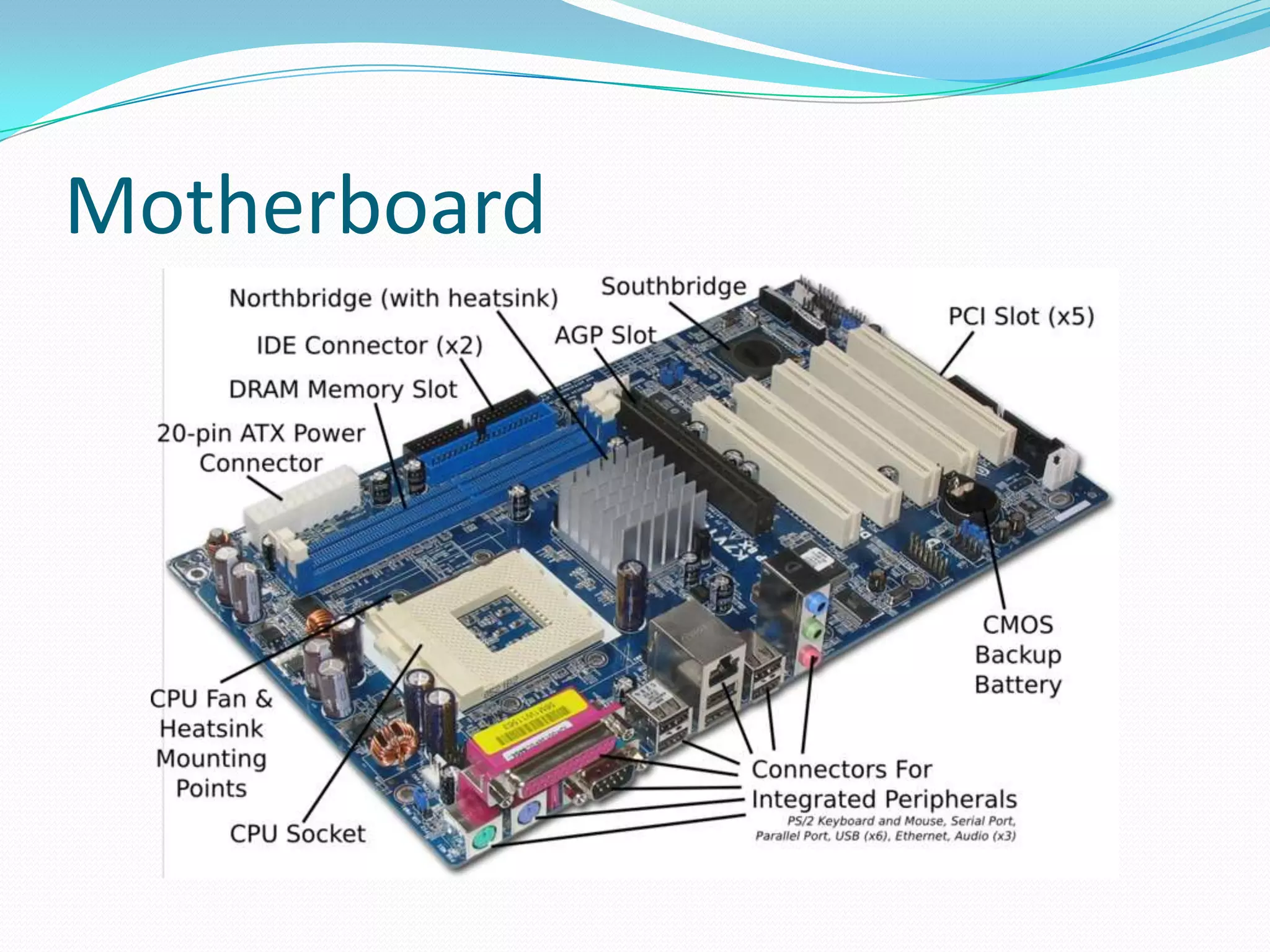
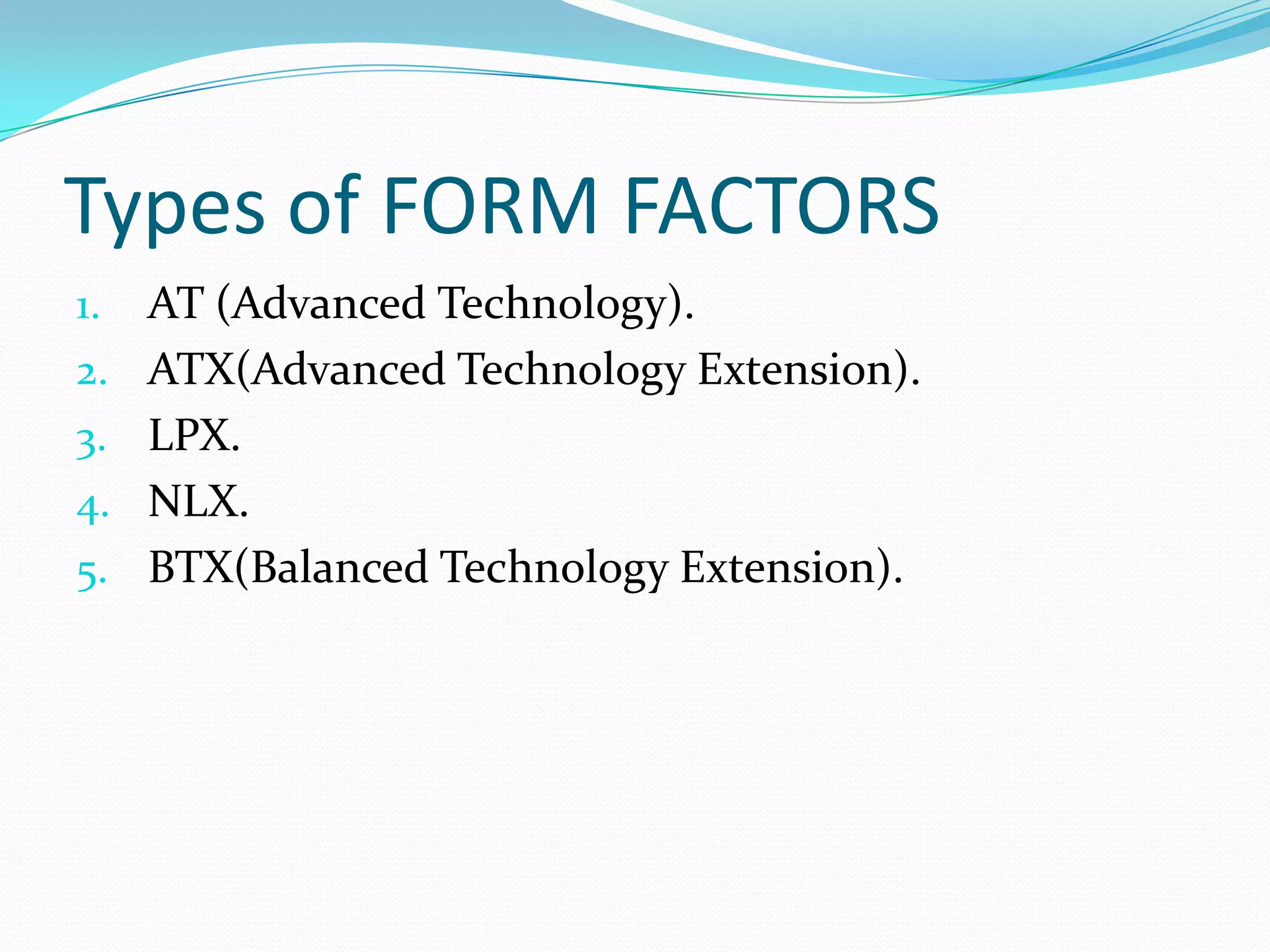
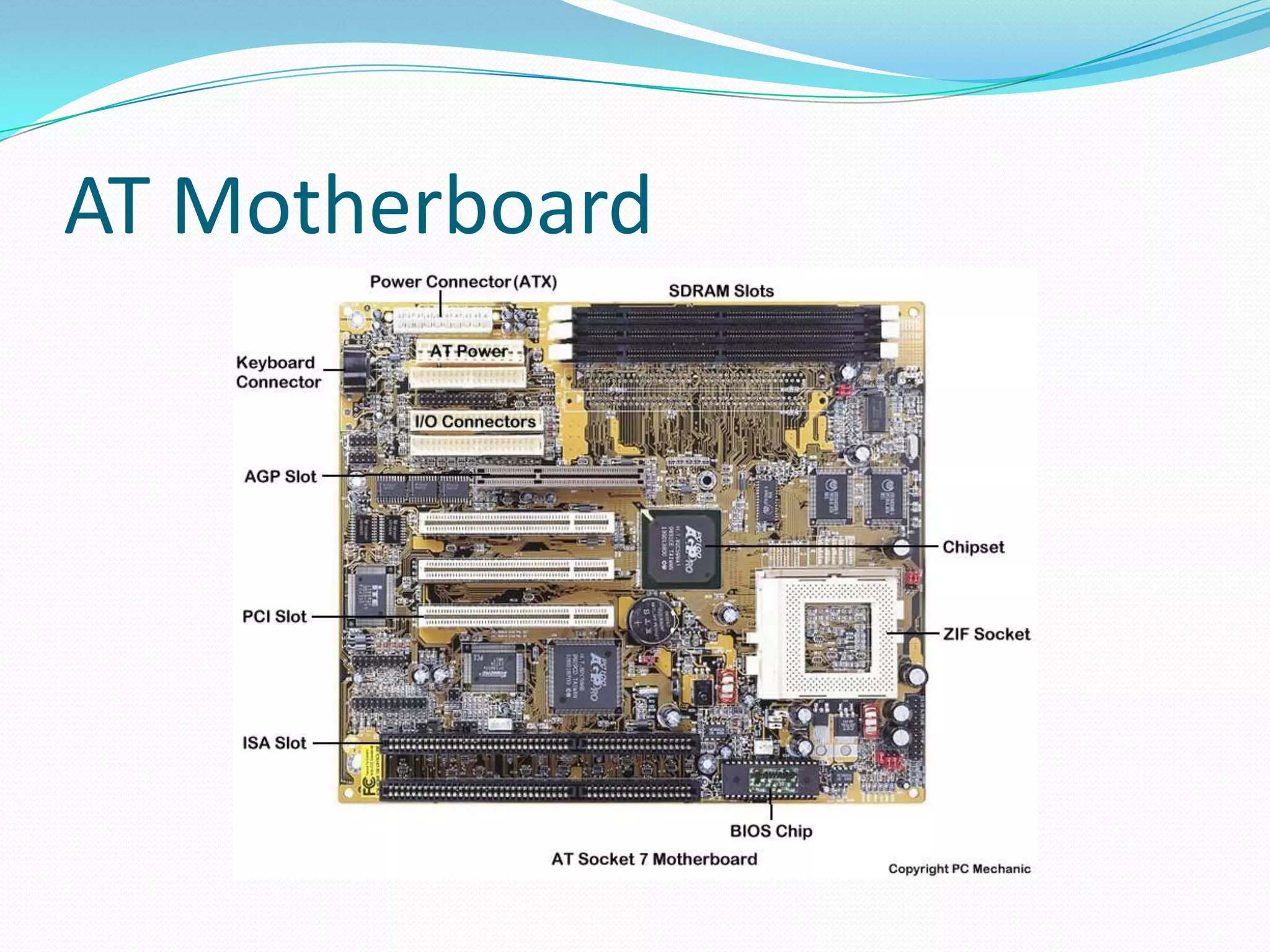
