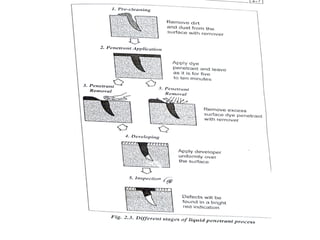
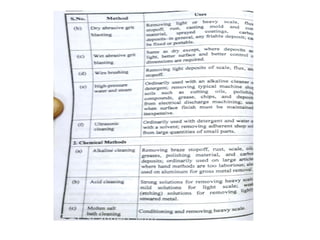
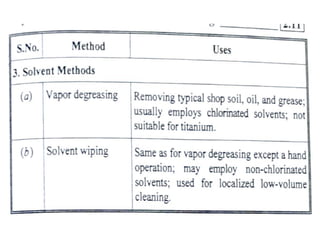
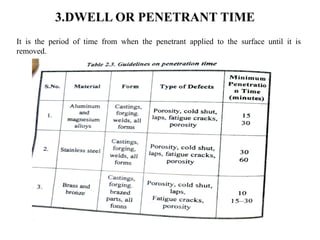
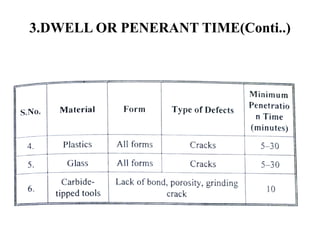
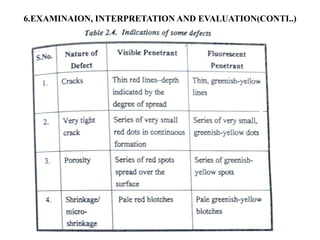
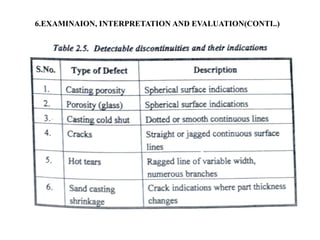
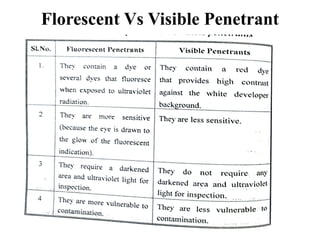
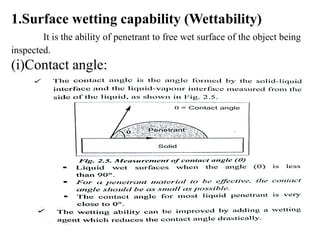
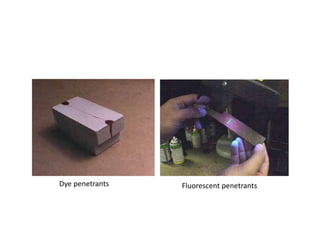
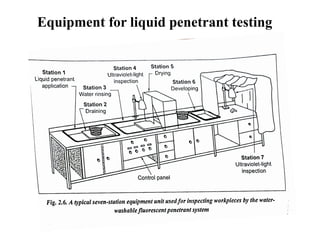
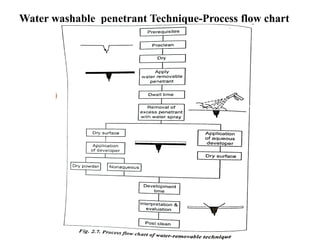
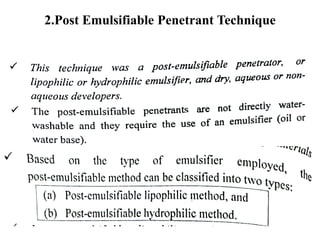
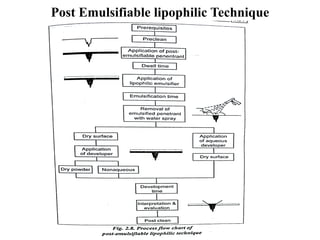
