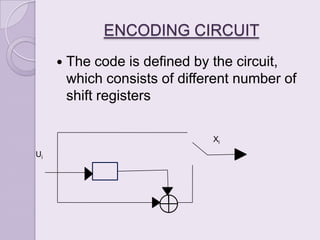
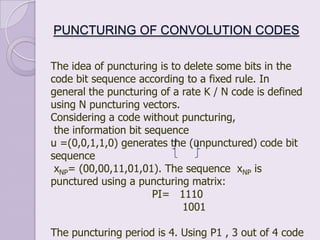
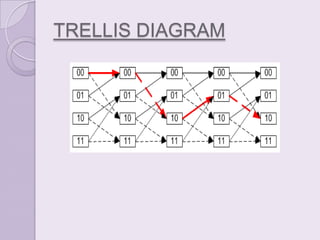
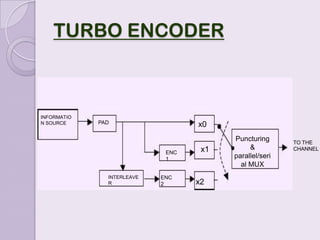
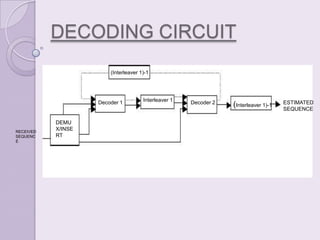
Convolution codes and turbo codes are error-correcting codes used to reliably transmit digital data over noisy communication channels. Convolution codes work by convolving the sequence of information bits according to some rule, spreading the bits along the coded sequence. Turbo codes achieve better error correction than convolution codes through the parallel concatenation of convolutional encoders separated by an interleaver, along with iterative decoding. The Viterbi algorithm is typically used to decode convolution codes by finding the most probable state sequence, while turbo codes use two decoders and feedback to iteratively improve the decoding of each encoded sequence.