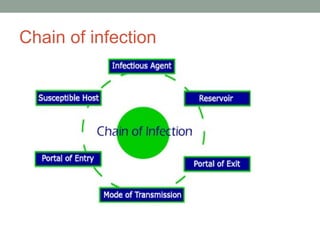
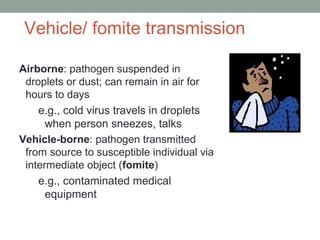
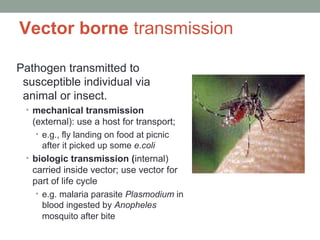
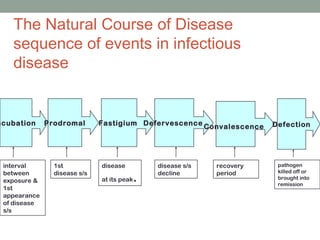
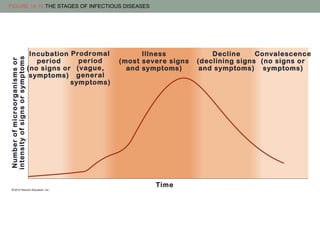
The document discusses key concepts related to host-pathogen relationships and the occurrence and spread of infectious diseases. It defines important terms like infection, disease, colonization, and defines the roles of the host and pathogen. It describes the chain of infection and factors that influence a host's resistance or susceptibility to disease. It also outlines common routes of entry for pathogens, signs and symptoms for different types of infections, and ways that pathogens can spread within the body and between hosts through different modes of transmission.