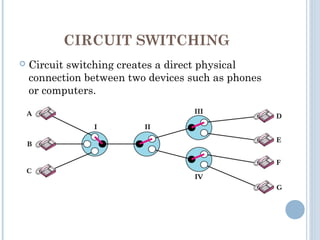
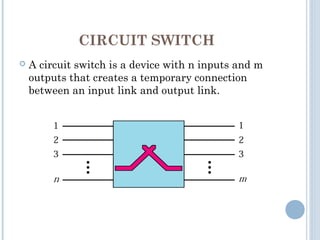
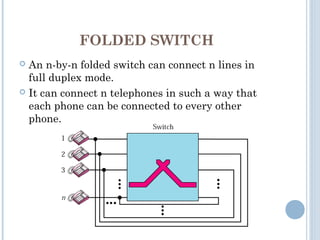
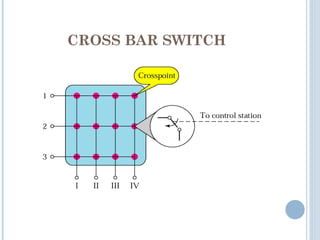
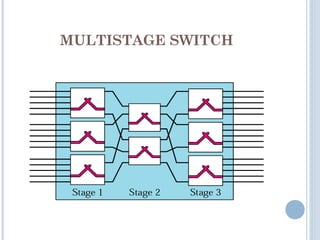
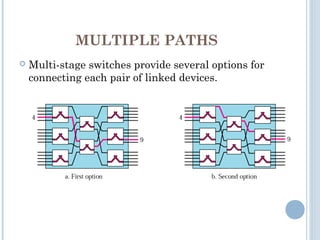
This document discusses communication between devices and circuit switching. It explains that a better solution than direct connections between all devices is to use switching, where switches can create temporary connections between devices. It describes two types of circuit switching: space division switching and time division switching. Space division switching uses either a cross-bar switch or a multistage switch to connect inputs to outputs. A multistage switch overcomes limitations of a cross-bar switch by combining multiple smaller cross-bar switches in stages.