This document discusses diagnosis of AIDS and HIV infection. It covers several key points:
1. AIDS is a global pandemic that affects all regions of the world. Accurate diagnosis is important for treatment and prevention of further transmission.
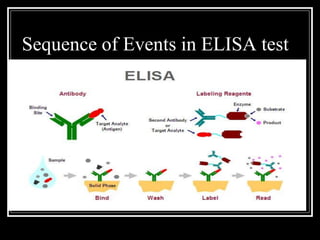
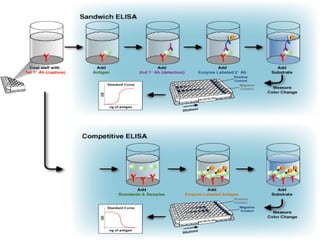
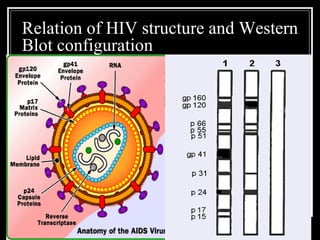
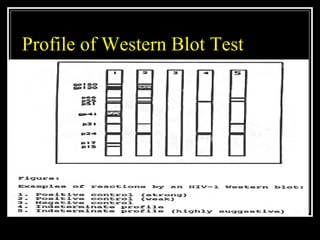
2. Both screening and confirmatory tests are needed to properly diagnose HIV/AIDS. Common screening tests include ELISA, while Western Blot is the gold standard confirmatory test.
3. Molecular tests like PCR and viral load tests can detect HIV even earlier than antibody tests, but are more expensive. CD4 counts are also useful for assessing disease progression.