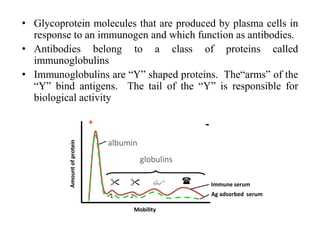
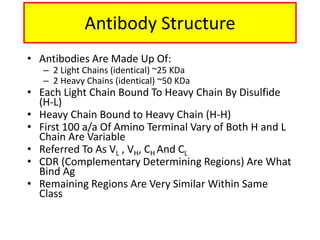
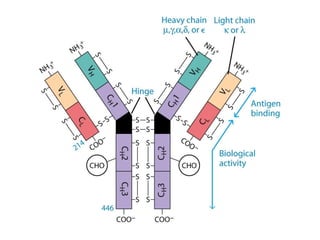
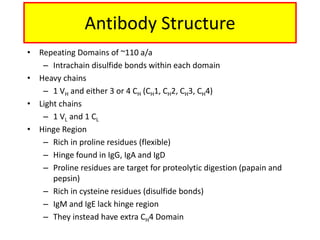
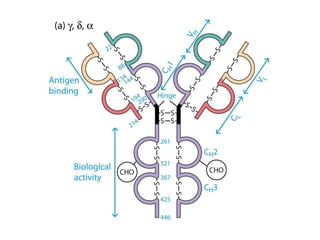
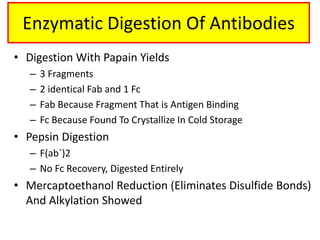
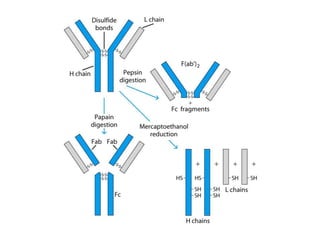
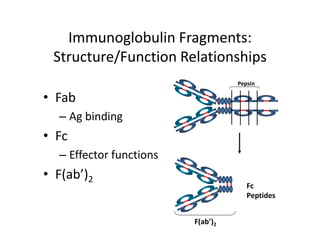
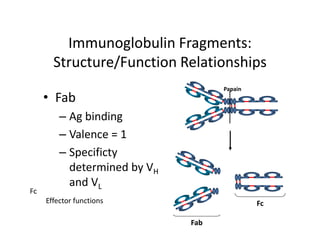
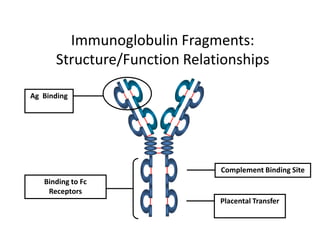
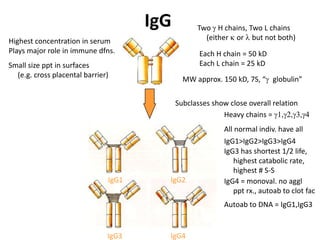
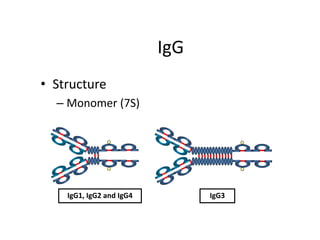
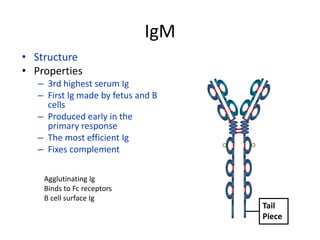
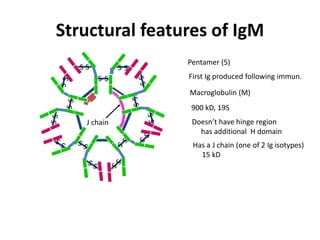
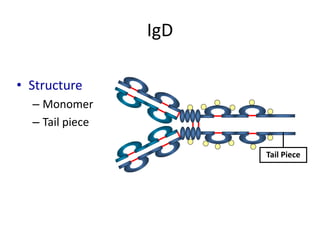
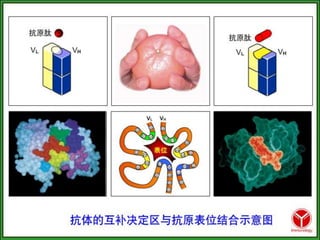
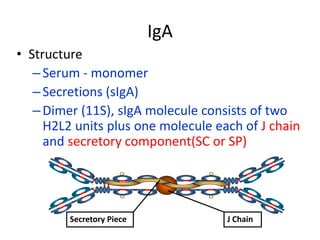
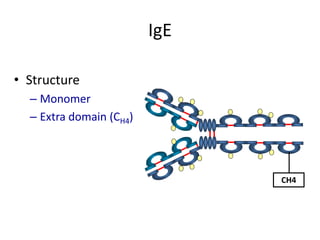
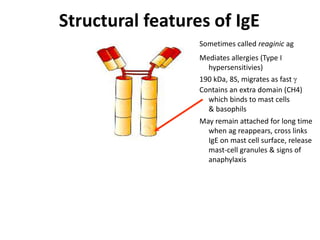
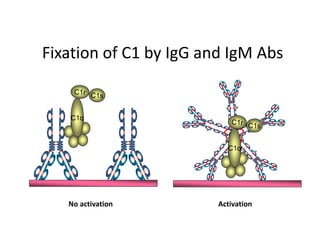
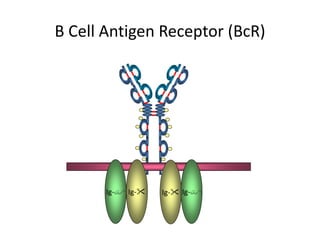
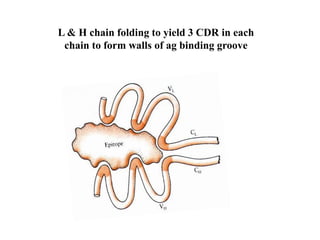
Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are Y-shaped glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells in response to antigens. They belong to a class of proteins called immunoglobulins. The arms of the Y bind antigens while the tail is responsible for biological activity. Antibodies are composed of two light chains and two heavy chains that give them different structures and functions. The five major classes of antibodies are IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, and IgE, which differ in size, structure, concentration in serum, and roles in the immune response.