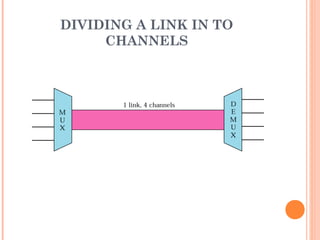
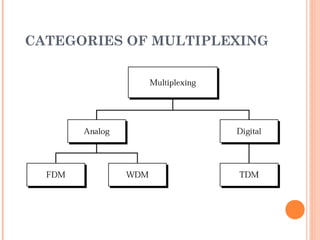
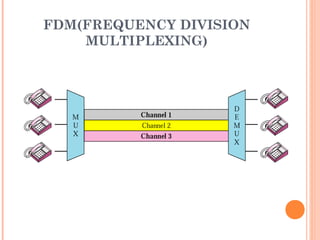
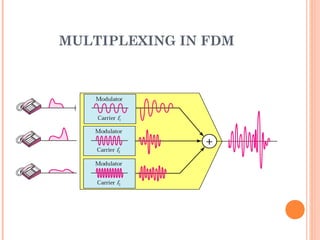
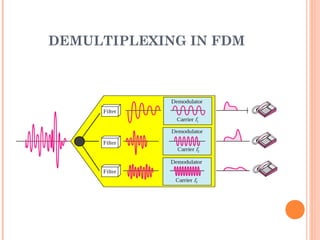
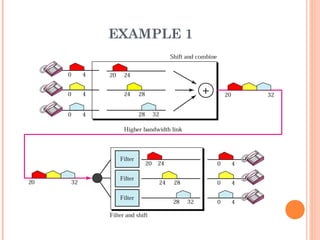
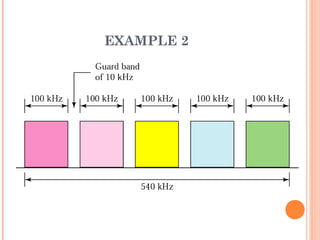
This document discusses frequency division multiplexing (FDM), an analog technique for multiplexing signals over a single communication link. FDM divides the bandwidth of the link into non-overlapping frequency bands, with each band carrying a separate signal. At the transmitting end, signals from different sources are modulated onto carrier frequencies before being combined into a composite signal. At the receiving end, the signals are demodulated by filtering each frequency band to recover the original signals. Examples show how FDM can be used to multiplex voice channels, data channels, and cellular phone signals. Common applications of FDM include radio, television broadcasting, and first-generation cellular systems.