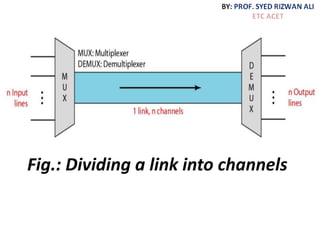
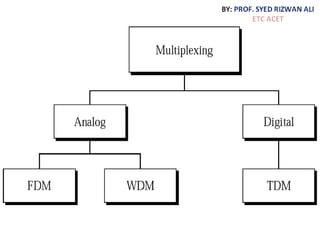
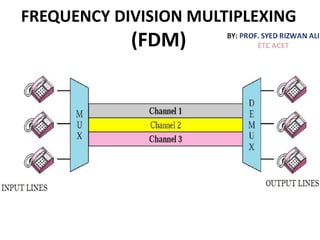
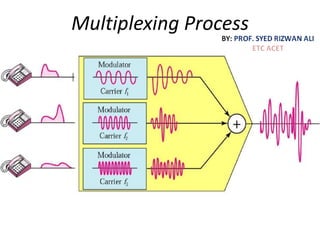
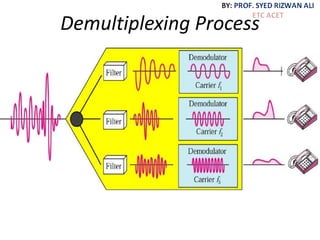
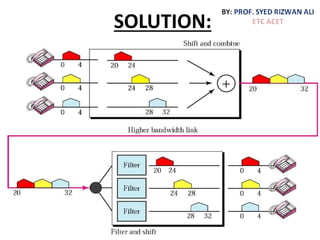
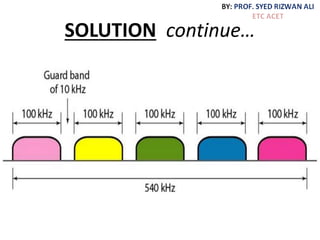
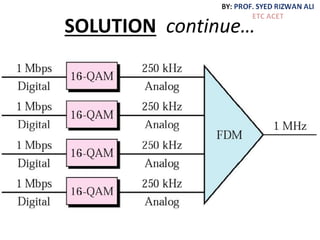
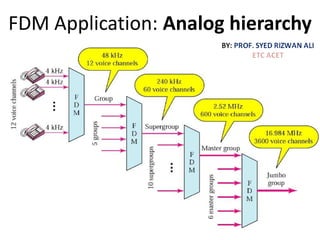
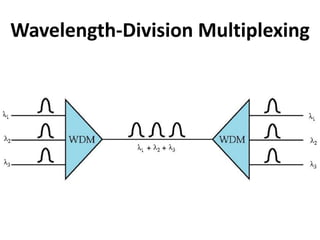
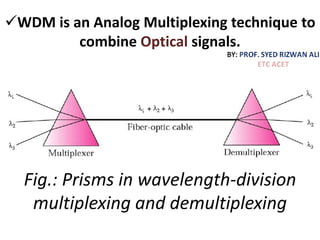
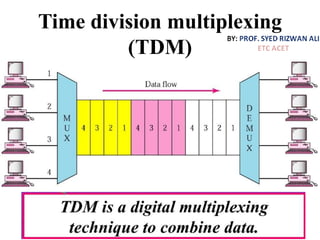
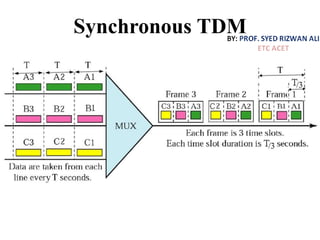
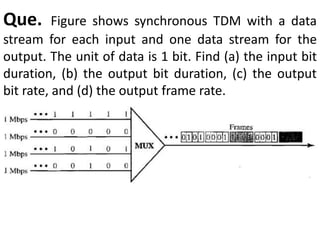
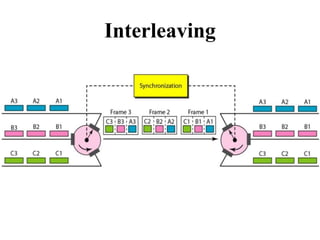
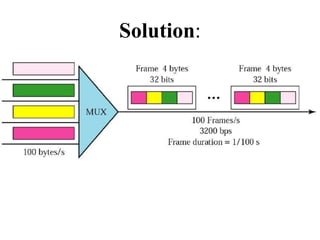
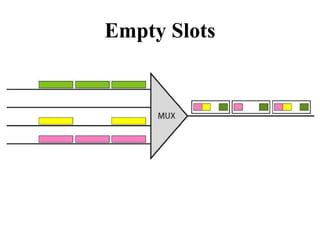
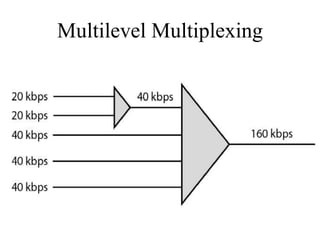
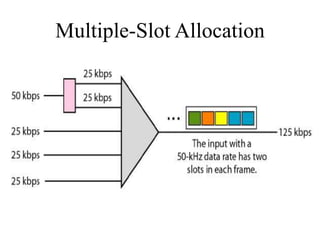
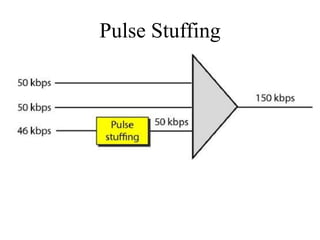
