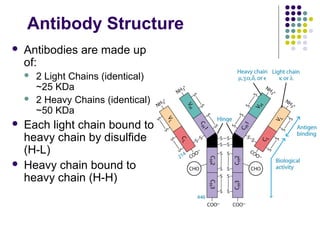
Antibodies are Y-shaped proteins that recognize antigens with high specificity. They are composed of two light chains and two heavy chains connected by disulfide bonds. The variable regions at the tips of the Y, known as the antigen binding sites, contain complementarity determining regions that bind to antigens. There are five classes of antibodies (IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, IgE) that differ in structure and function. The Fc region mediates effector functions like activation of complement and binding to immune cells.