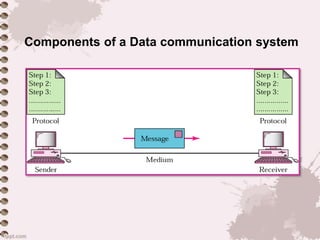
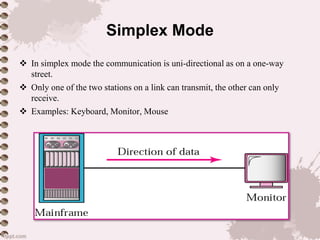
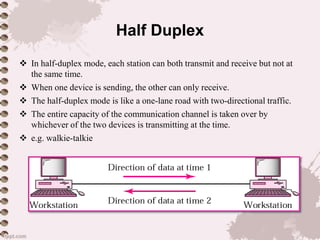
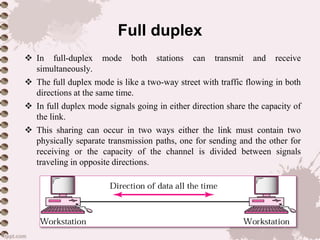
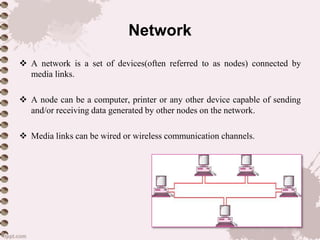
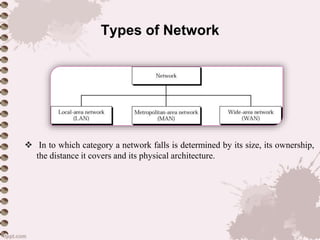
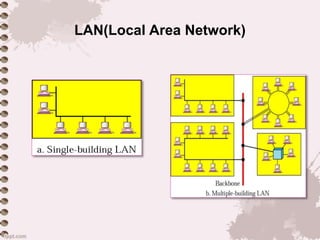
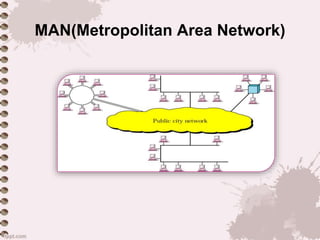
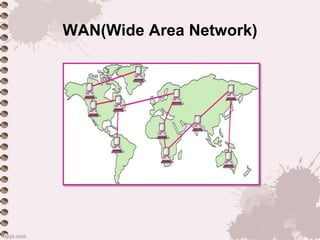
This document provides an overview of a lecture on data communication and computer networks. It defines key concepts like data communication, components of a communication system, transmission modes (simplex, half-duplex, full-duplex), characteristics of networks, types of networks (LAN, MAN, WAN), applications of networks, and a brief history of the Internet and World Wide Web. The document is presented as part of a lecture on introduction to computer networks.