Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

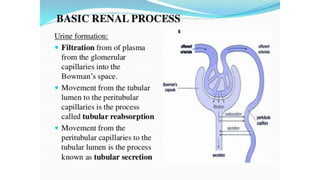
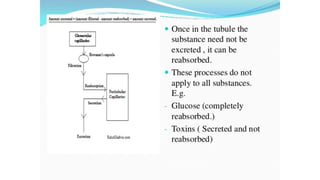

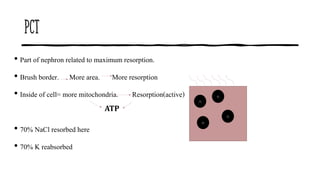

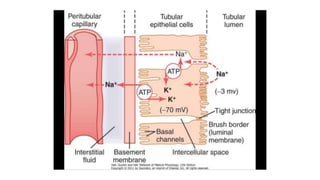
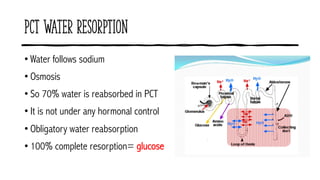

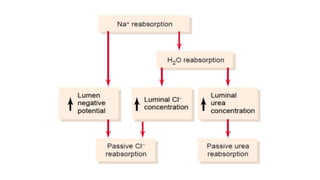


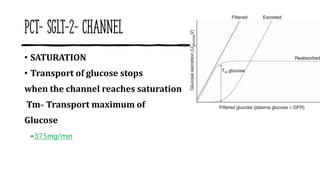

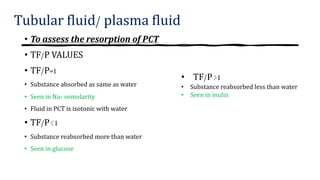




The document discusses the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) of the nephron, highlighting its role in the resorption of essential substances such as NaCl, K, and water, with 70% of water being reabsorbed through osmosis. It also covers glucose resorption via the Na+-glucose co-transporter (SGLT-2) and the implications of SGLT-2 blockers in diabetes treatment, including potential side effects. Additionally, it introduces concepts such as transport maximum and renal threshold for glucose, along with the assessment of resorption efficiencies using TF/P values.




















