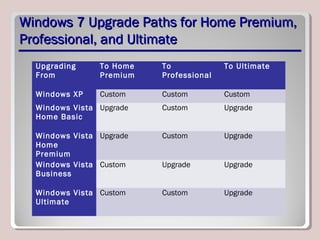
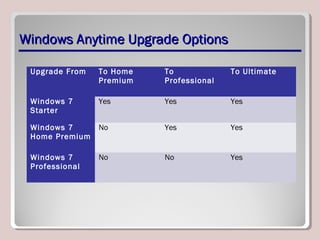
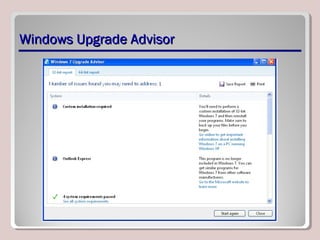
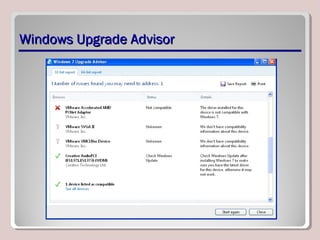
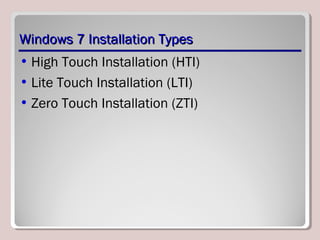
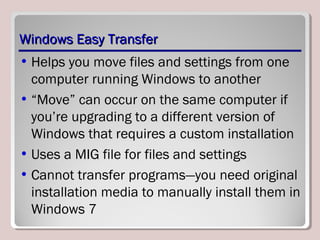
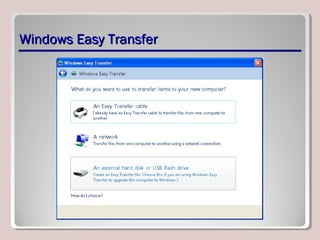
The document discusses introducing, installing, and upgrading Windows 7. It covers the different editions of Windows 7, system requirements, upgrade paths from previous versions of Windows, and installation methods including high touch, lite touch, and zero touch installations. It also discusses using the Windows Upgrade Advisor, application compatibility, product keys, and transferring files and settings between computers using Windows Easy Transfer.