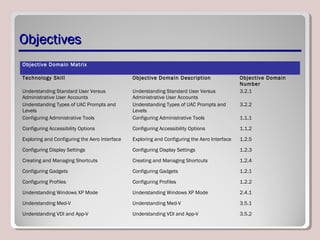
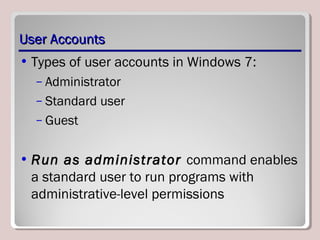
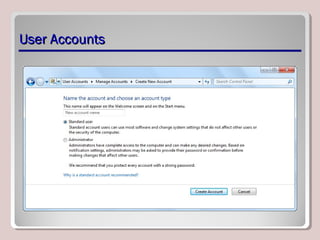
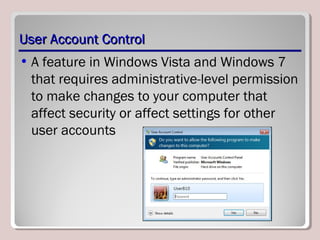
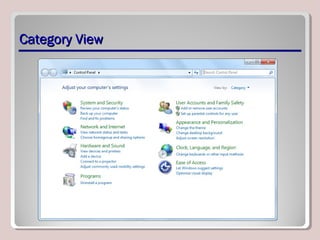
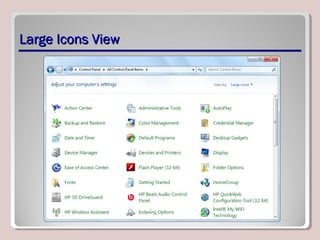
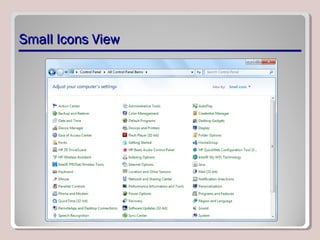
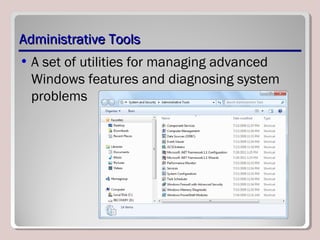
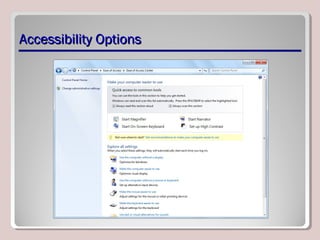
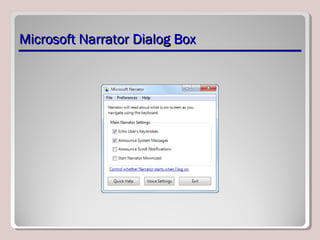
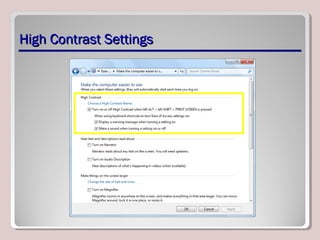
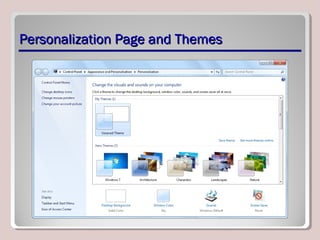
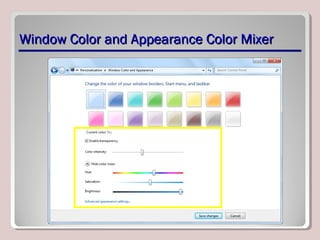
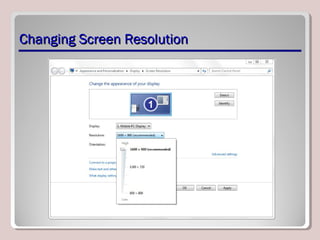
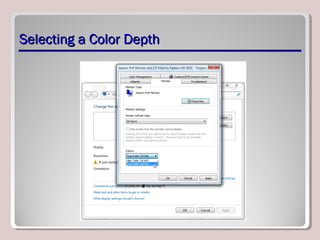
The document discusses various aspects of operating system configurations in Windows 7, including user accounts, User Account Control (UAC), the Control Panel, accessibility options, desktop settings, and Microsoft virtualization products. It describes the different types of user accounts, UAC prompts and levels, tools in the Control Panel, how to configure desktop settings, and virtualization technologies like Windows XP Mode, Med-V, App-V, and VDI.