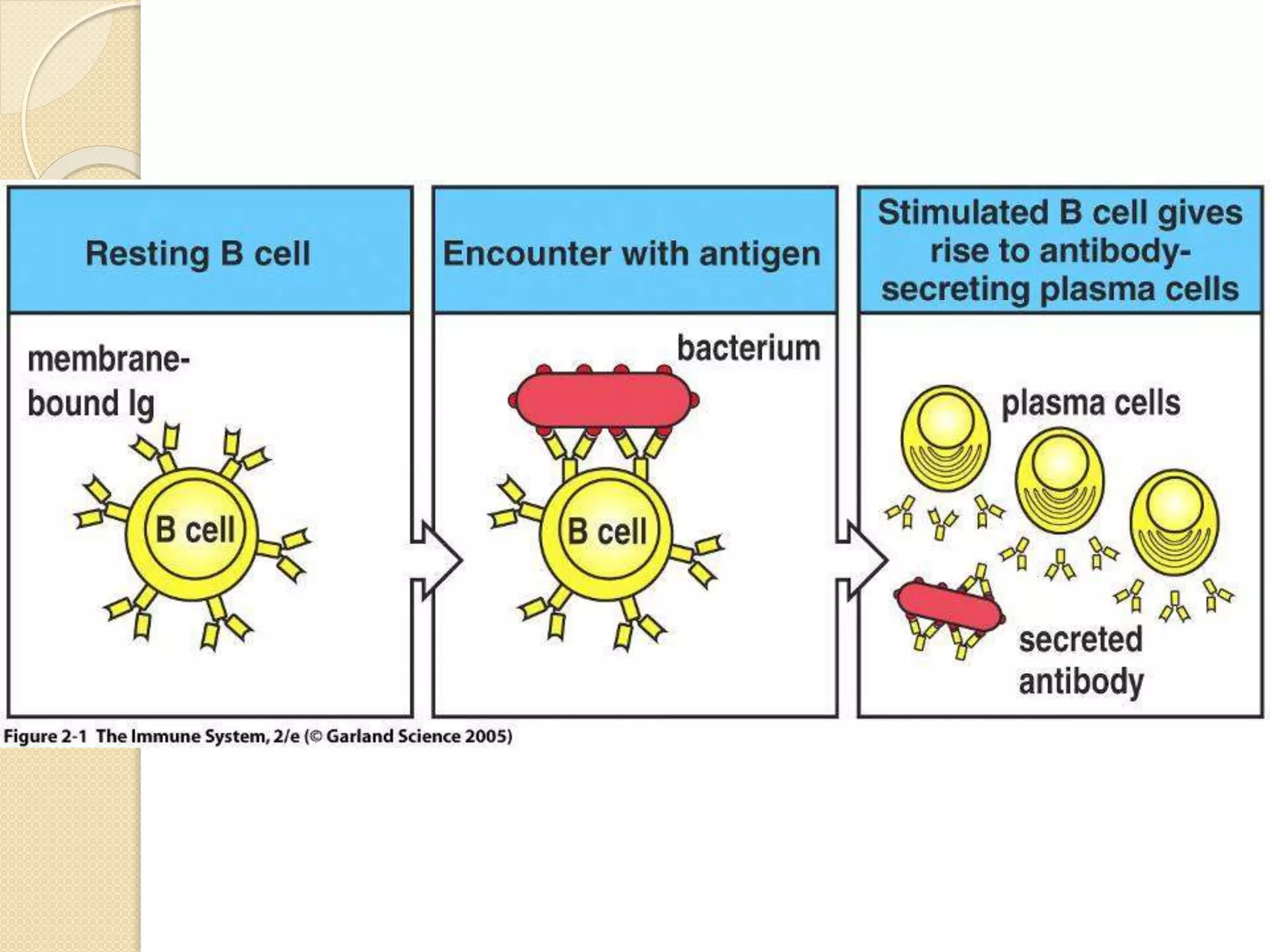
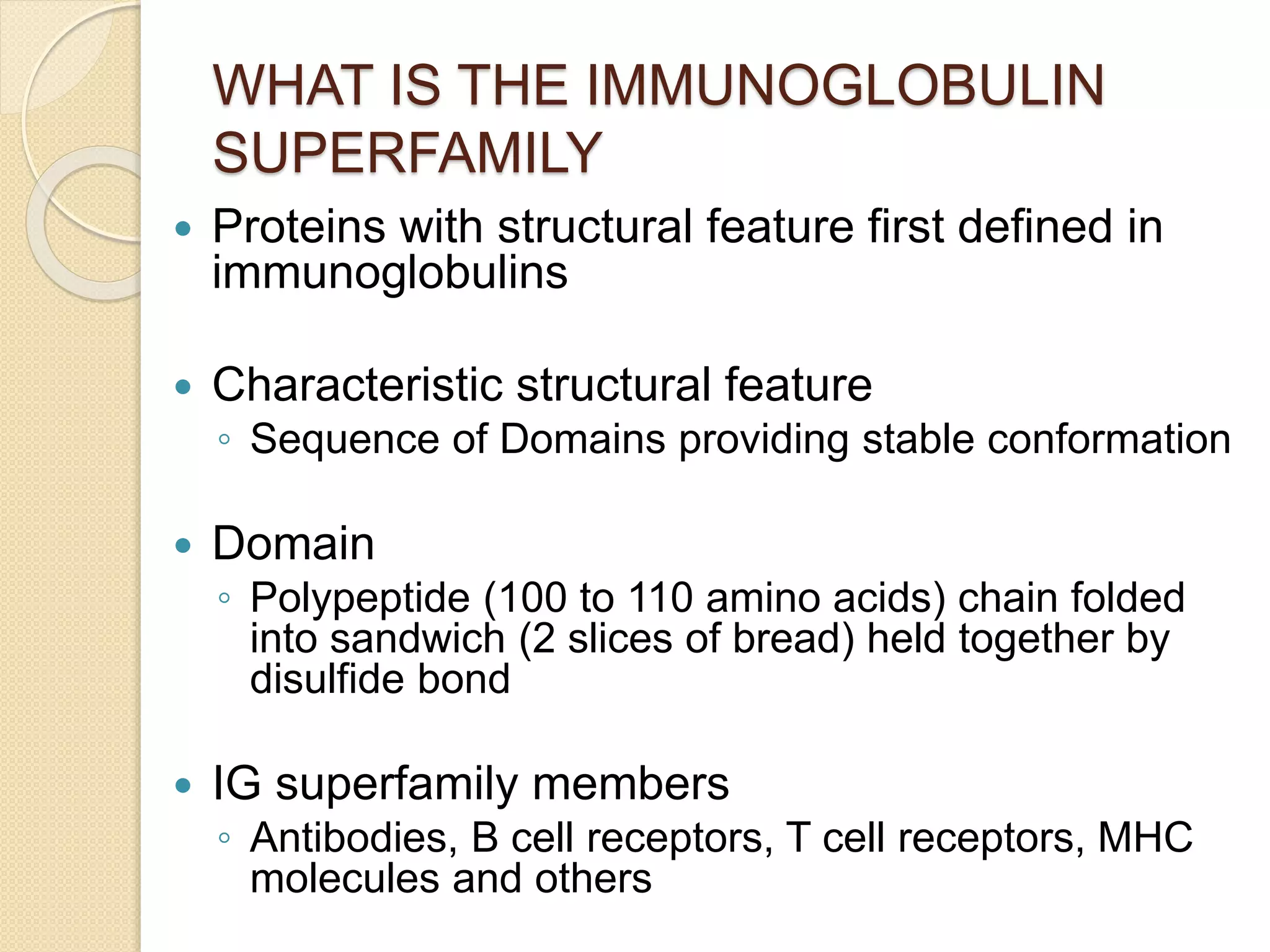
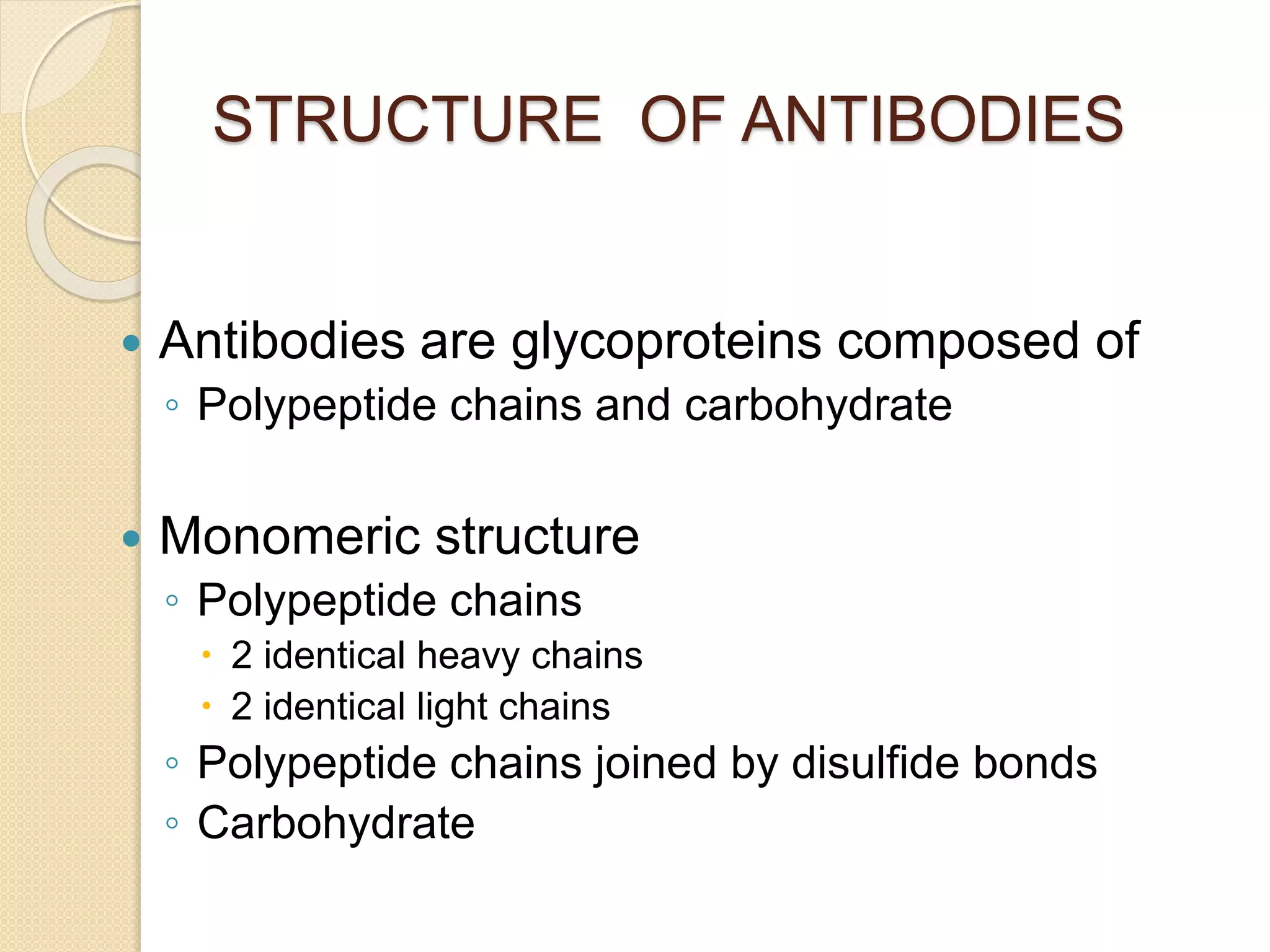
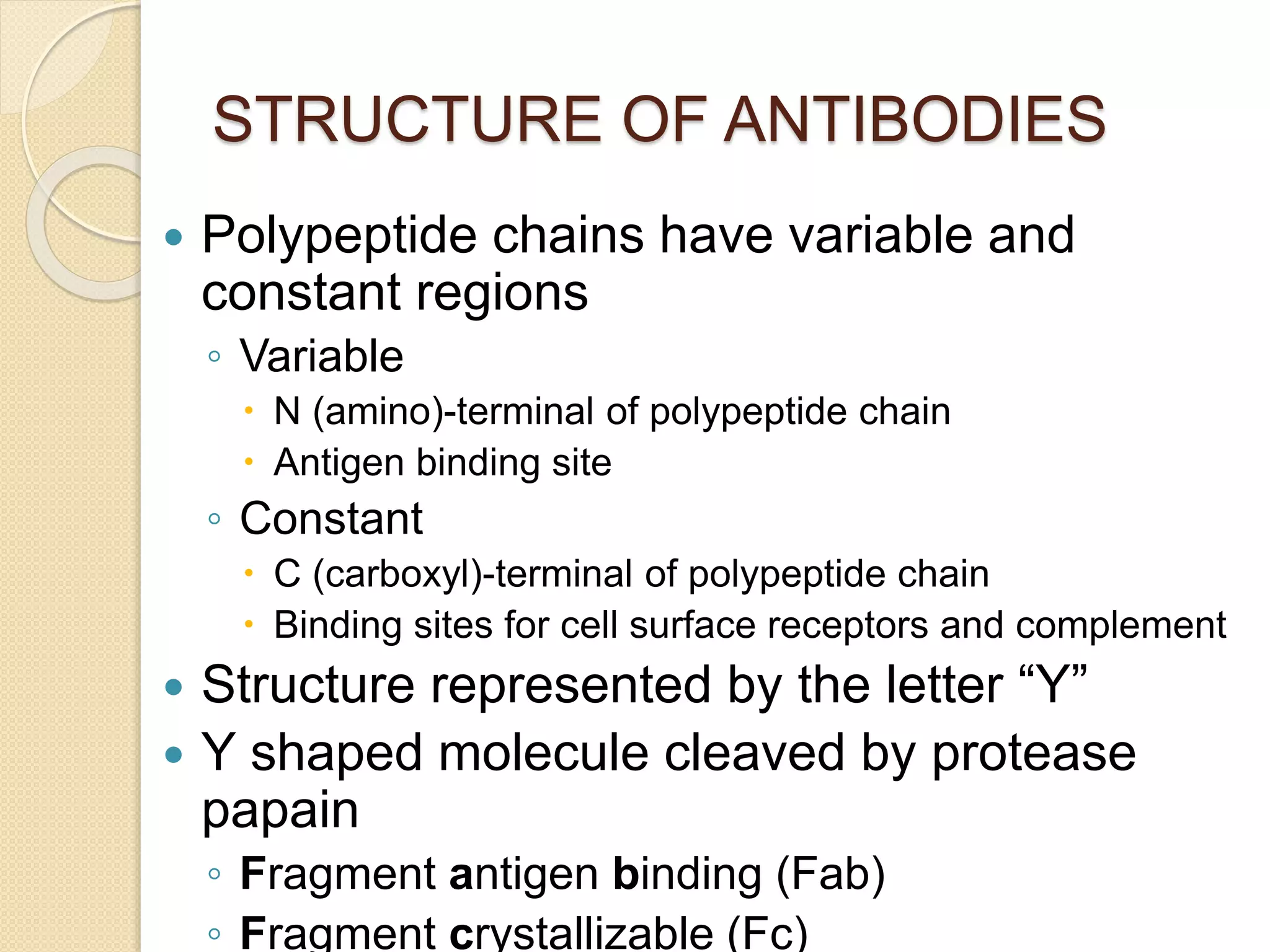
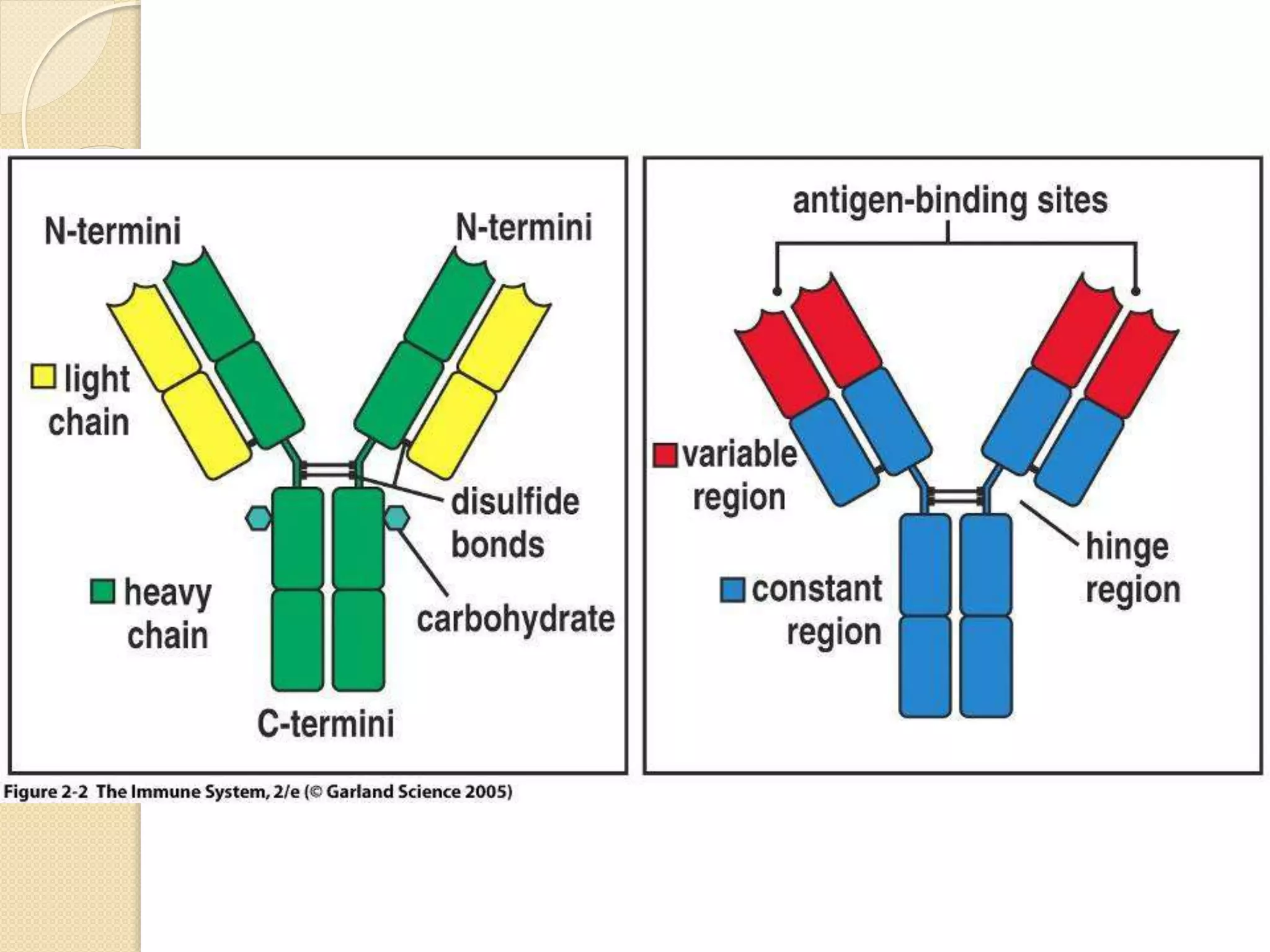
