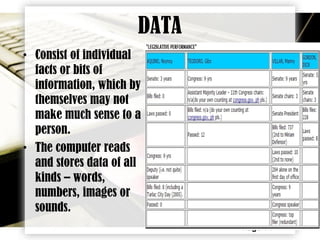
A computer system consists of four major parts: hardware, software, users, and data. Hardware refers to the physical components of the computer like processors and monitors. Software includes the programmed instructions that tell the computer what tasks to perform. Users are the people who operate computers. Data comprises the individual facts and pieces of information that are processed by the computer system.