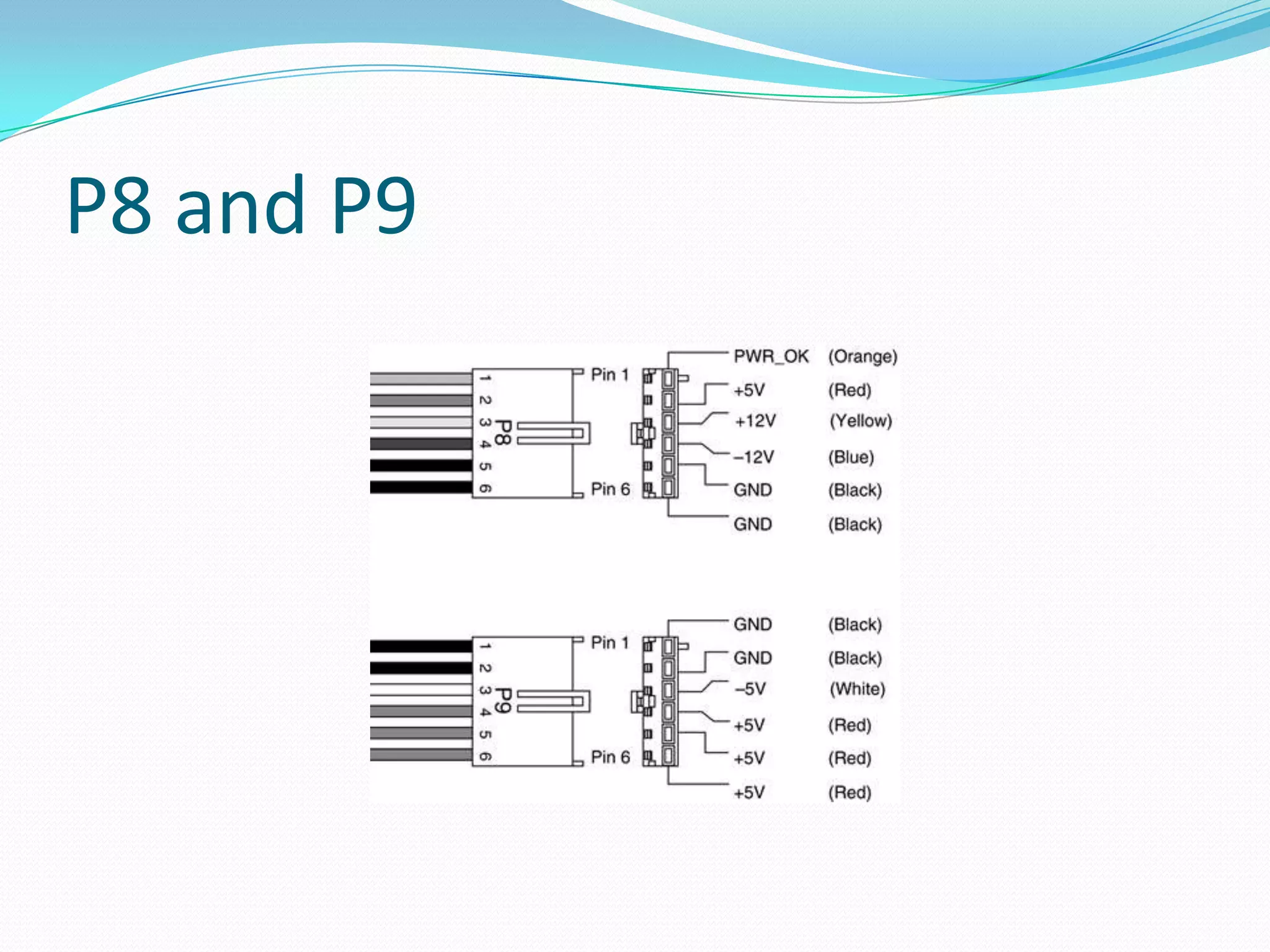
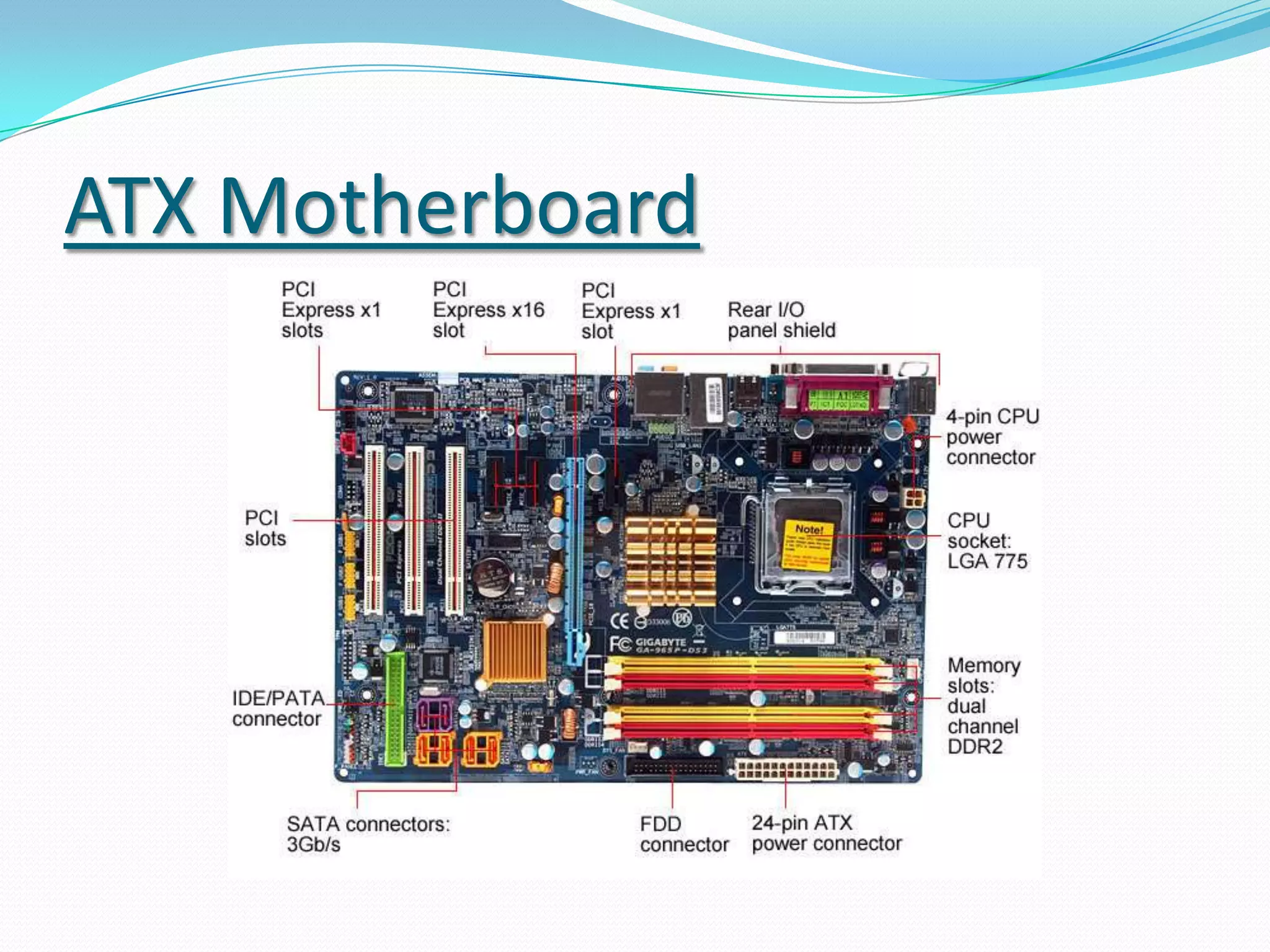