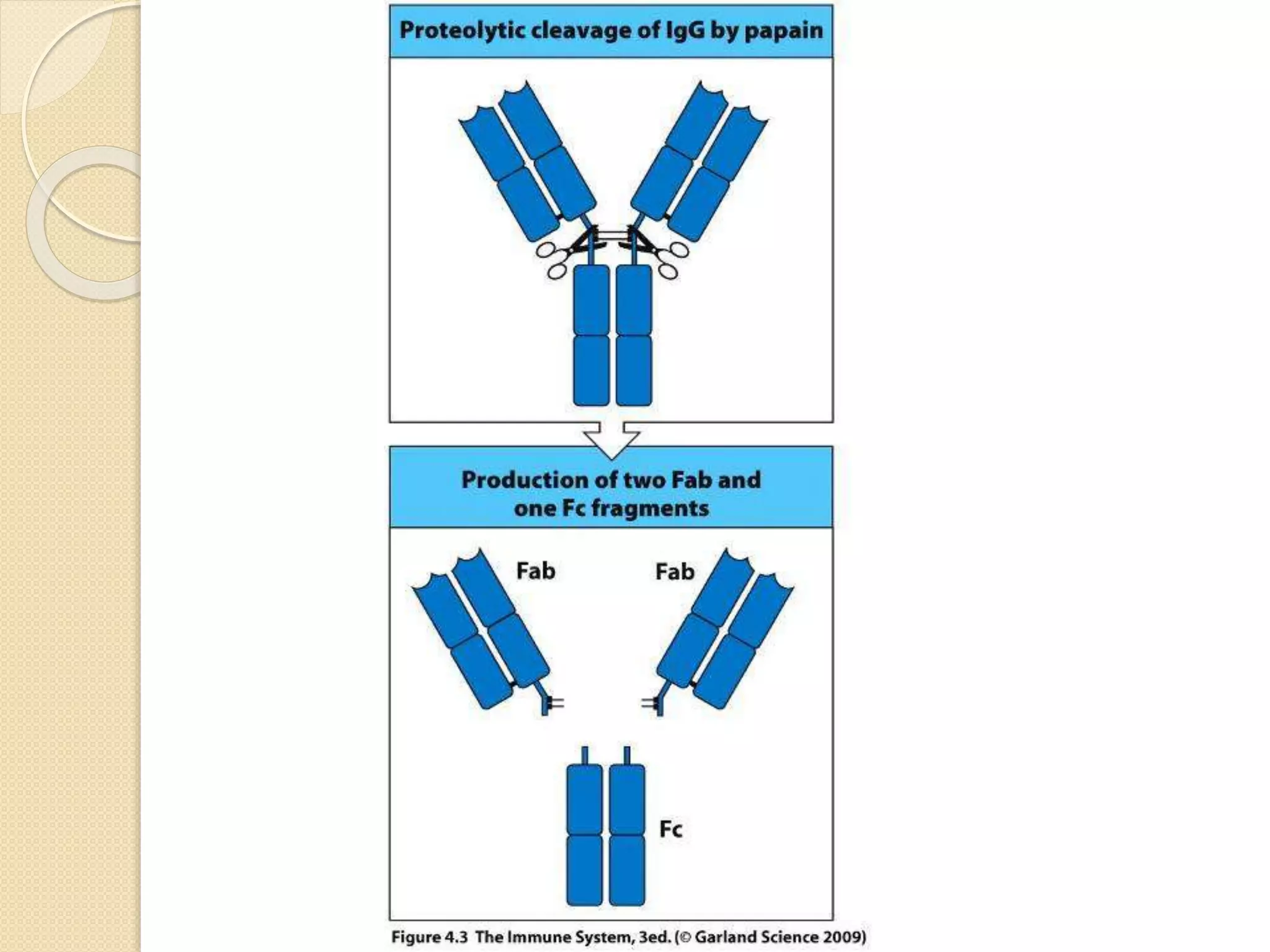
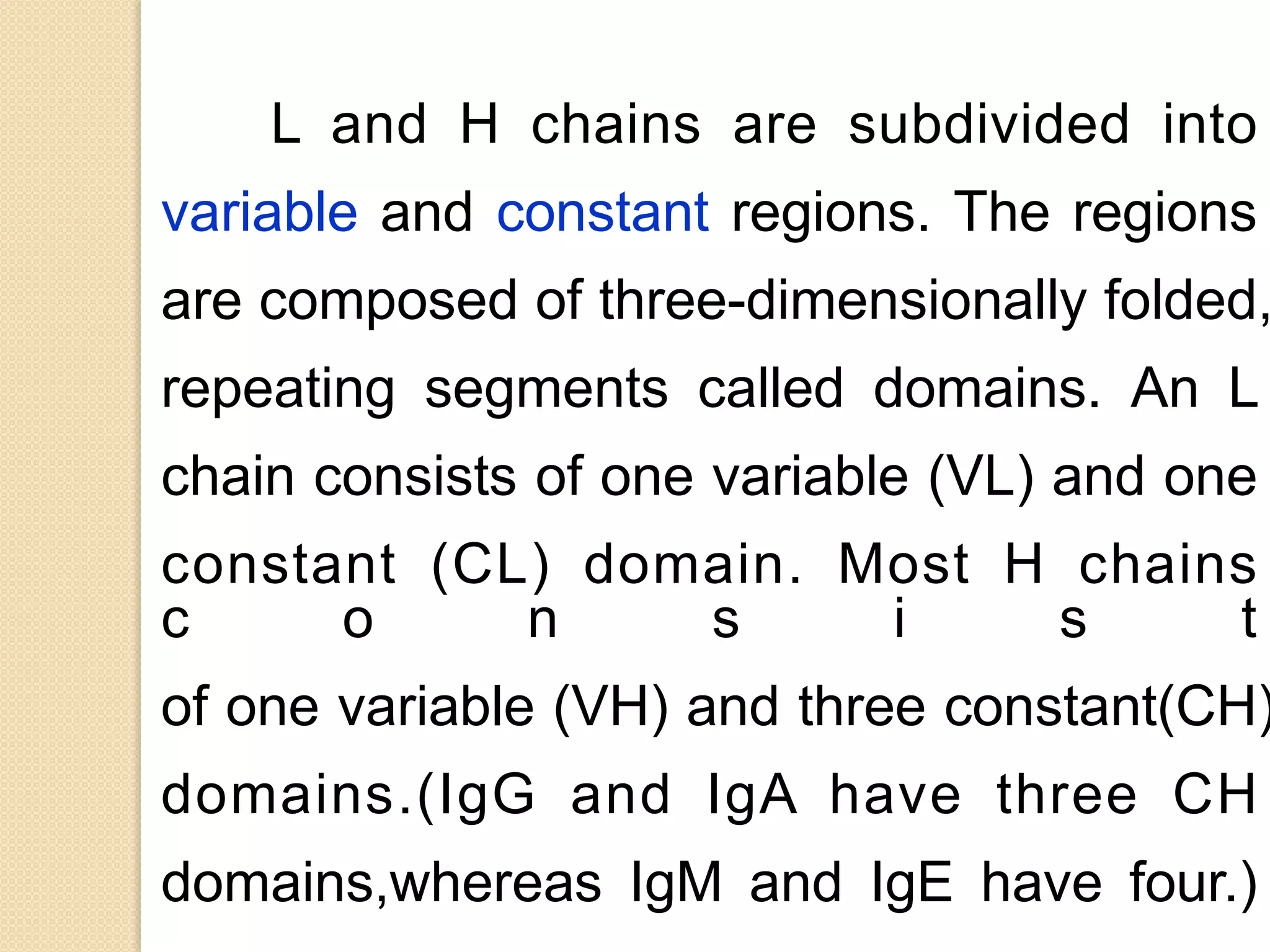
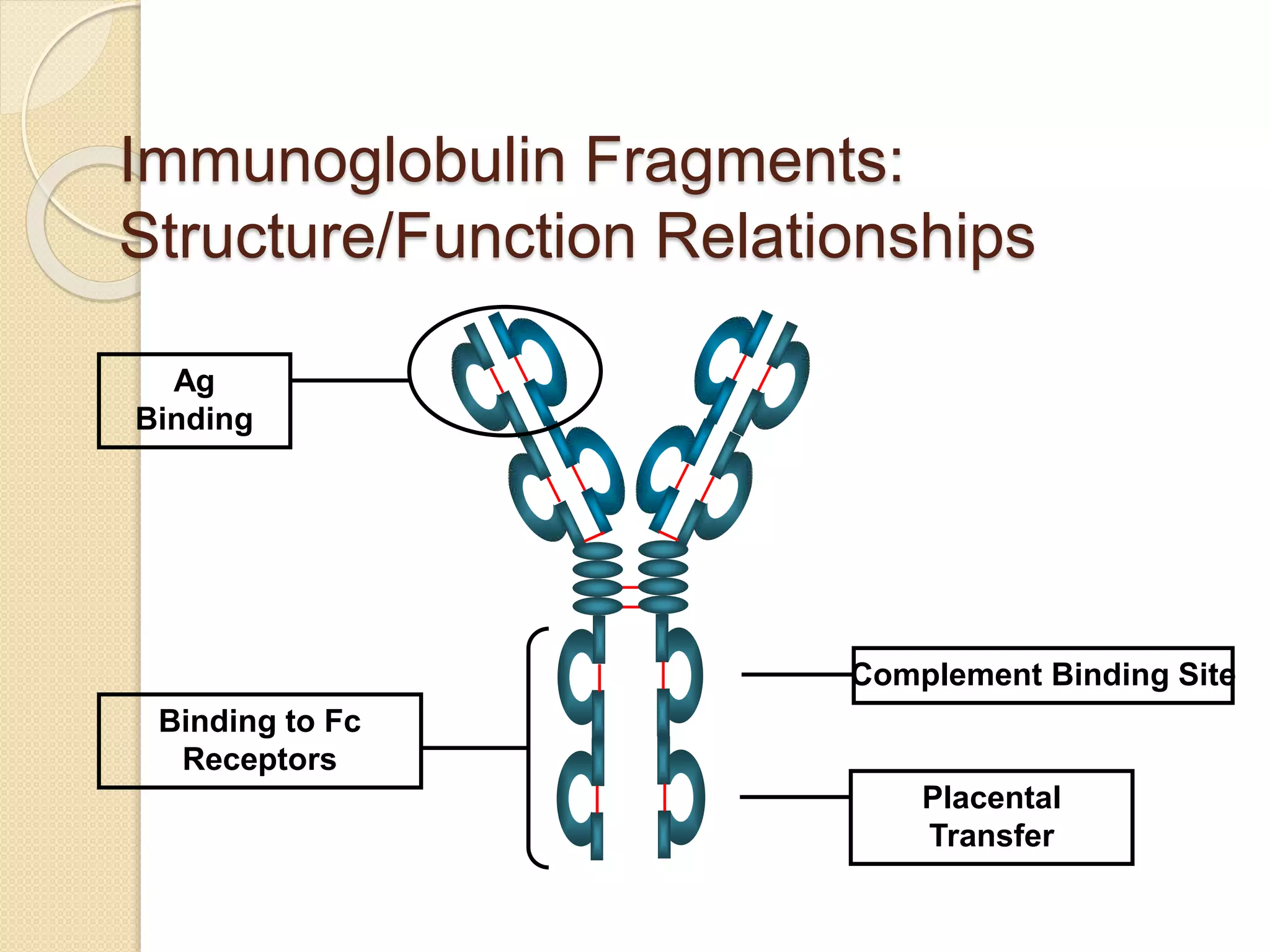
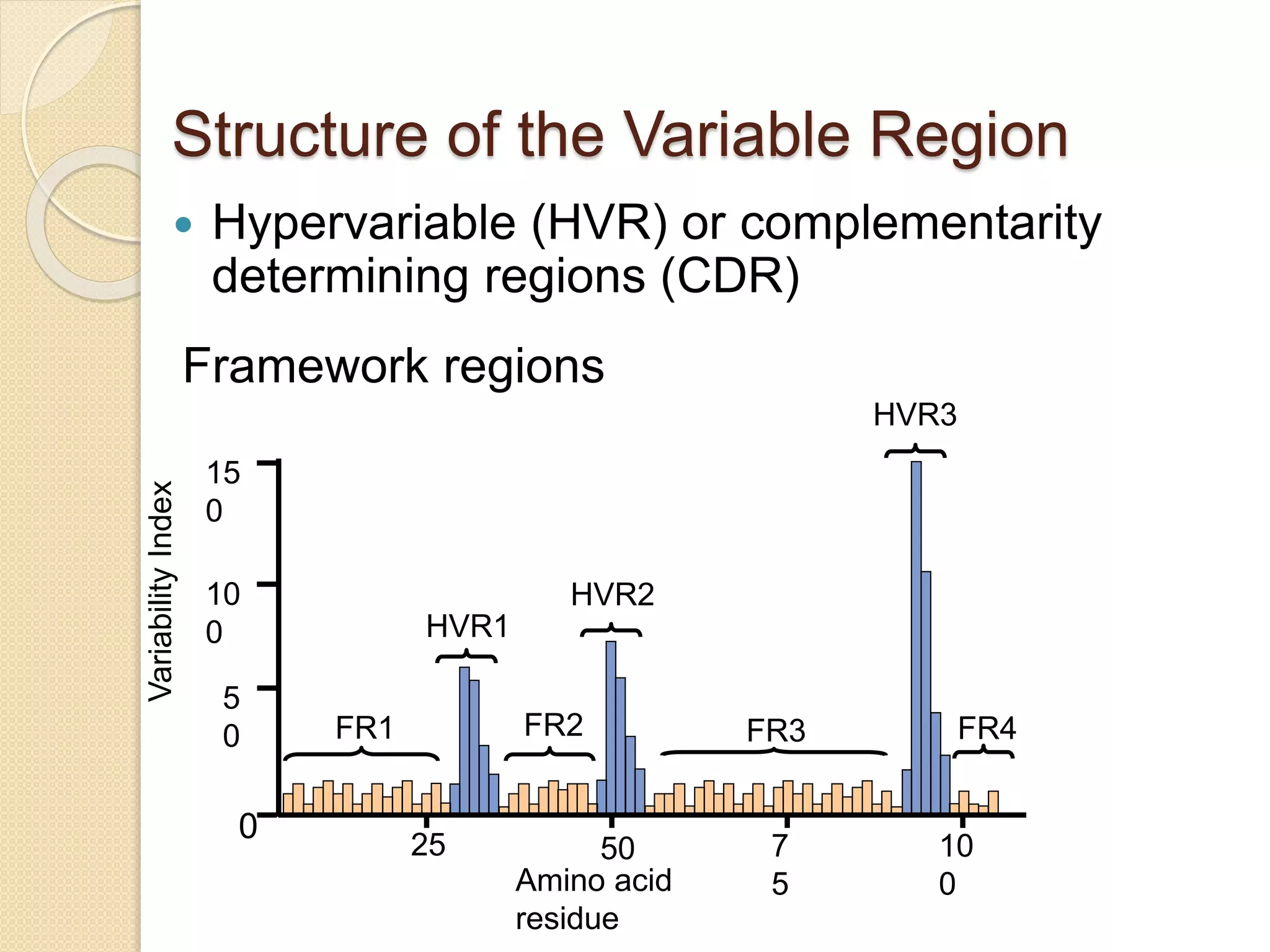
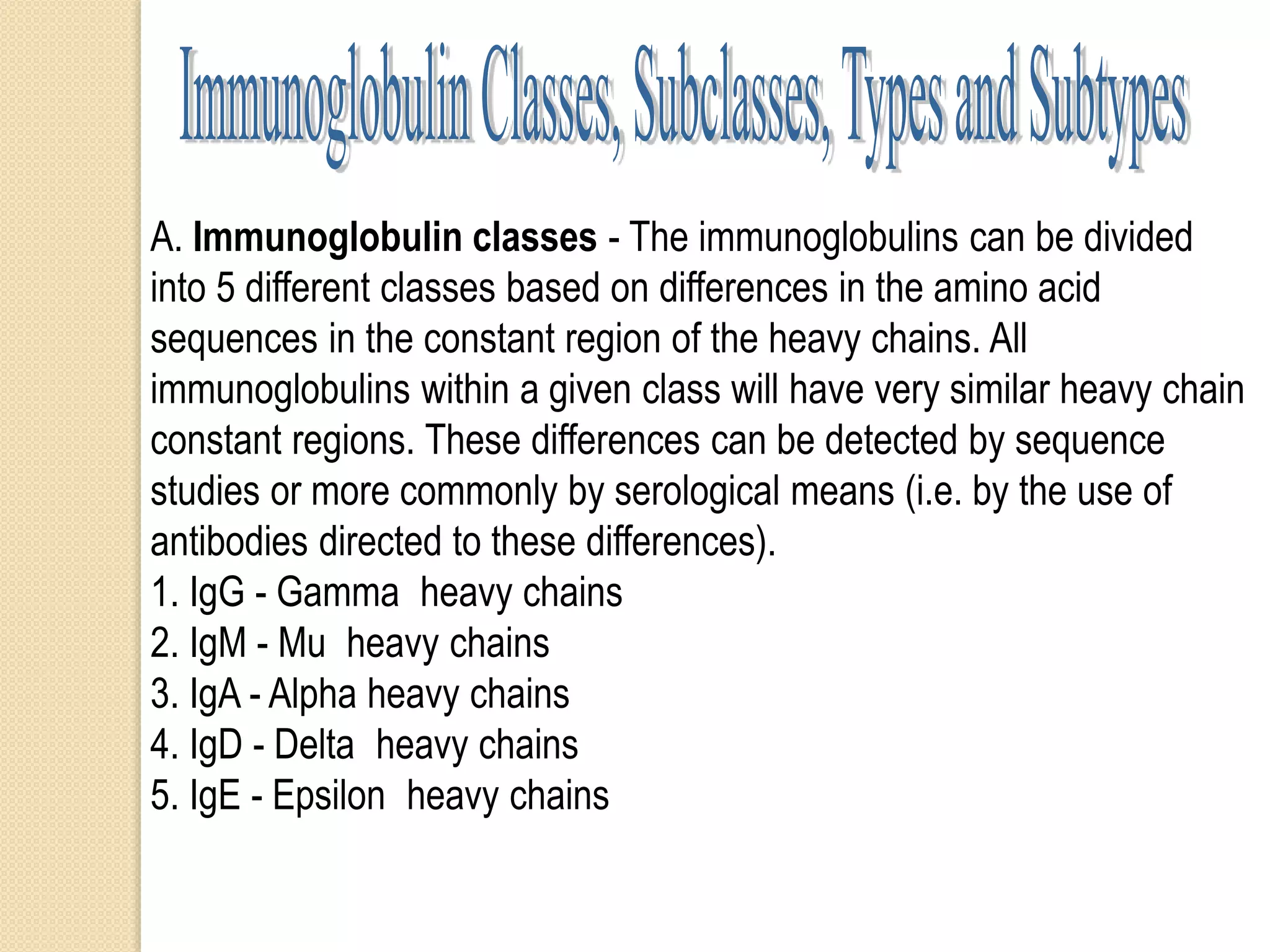
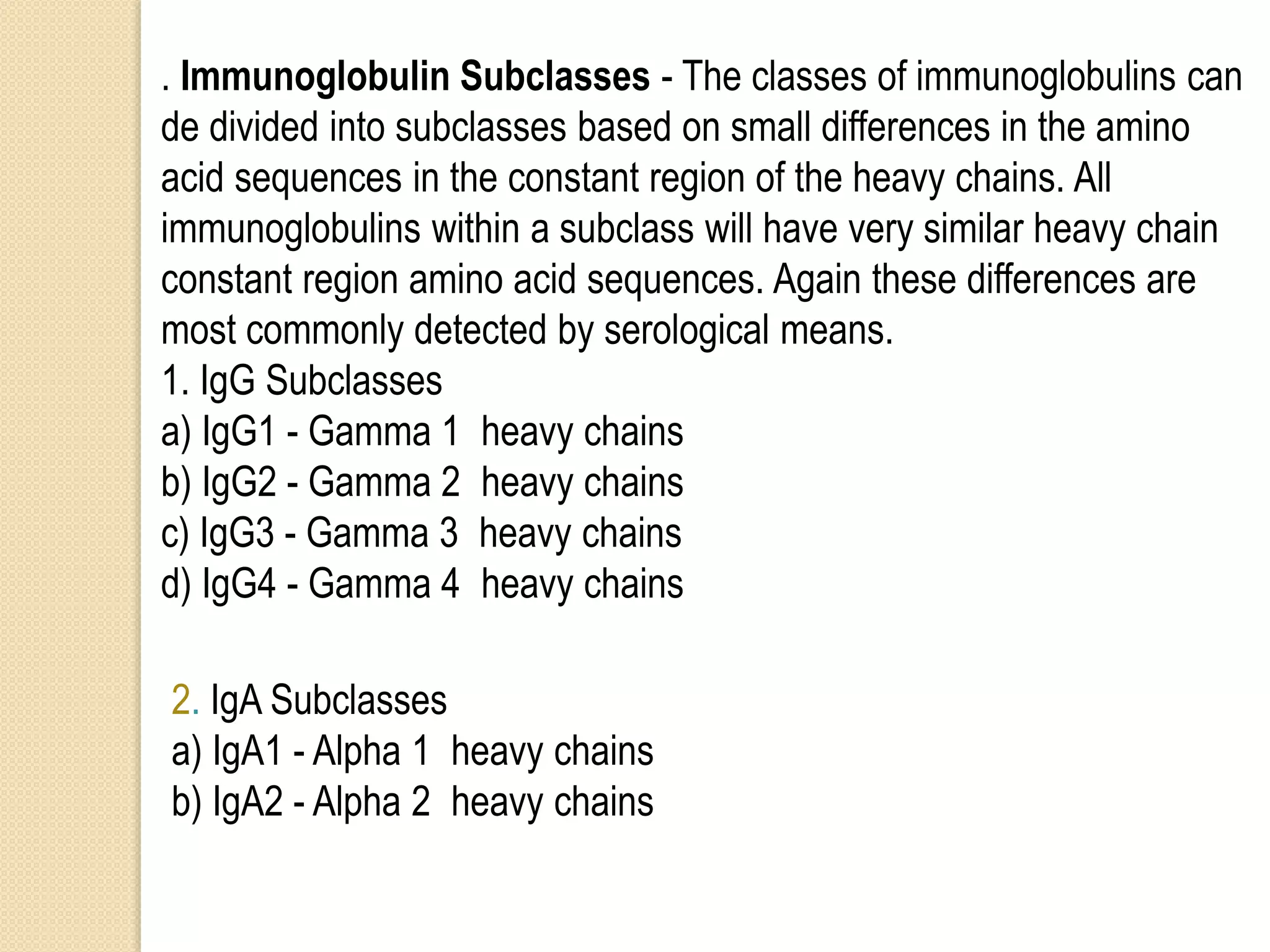