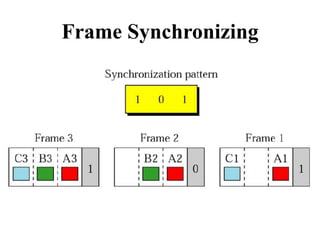
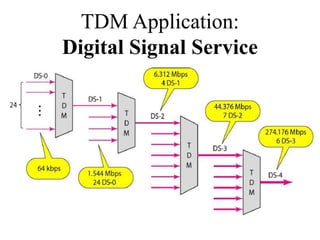
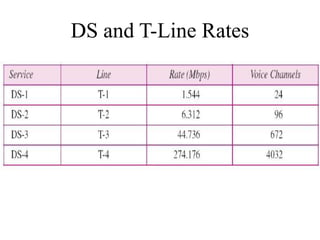
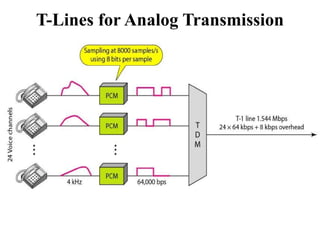
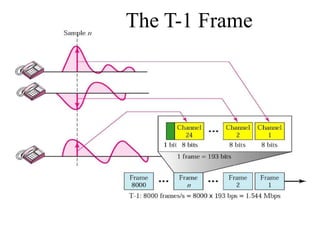
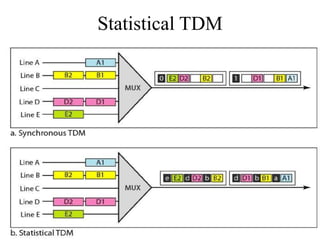
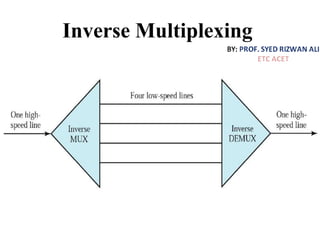
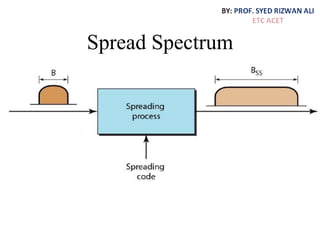
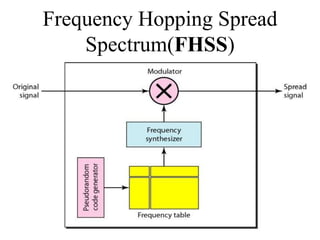
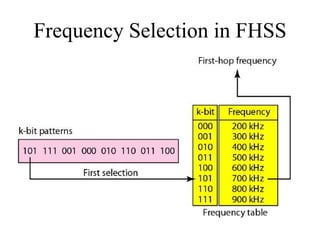
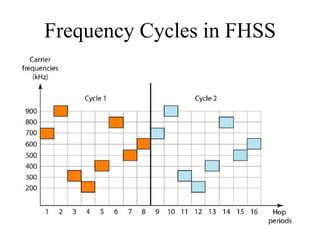
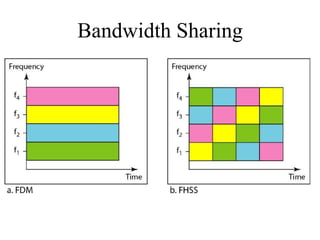
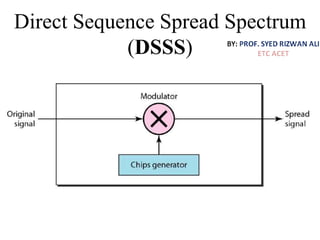
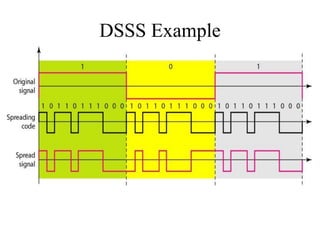
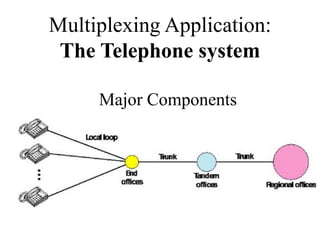
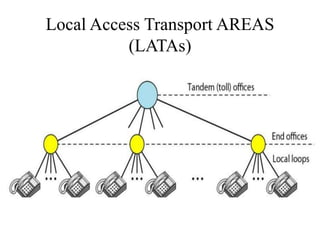
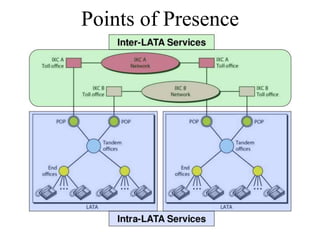
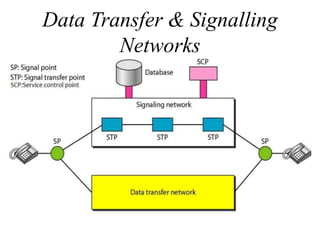
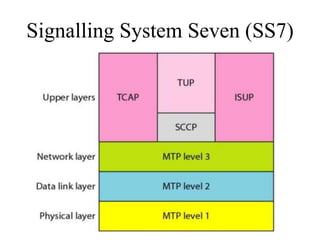
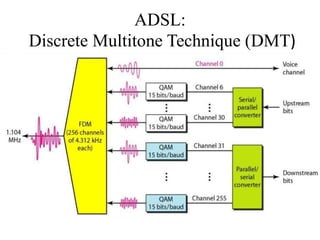