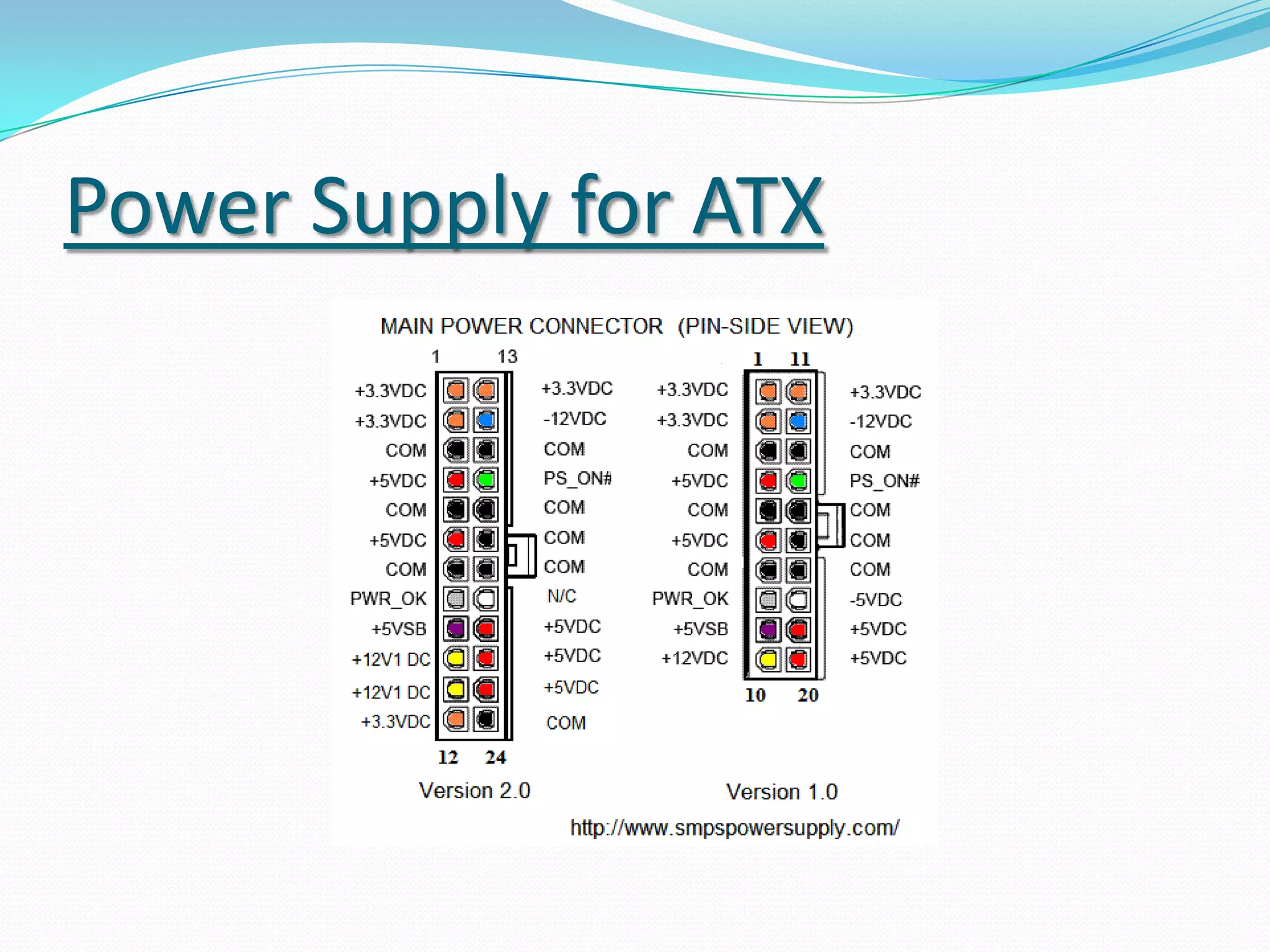
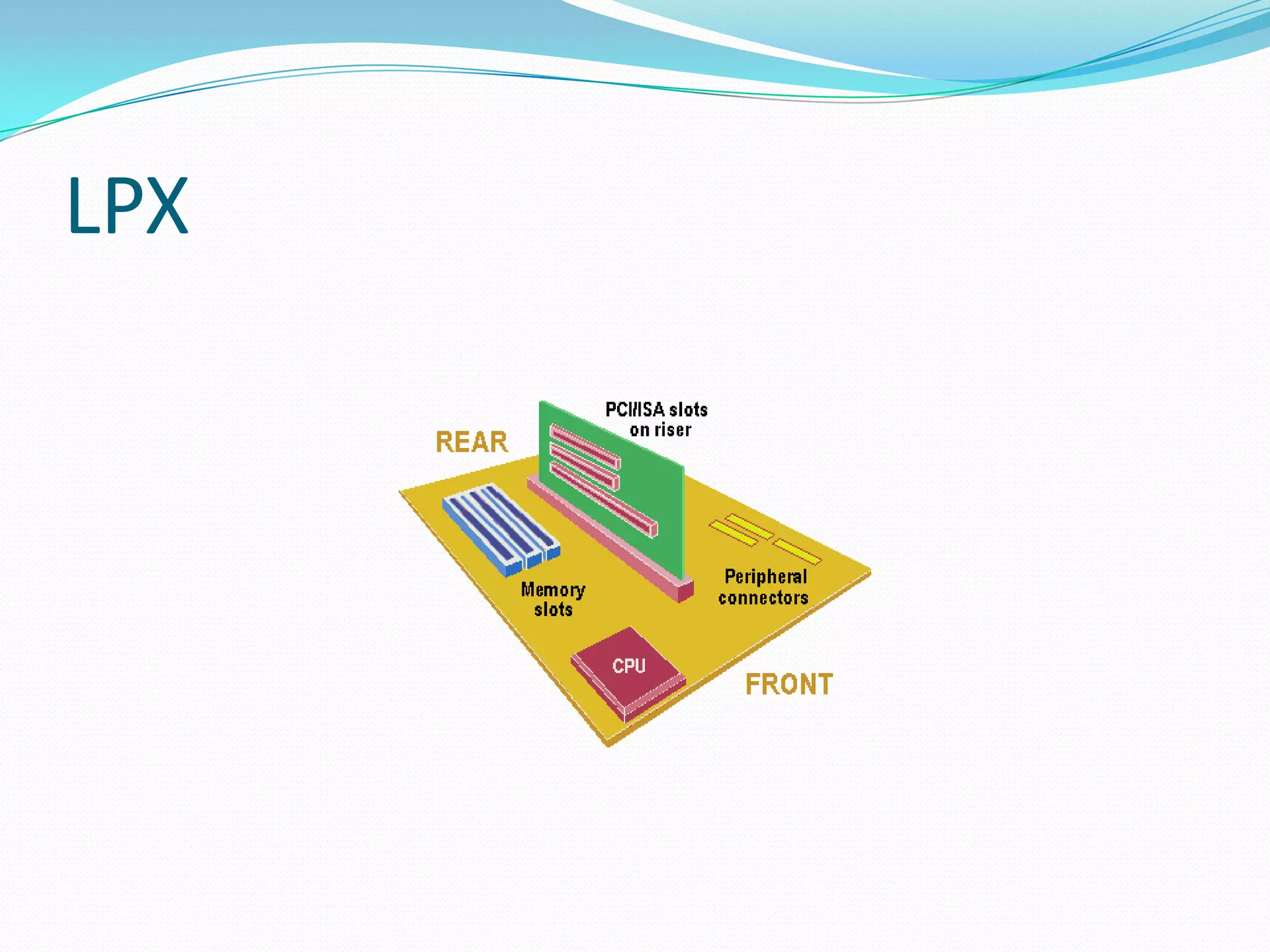
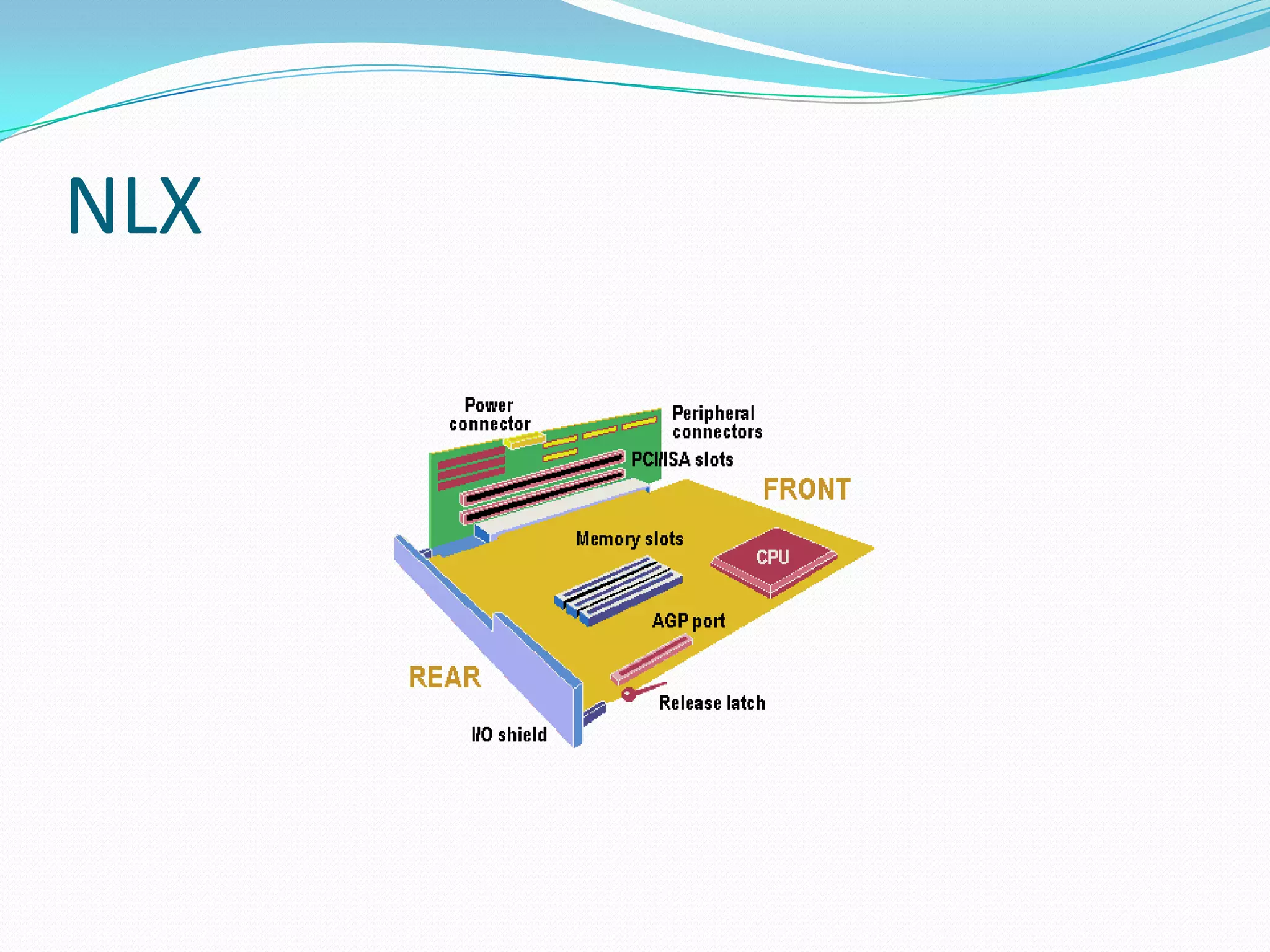
