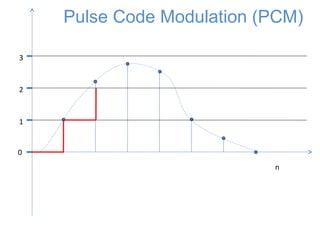
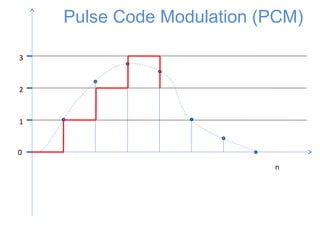
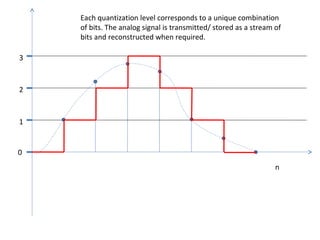
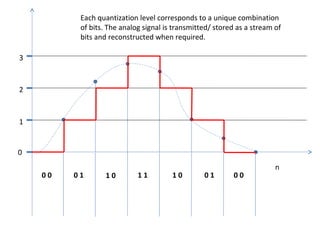
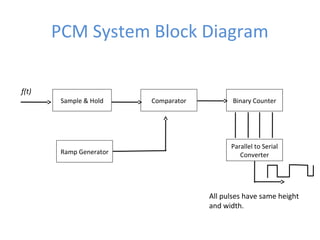
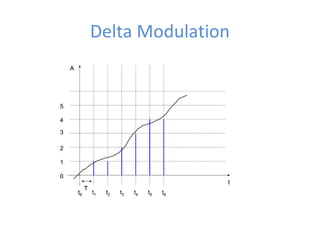
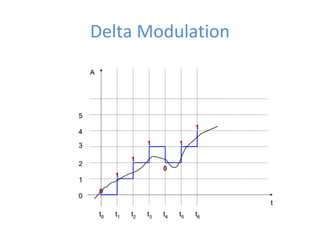
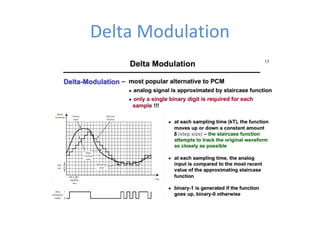
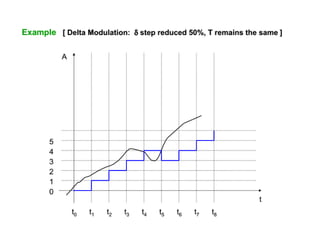
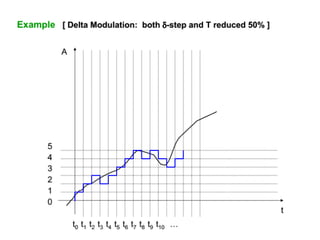
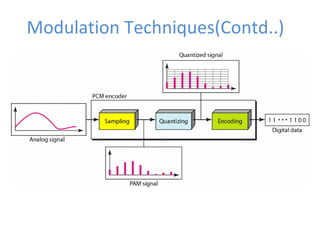
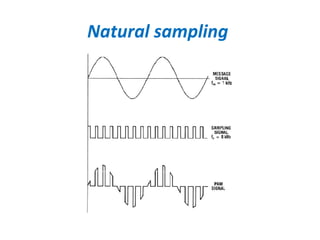
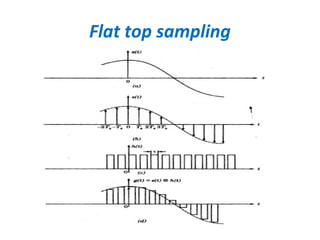
The document discusses modulation techniques, specifically focusing on pulse amplitude modulation (PAM), pulse code modulation (PCM), and delta modulation. It explains the conversion of analog signals to digital through sampling and emphasizes the importance of sampling rates to preserve signal information, introducing the Nyquist rate. It also outlines the characteristics and differences between natural and flat-top sampling in PAM, as well as the basics of PCM and delta modulation for efficient transmission and reconstruction of signals.


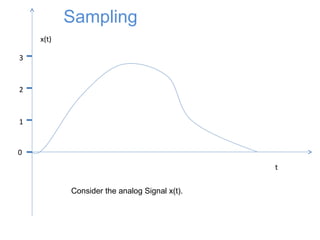
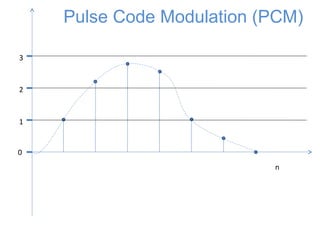
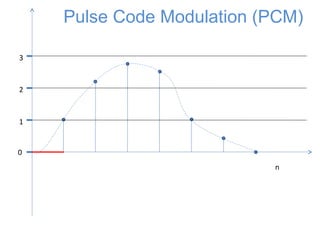
![0
1
2
3
n
x[n]
Sampling
The signal is first sampled](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcm-170722141719/85/Pcm-5-320.jpg)
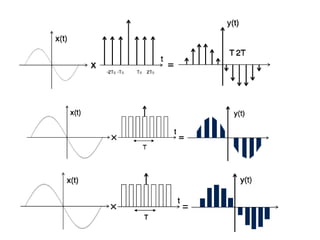








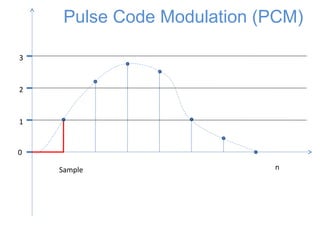
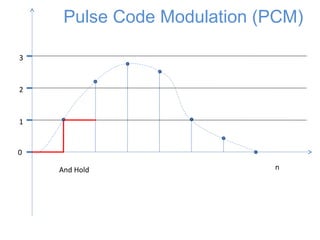
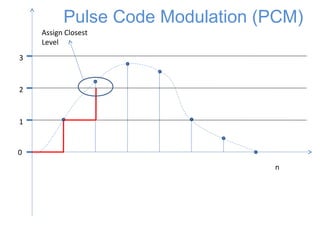
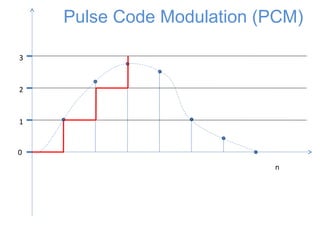
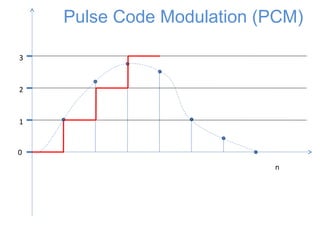
![0
1
2
3
n
x[n]
Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)
The signal is first sampled](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pcm-170722141719/85/Pcm-18-320.jpg)