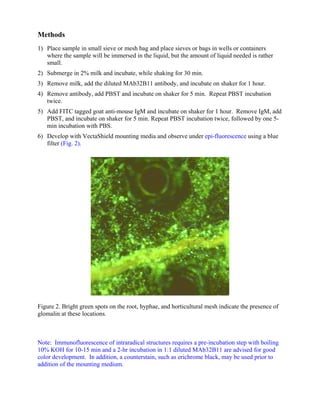
This procedure uses an indirect immunofluorescence assay to determine the location of glomalin on fungal structures, roots, and soil particles. A fluorescent tag (FITC) is added to an IgM antibody that detects glomalin. Under certain light wavelengths, the FITC produces a greenish color where the antibody has bound, indirectly showing where glomalin is located. The sample is incubated with the primary antibody and then a FITC-tagged secondary antibody before being visualized under a fluorescence microscope to see the green spots indicating glomalin.