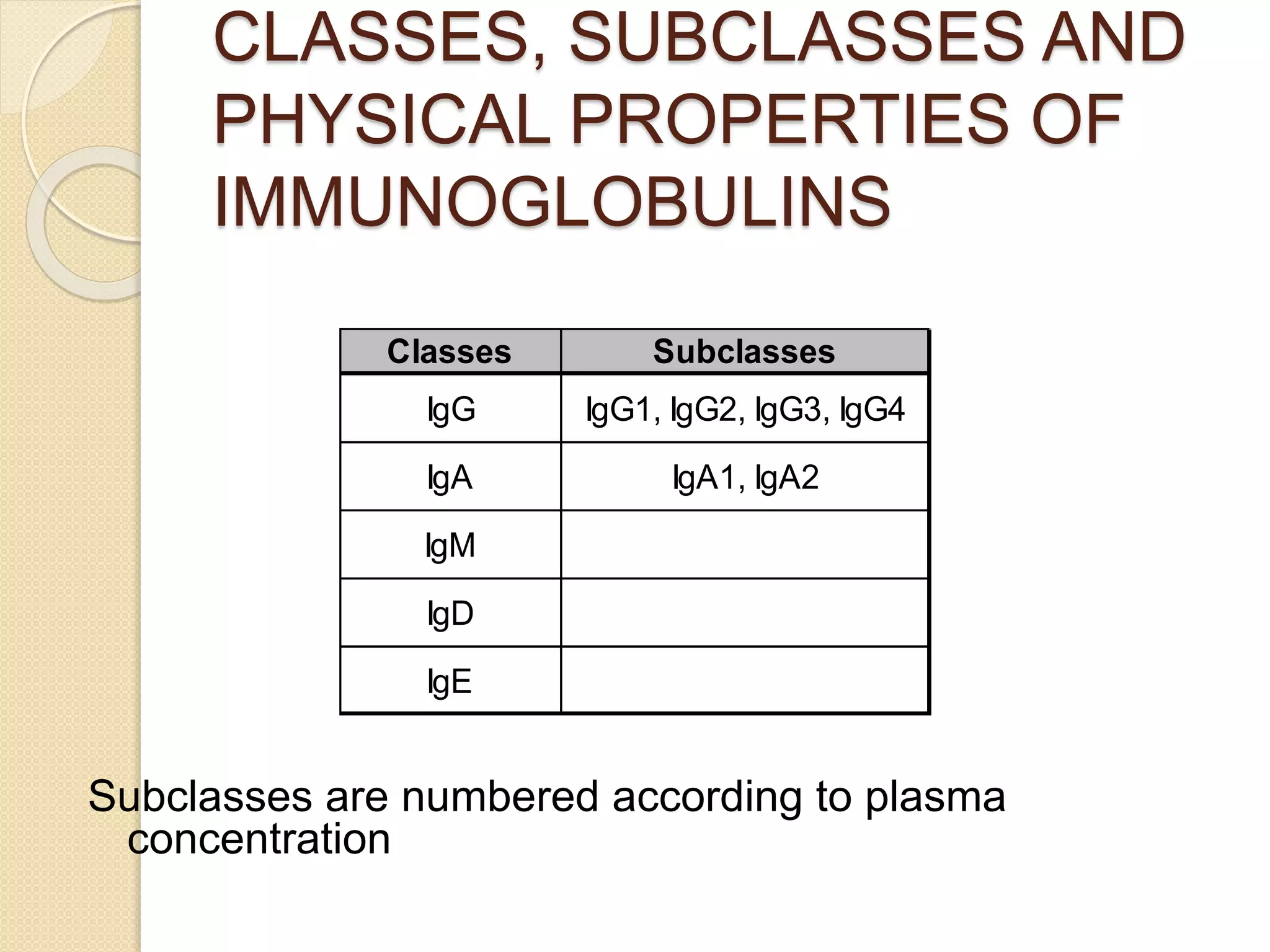
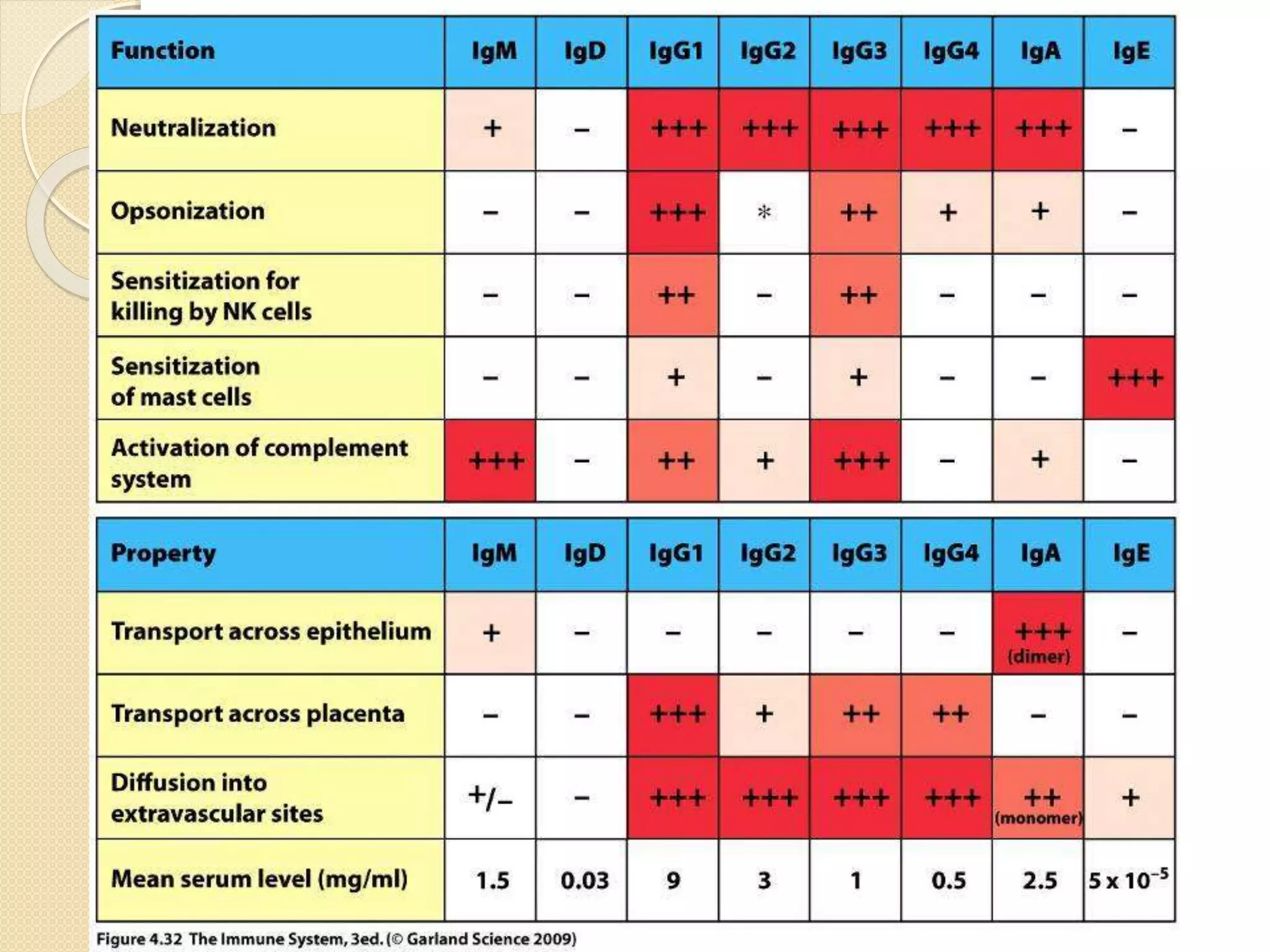
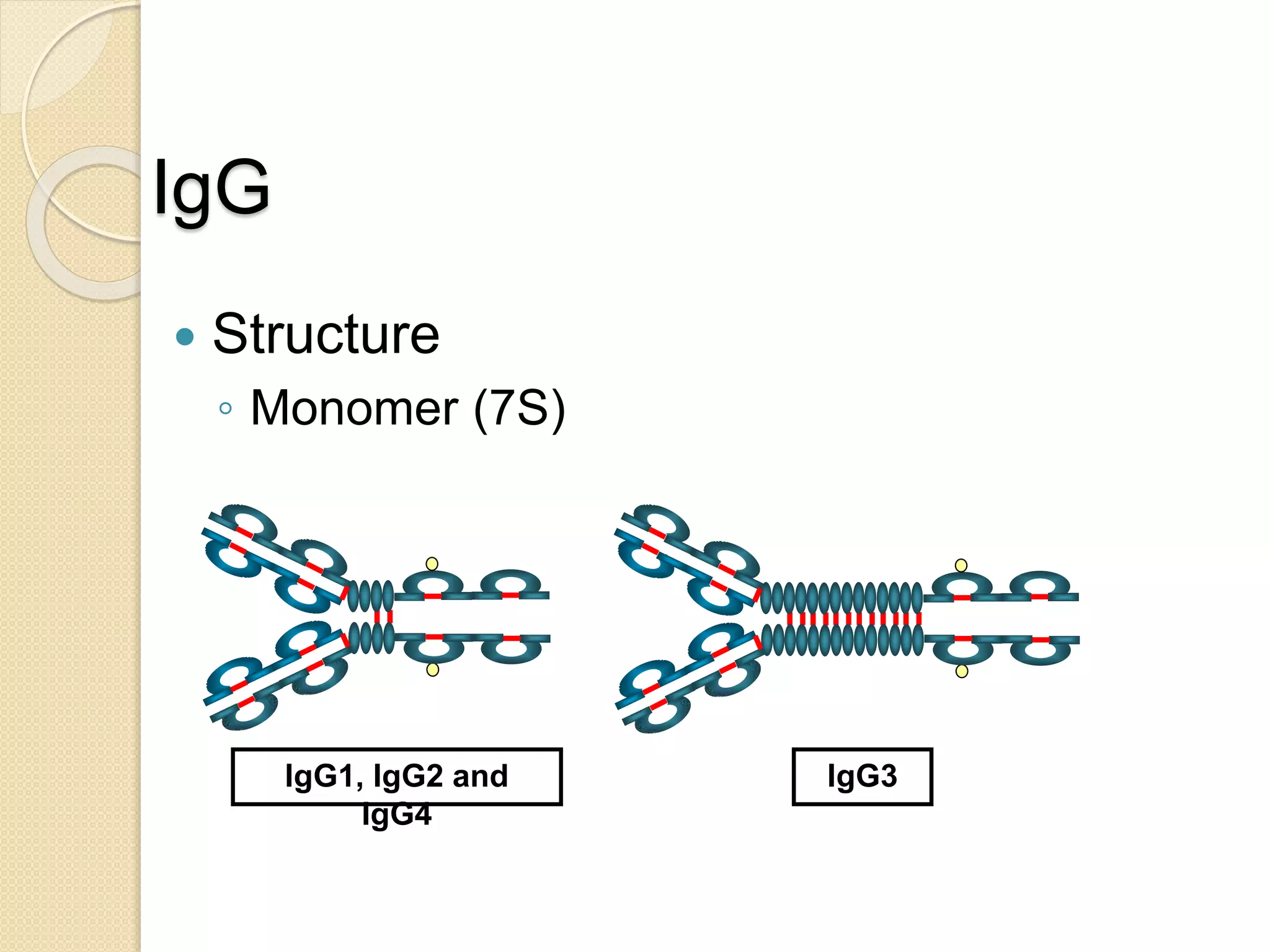
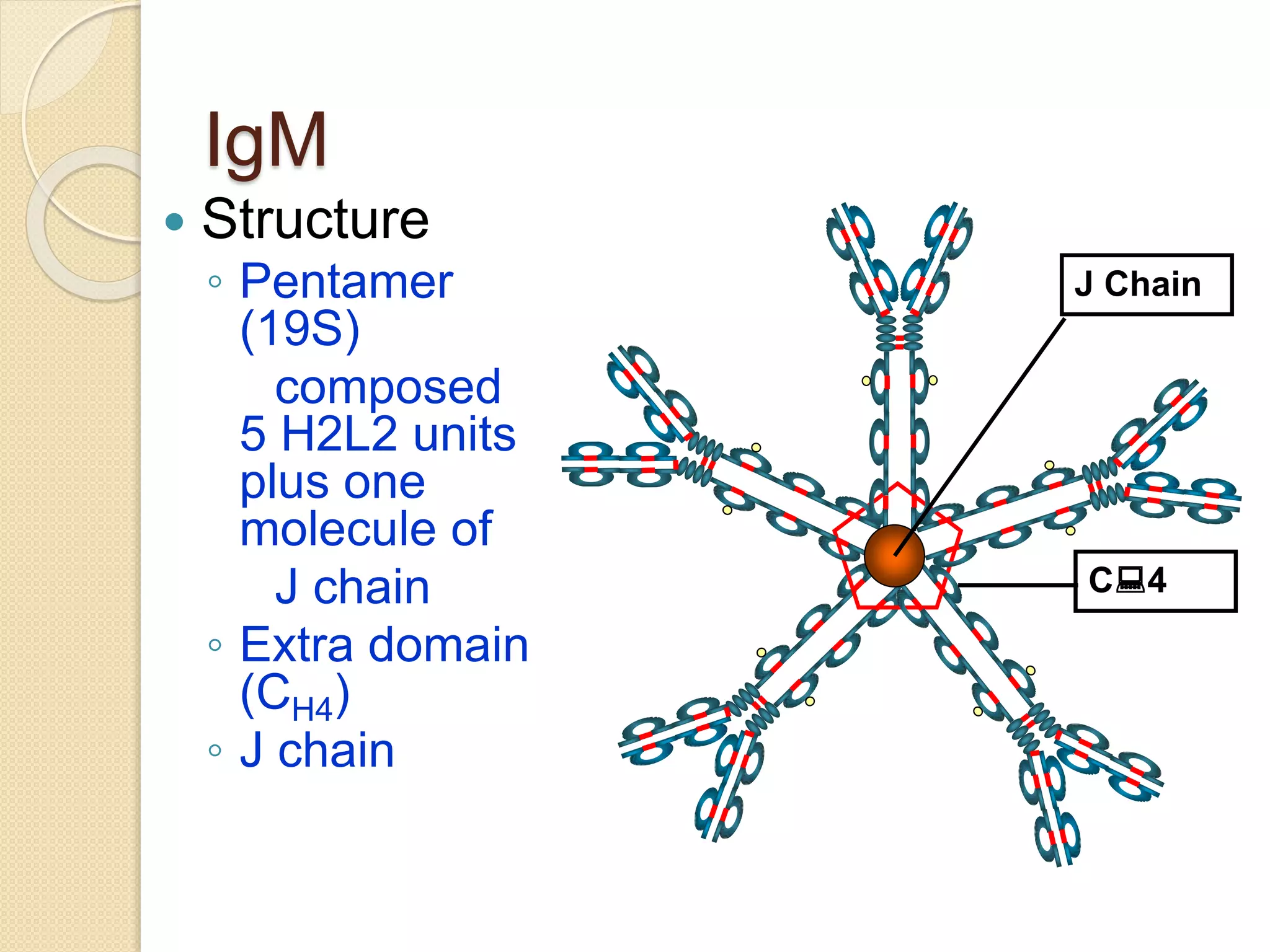
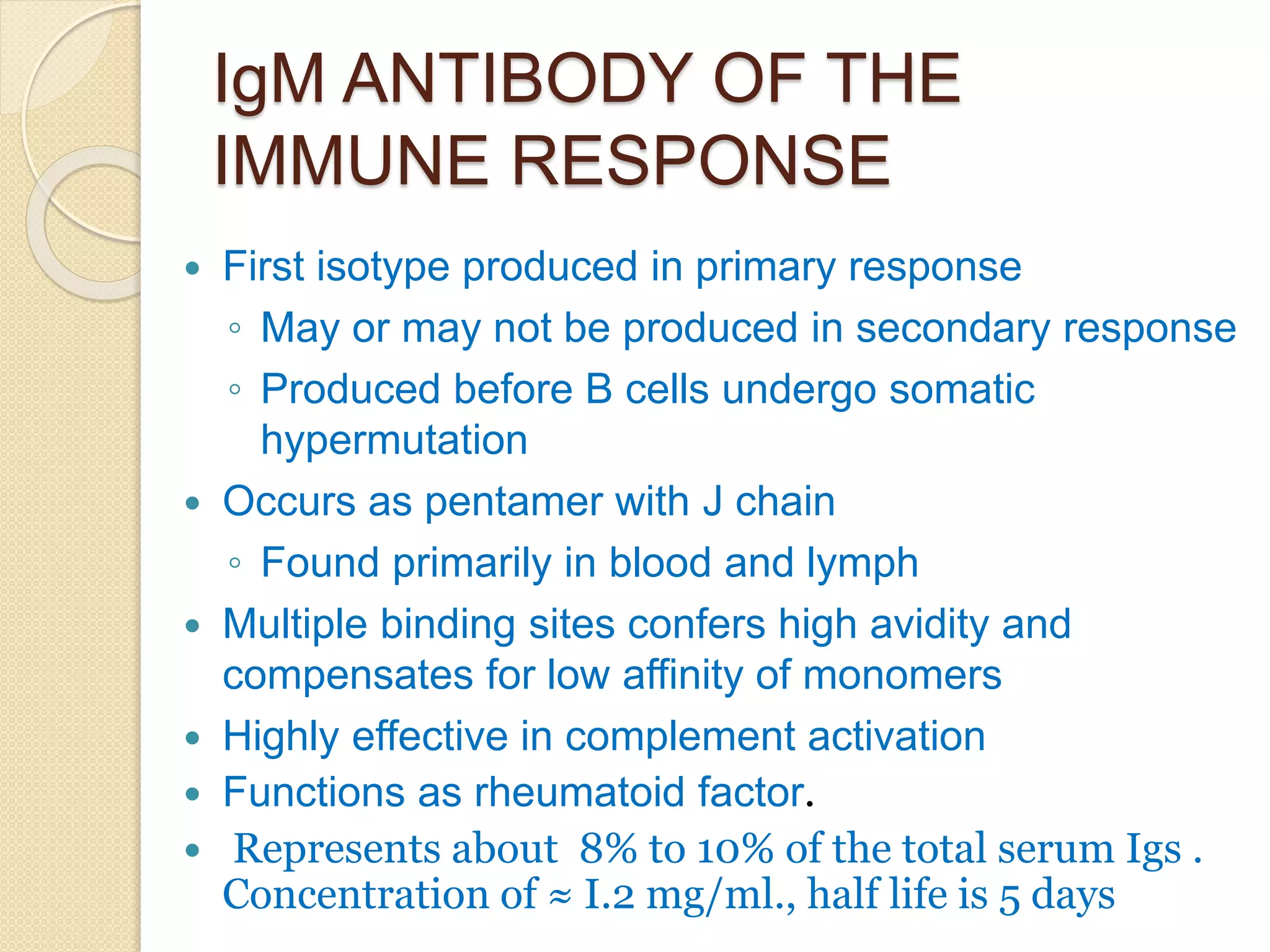
