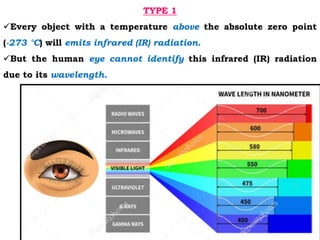
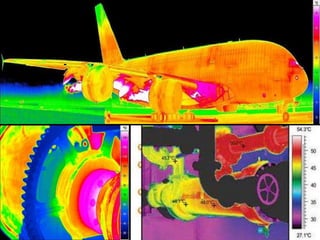
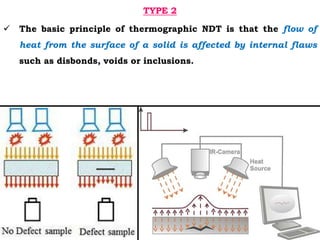
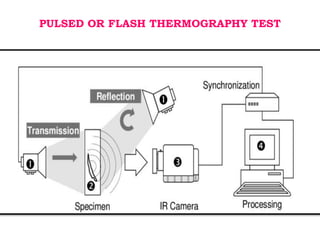
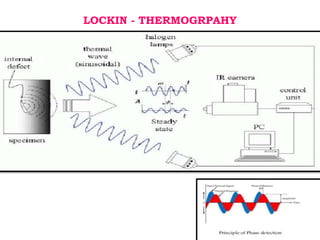
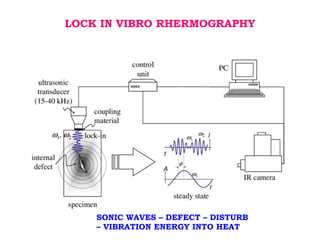
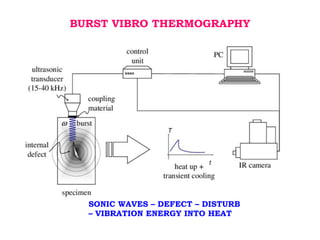
This document discusses thermography testing, which is a non-contact, non-destructive testing method that uses infrared cameras to detect flaws in structures. It can detect a range of defects and be used over large areas. There are different types of thermography including pulsed, lock-in, burst vibro, and lock-in vibro thermography. Thermography has advantages like fast scanning of large areas but limitations in penetration depth. It has applications in aerospace, defense, and other industries to detect issues like voids, delamination, and cracks.