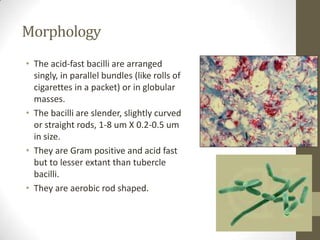
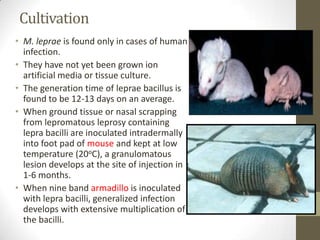
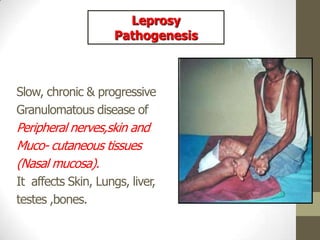
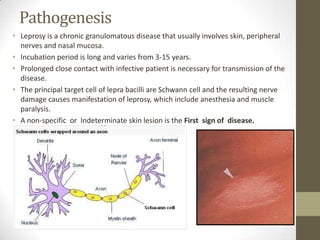
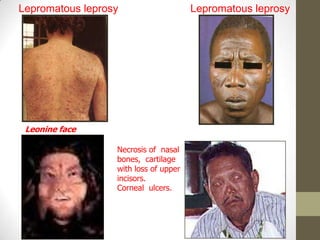
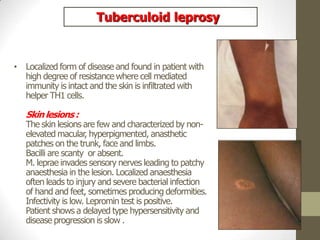
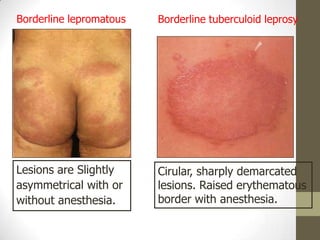
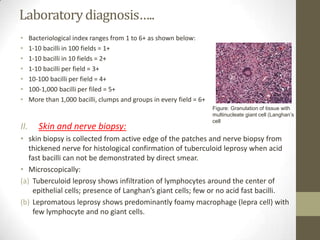
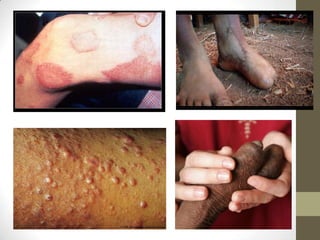
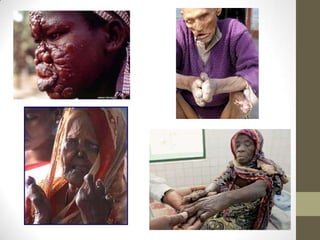
M. leprae is the bacteria that causes leprosy. It is found in the nose and respiratory tract of infected individuals. While it can survive in the environment for some time, it is transmitted through direct contact with infected individuals. M. leprae causes a chronic granulomatous disease that primarily affects the skin, nerves, and nasal mucosa. There are several forms of leprosy depending on the immune response of the infected individual, ranging from tuberculoid leprosy where immune response is strong to lepromatous leprosy where immune response is weak. Diagnosis is based on clinical signs and confirmation is through visualization of acid-fast bacilli in skin or nerve biopsies