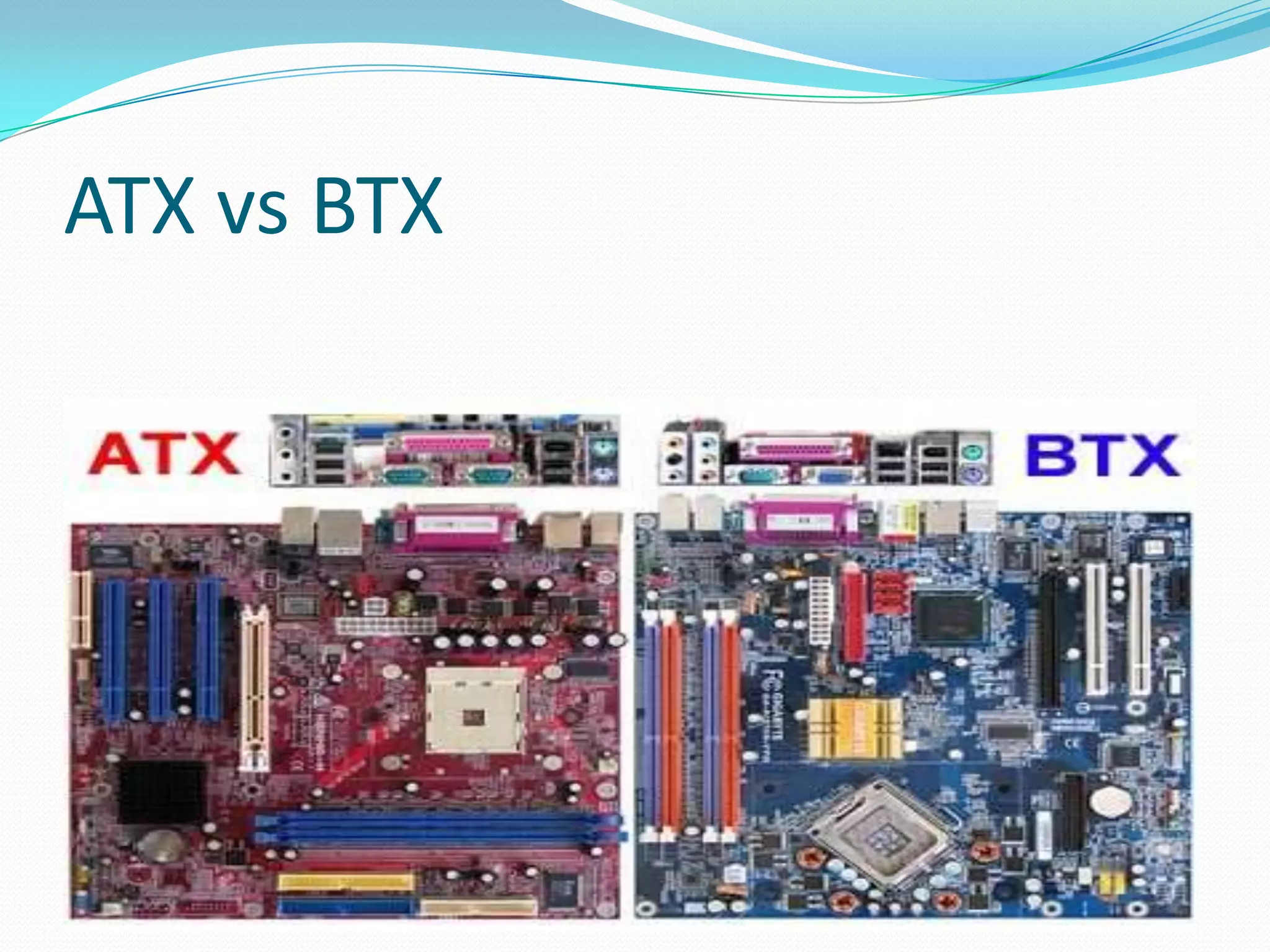
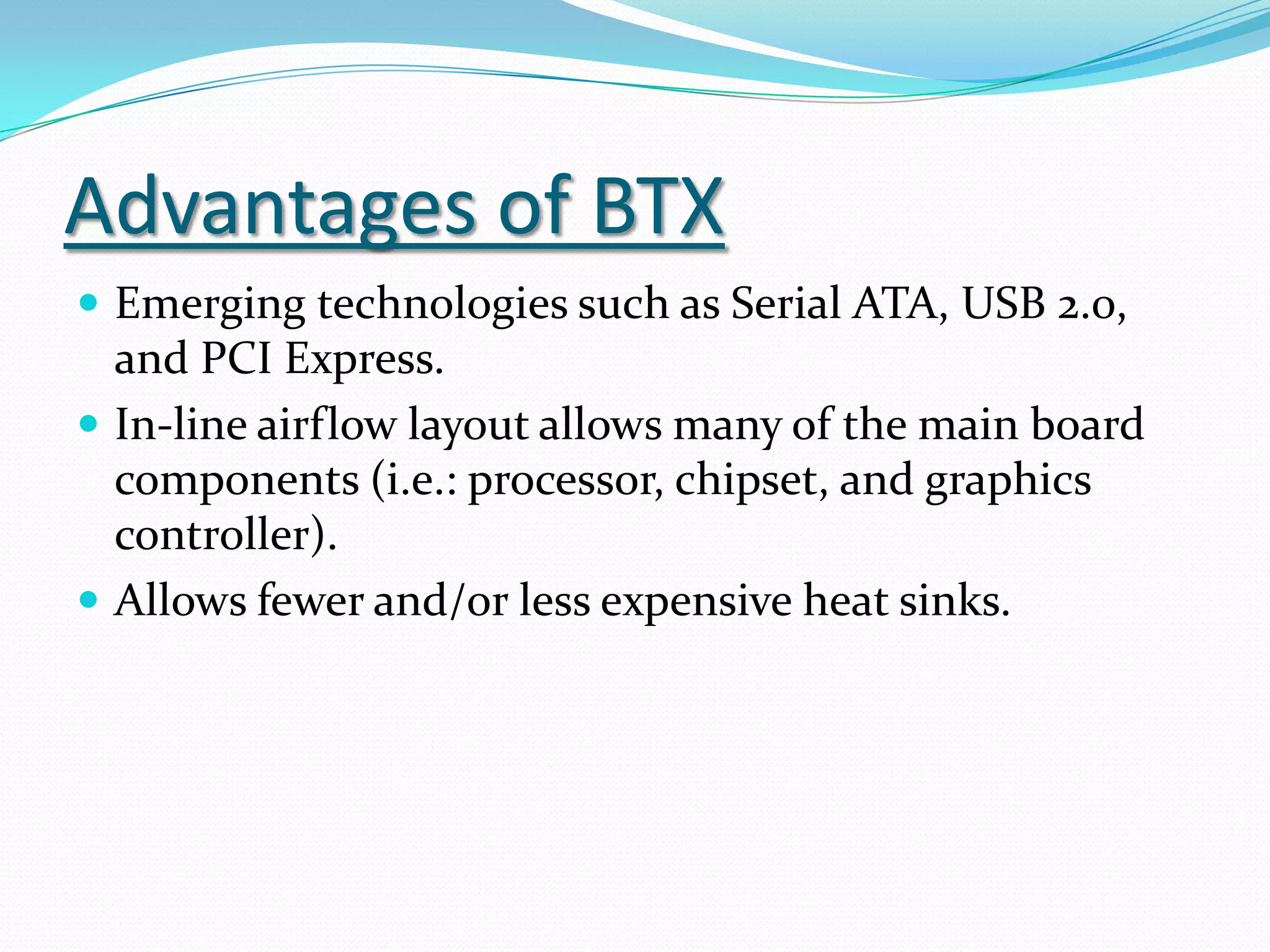
The document discusses different motherboard form factors including ATX, Micro ATX, Flex ATX, NLX, and BTX. It provides details on the size and key features of each form factor. For example, it states that ATX motherboards measure 305x244x10mm while Micro ATX measures 244x244x10mm. It also explains that newer form factors like BTX were designed for better airflow and easier component access compared to older styles like AT.