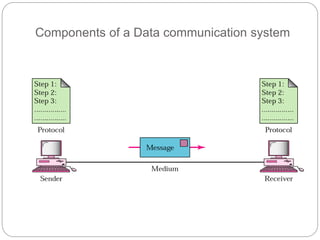
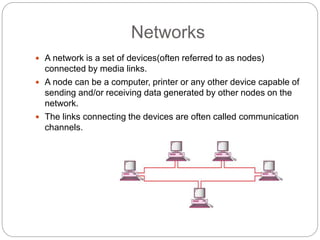
The document is a lecture overview on data communications and networking, detailing its significance, components, and fundamental characteristics. It defines data communication as the exchange of binary data between devices and outlines the structure of communication systems, including networks and distributed processing. Key aspects discussed include the importance of data communication across various fields and the characteristics of effective communication systems: delivery, accuracy, and timeliness.