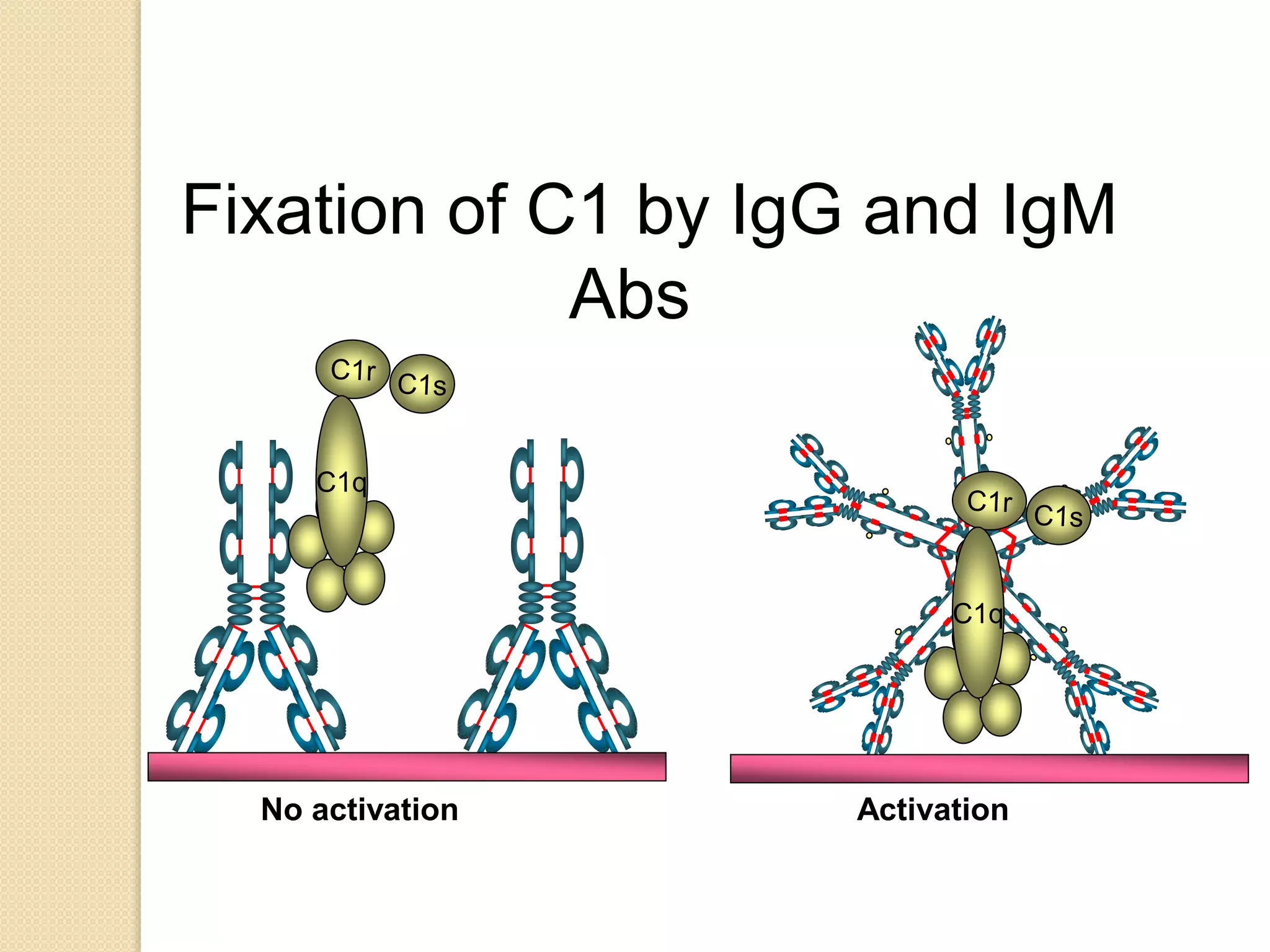
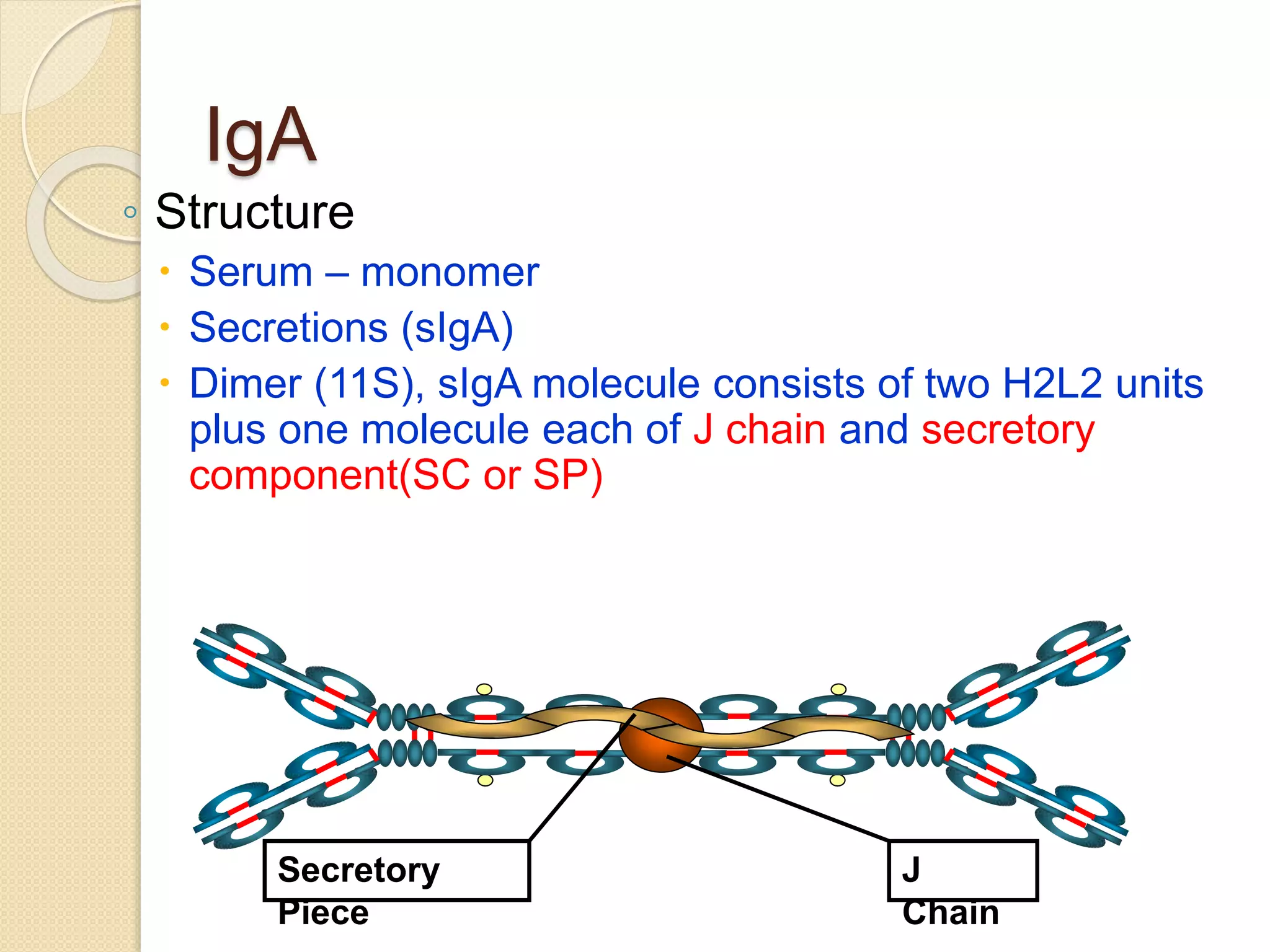
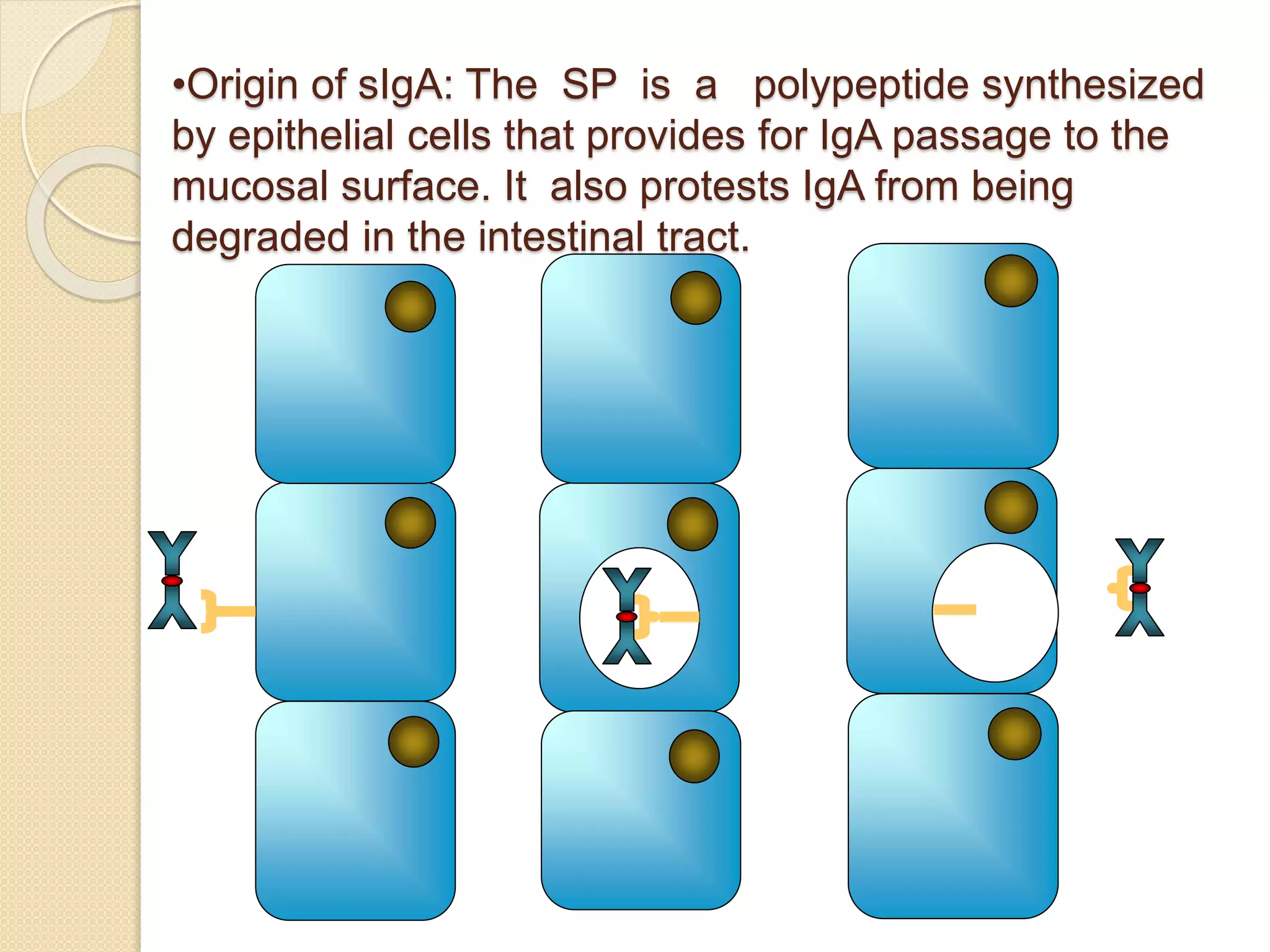
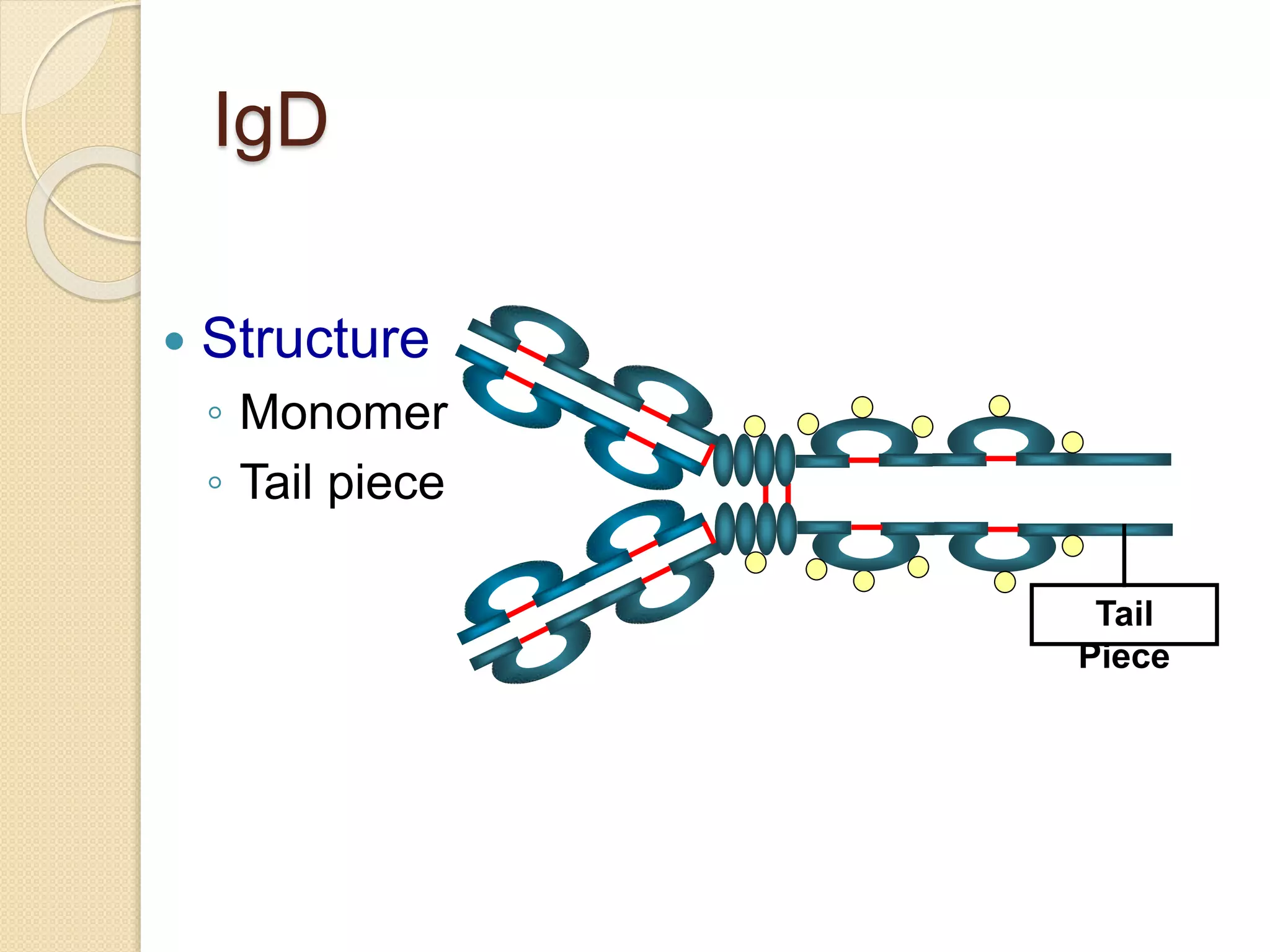
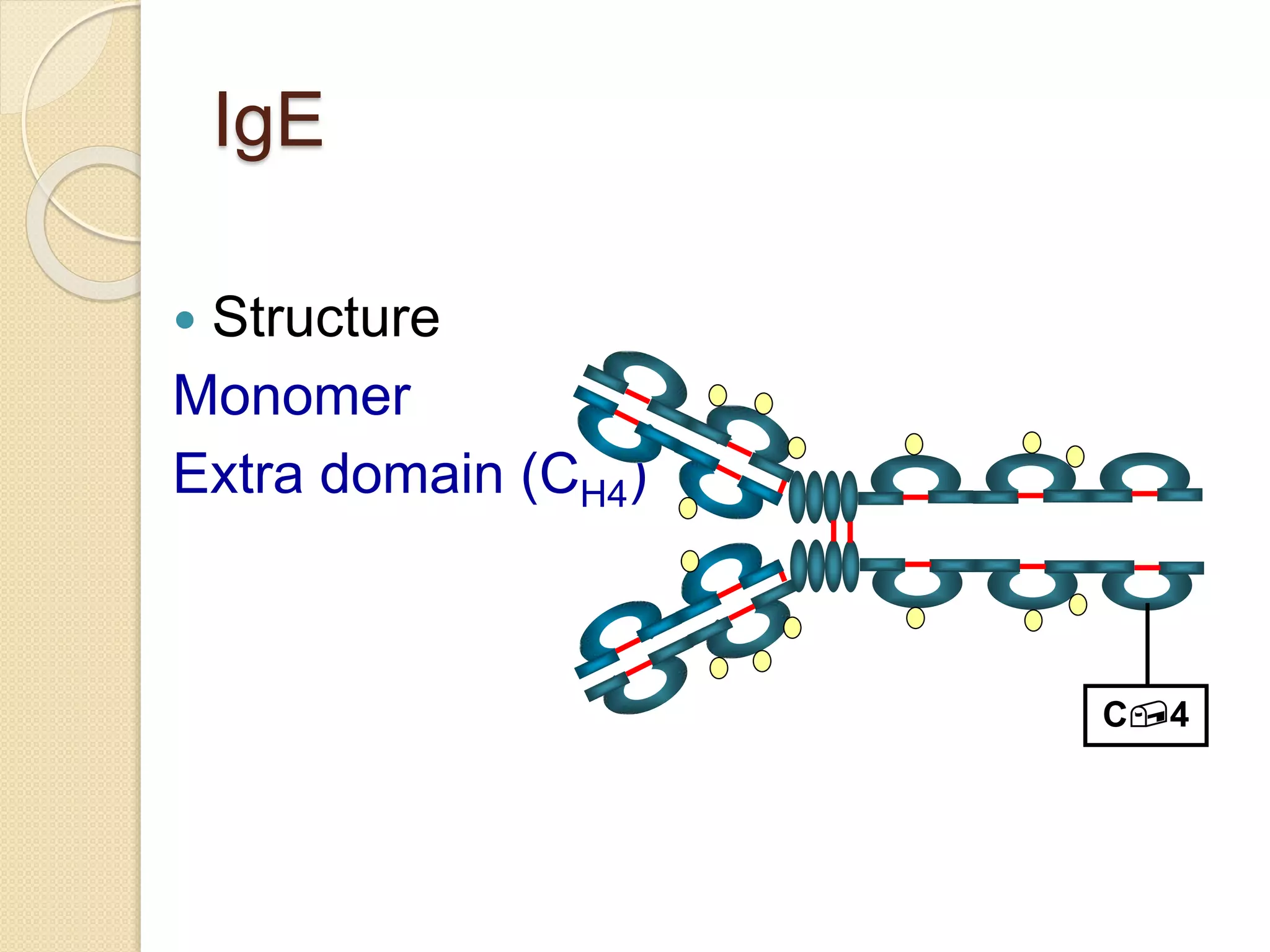
