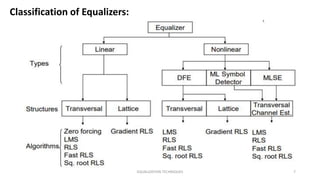
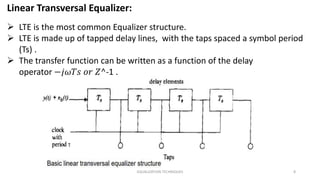
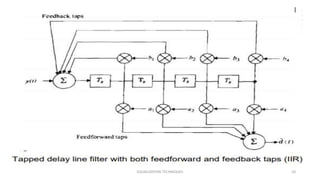
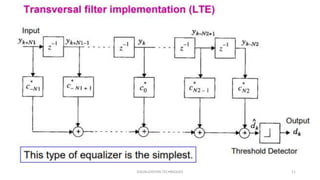
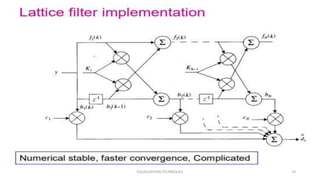
This document discusses various equalization techniques used in mobile communication systems. It describes that equalization is used to compensate for inter-symbol interference caused when the modulation bandwidth exceeds the coherence bandwidth of the radio channel. There are three main techniques discussed: equalization, diversity, and channel coding. Equalization counters inter-symbol interference, diversity reduces fading, and channel coding improves link performance by adding redundant data bits. Linear transversal equalizers and lattice equalizers are described as common equalizer structures.