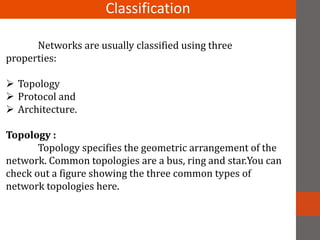
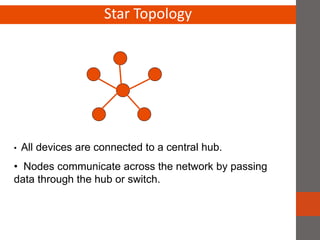
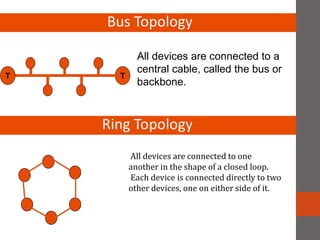
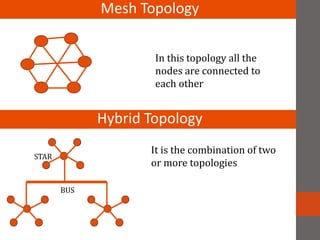
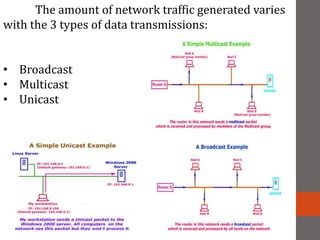
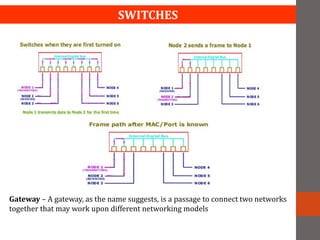
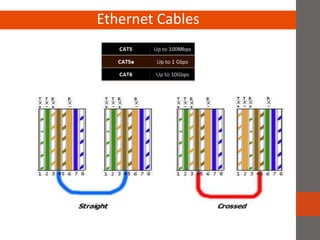
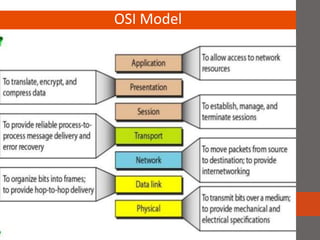
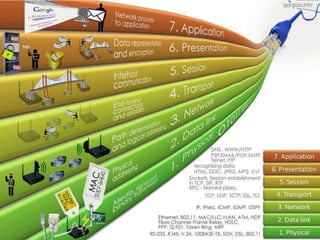
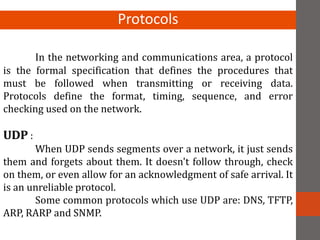
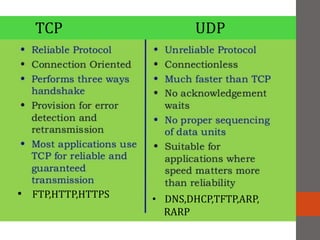
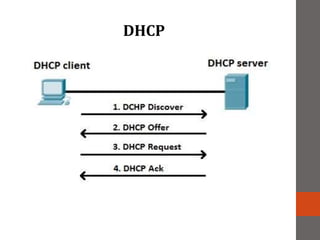
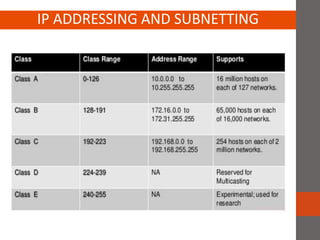
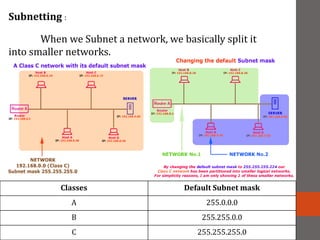
A network connects two or more computers together. Networks are classified based on their topology, protocols, and architecture. Common topologies include bus, ring, and star. Protocols like Ethernet and Token Ring define how computers communicate. Architectures are either peer-to-peer or client/server. Devices connect directly in peer-to-peer while clients rely on a central server in a client/server network.