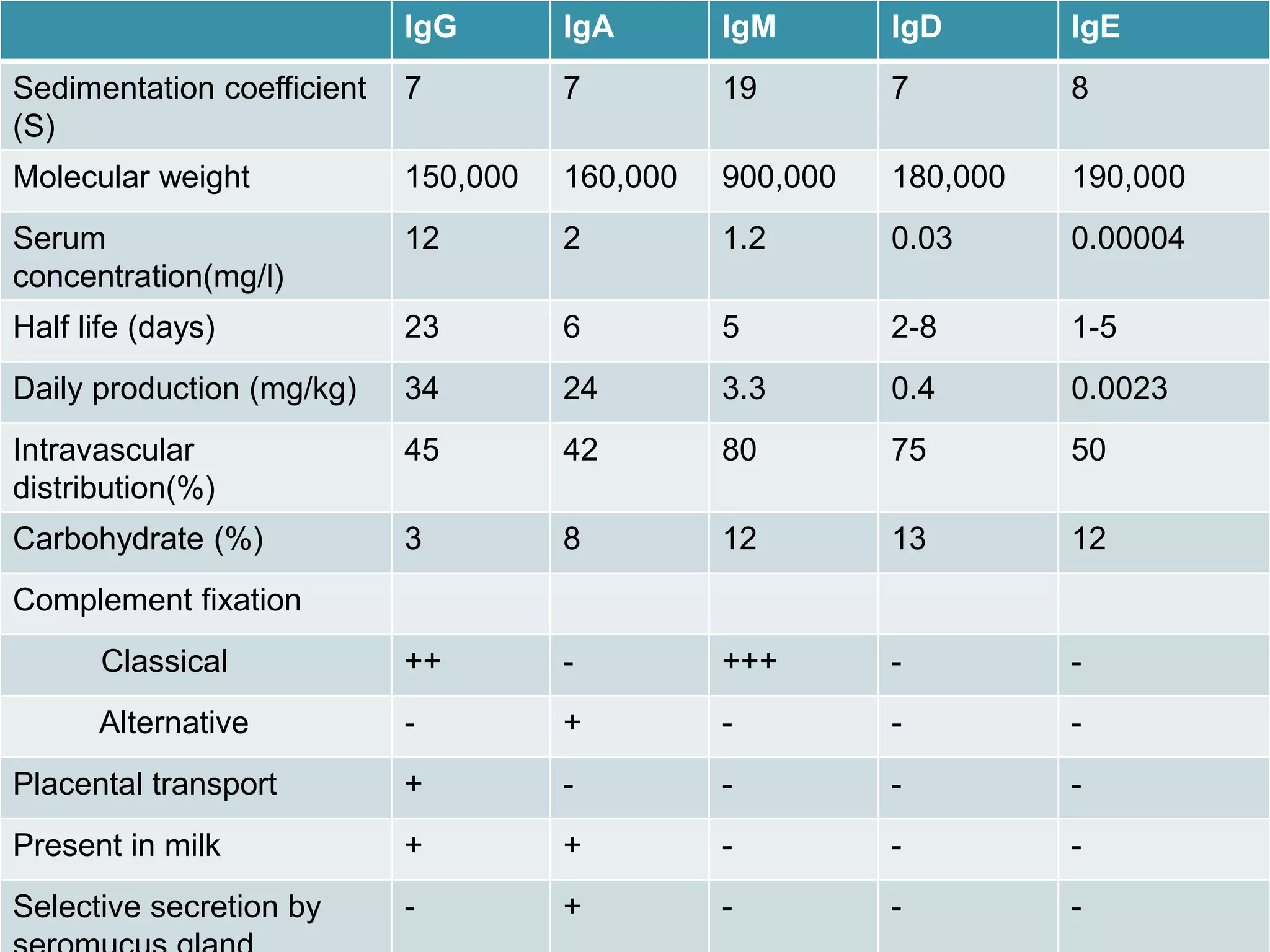
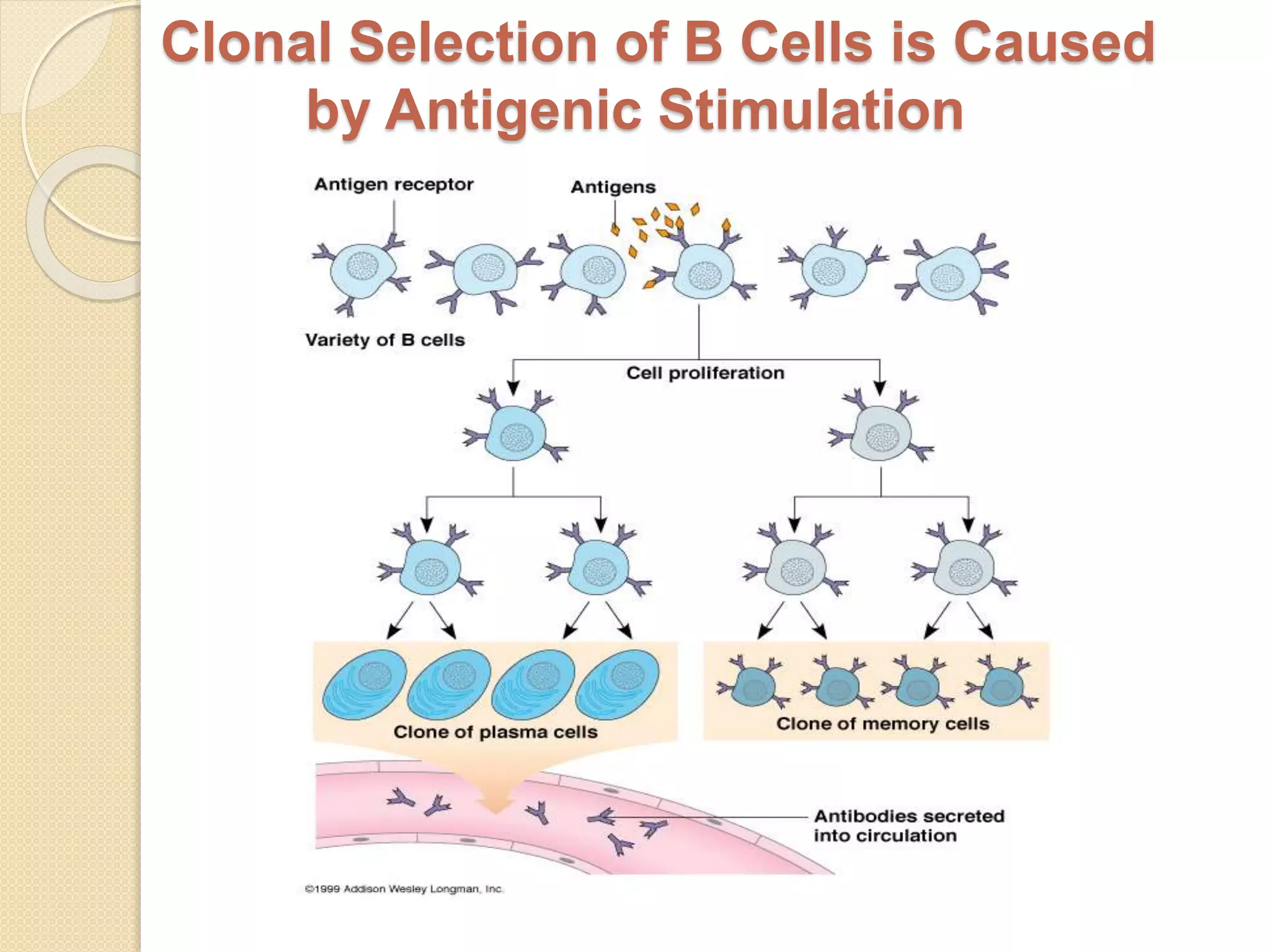
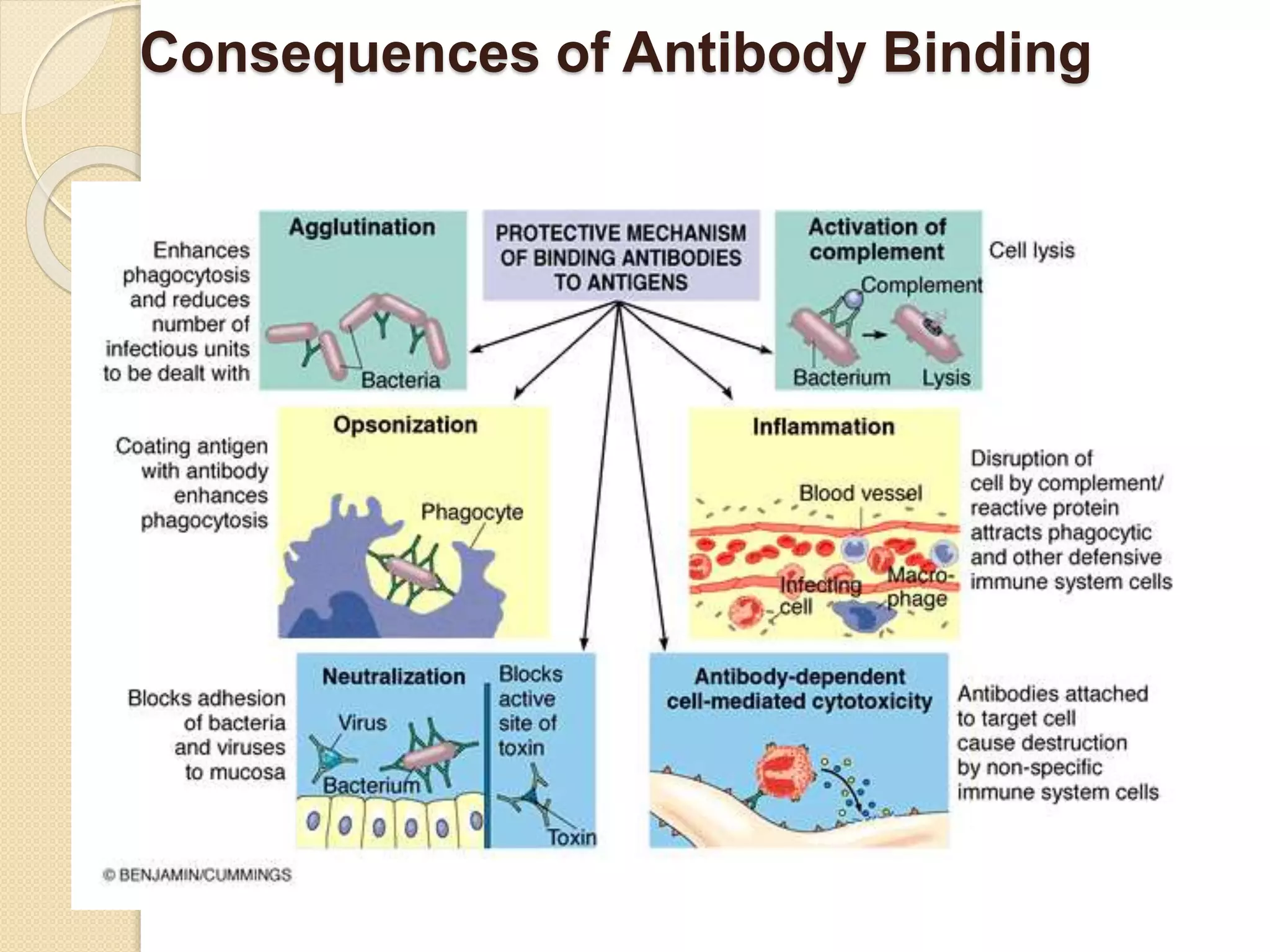
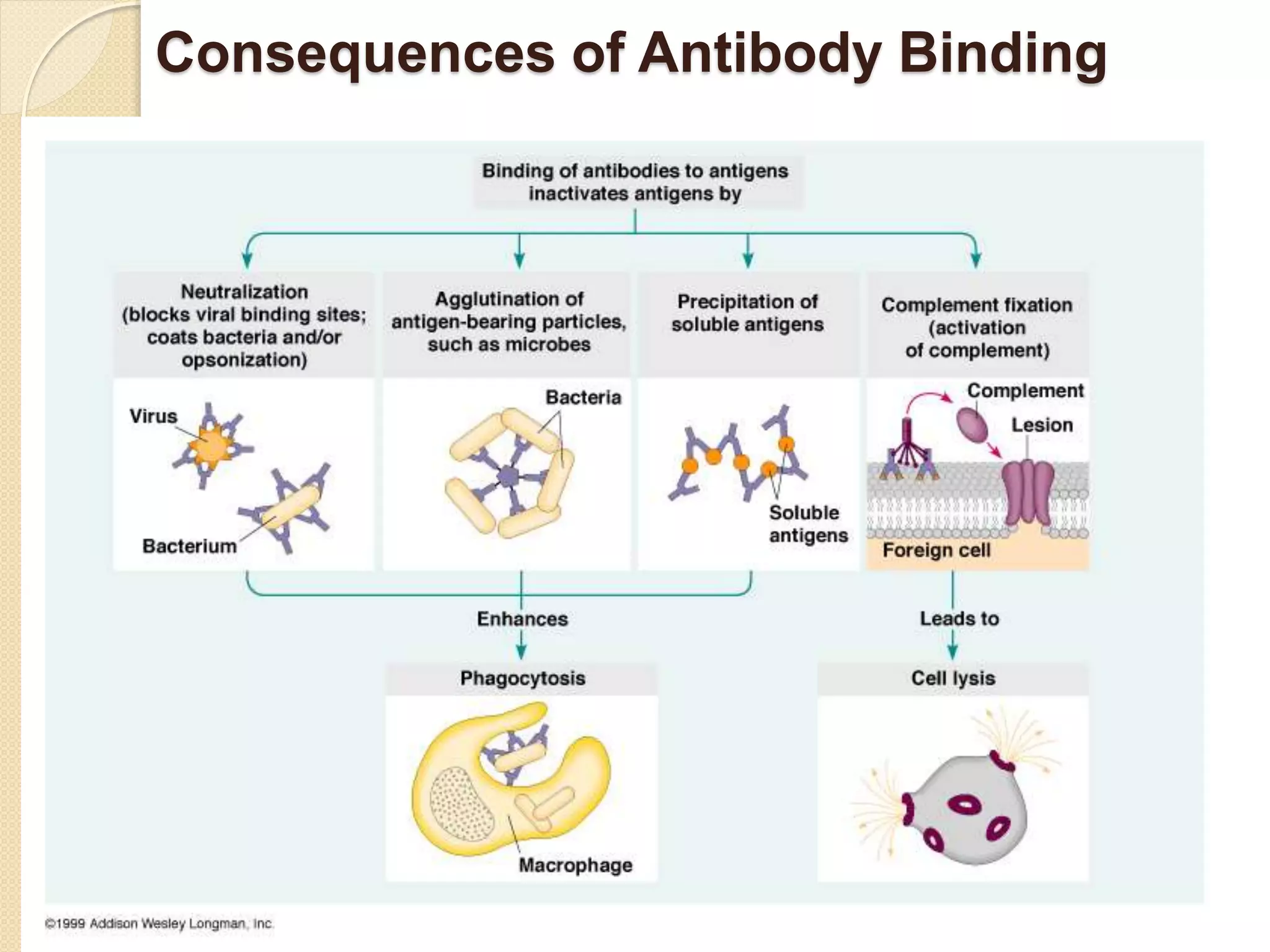
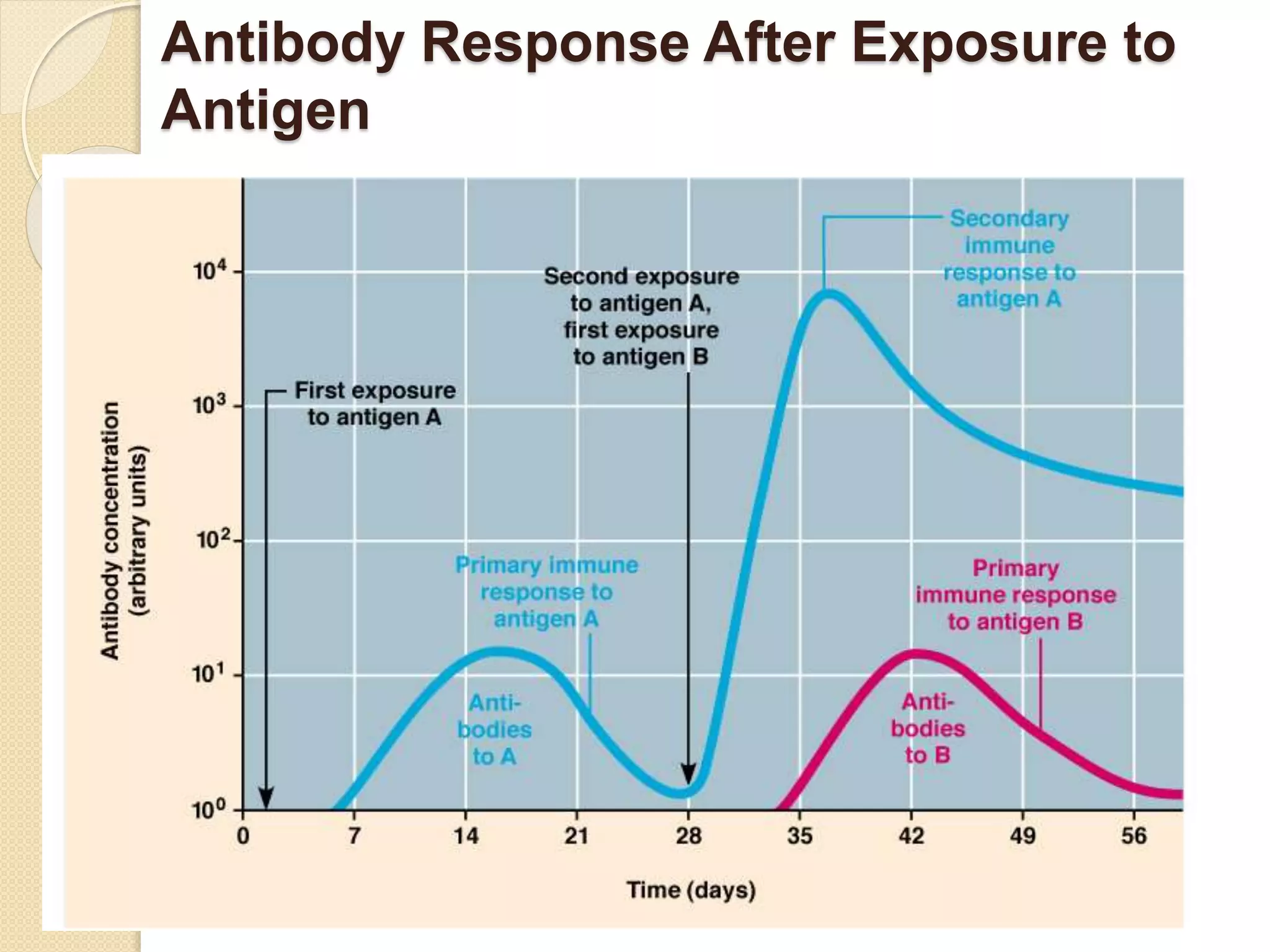
Immunoglobulins (Igs) or antibodies are proteins produced by plasma cells that recognize and bind to specific antigens. There are five classes of Igs (IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, IgE) which have different structures and properties. IgG is the most abundant Ig and provides long-term immunity. IgM is the first antibody produced during initial infection and activates the complement system. IgA is found in secretions and provides immunity at mucosal surfaces. B cells produce antibodies through clonal selection in response to antigens. Antibody binding leads to processes like neutralization, opsonization, and complement activation that help clear pathogens.