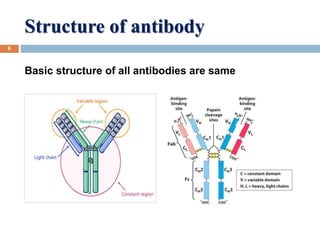
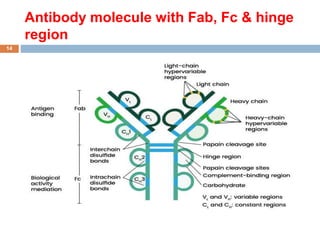
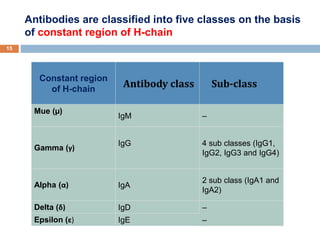
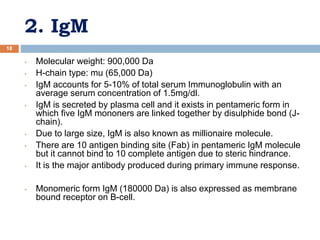
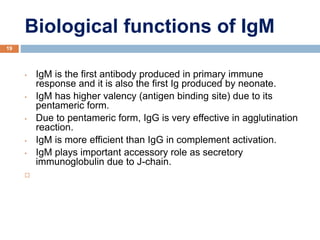
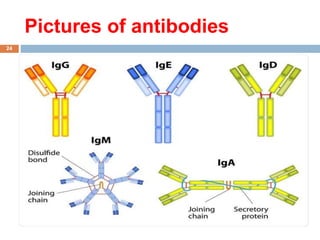
The document provides an overview of antibodies, including their definition, characteristics, structure, classification, and biological functions. Antibodies, or immunoglobulins, are Y-shaped proteins produced by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as viruses and bacteria. The document also categorizes antibodies into five classes (IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, IgE) based on their heavy chain structure and details their specific roles within the immune response.