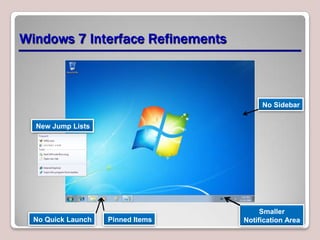
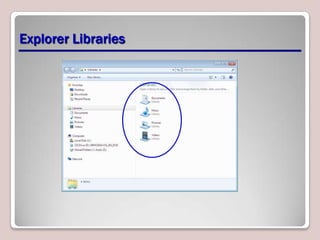
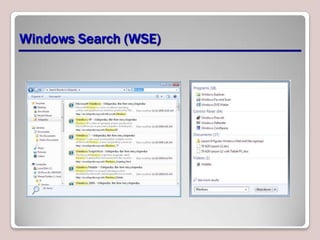
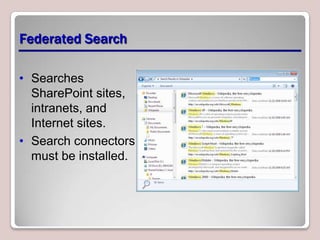
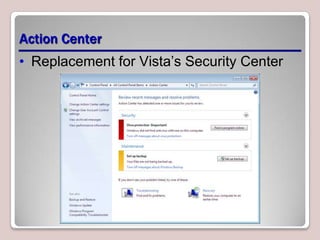
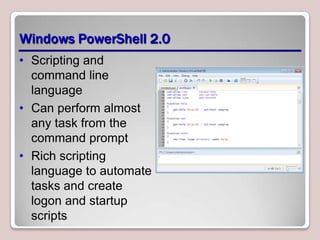
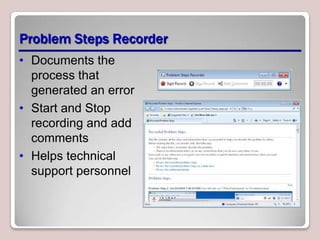
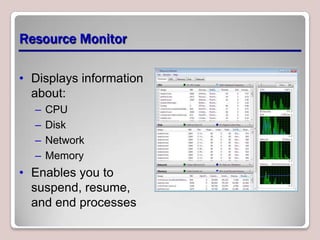
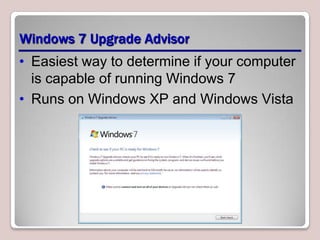
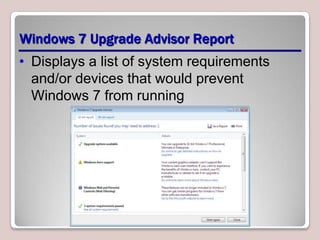
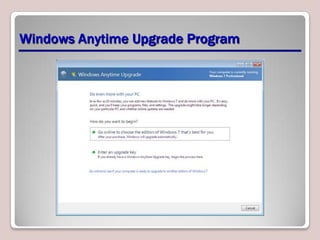
The document introduces Windows 7, outlining its interface refinements, new features, and six editions. Key highlights include enhanced desktop functionality, tools like the Action Center and BranchCache, and a detailed upgrade process from previous Windows versions. The Windows 7 Upgrade Advisor assists users in verifying hardware and software compatibility for installation.