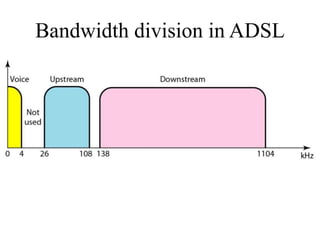
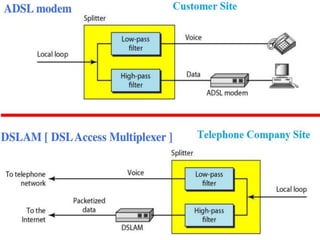
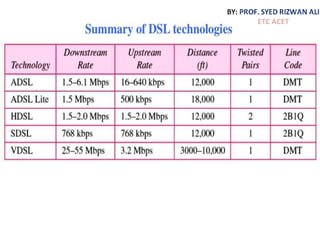
This document discusses multiplexing and spreading techniques for bandwidth utilization and privacy/anti-jamming. It covers frequency division multiplexing (FDM), wavelength division multiplexing (WDM), time division multiplexing (TDM), statistical TDM, inverse multiplexing, frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS), and direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS). Examples are provided for combining voice channels using FDM, optical signal multiplexing with WDM, and modulating data streams for transmission using TDM, FHSS, and DSSS. Common applications discussed include radio/TV broadcasting, fiber optic networks, telephone systems, and digital subscriber lines.