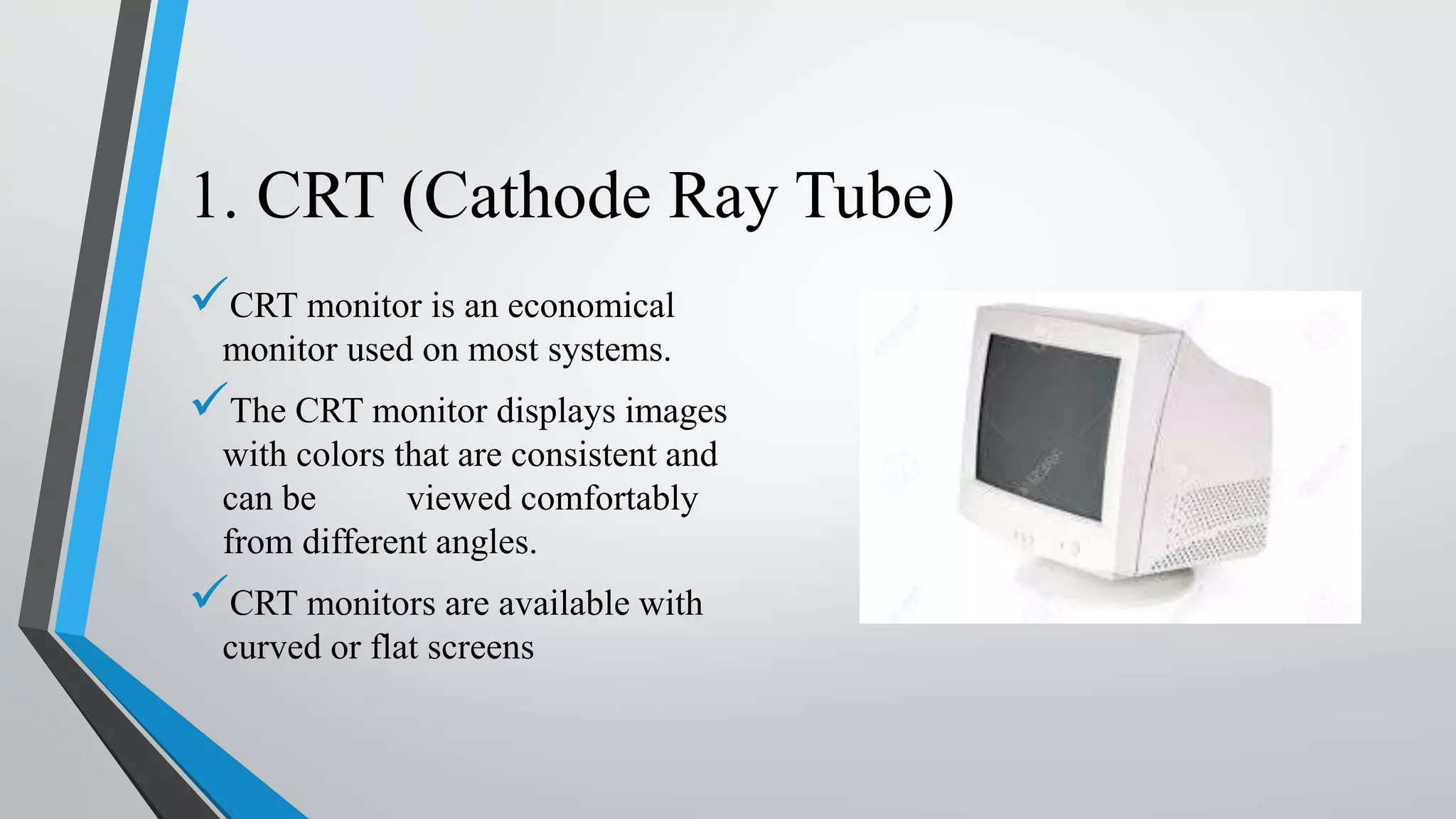
The document discusses different types of computer monitors and display technologies. It describes CRT monitors which use cathode ray tubes and are economical but can cause eye strain. Flat panel displays like LCD, LED, OLED are thinner and cause less eye strain but are more expensive. Other display technologies discussed include plasma display panels, digital light processing, electroluminescent displays, field emission displays, and nano-emissive displays. The document also covers different audio channel technologies including mono, stereo, and surround sound systems.