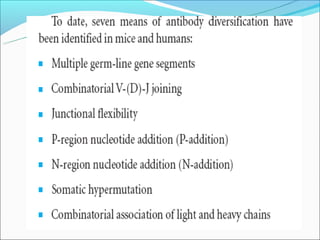
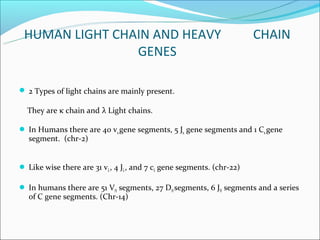
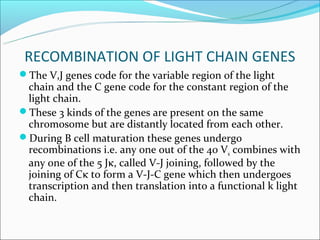
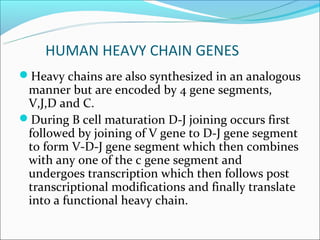
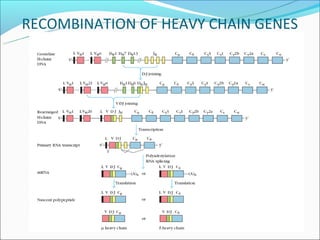
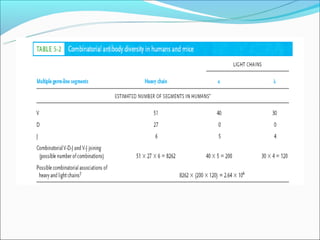
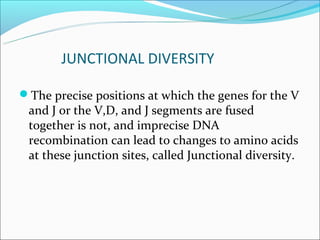
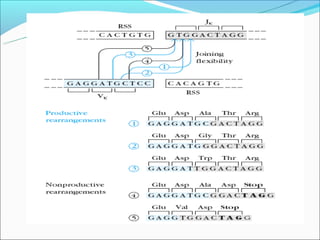
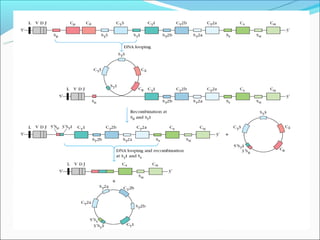
The document summarizes the key mechanisms by which the human immune system generates a diverse repertoire of antibodies from a relatively small number of genes. It describes the somatic variation theory where mutation and recombination of immunoglobulin genes in somatic cells results in high antibody diversity. It explains processes like V(D)J recombination of light and heavy chain genes, junctional diversity, allelic exclusion, somatic hypermutation, and class switching which all contribute to antibody diversity.