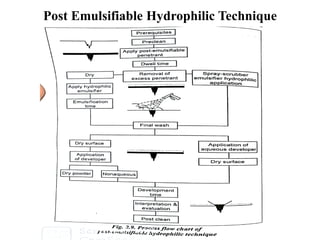
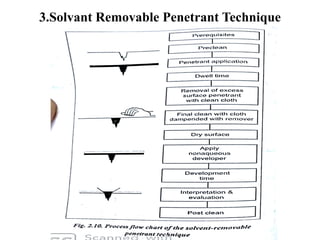
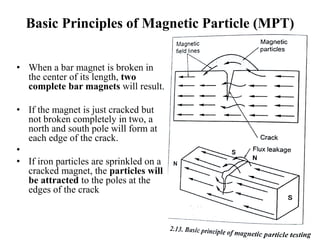
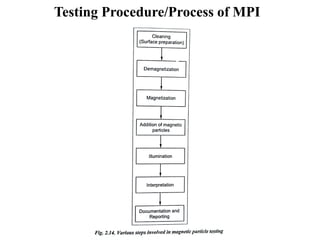
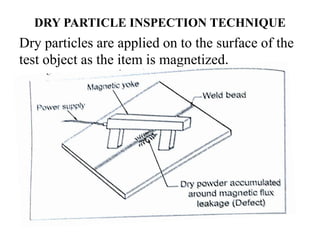
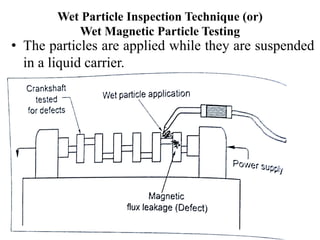
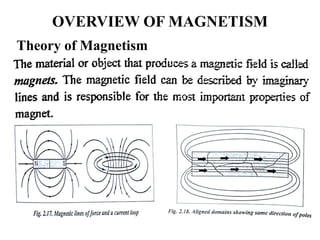
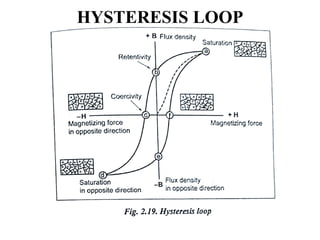
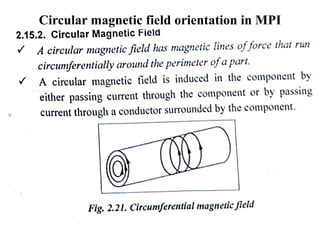
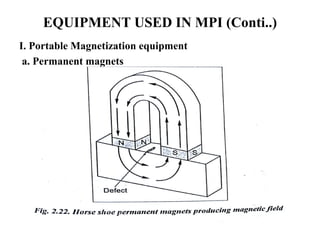
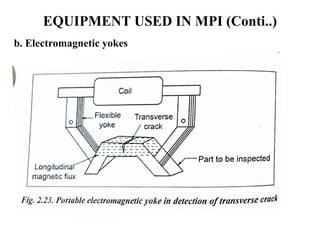
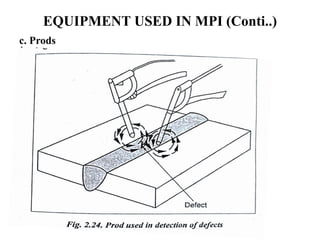
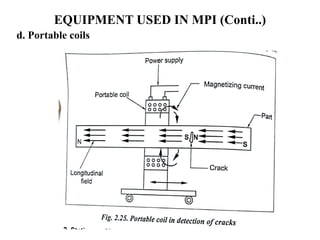
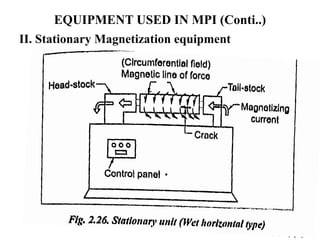
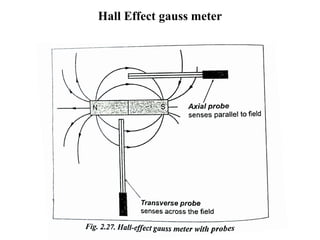
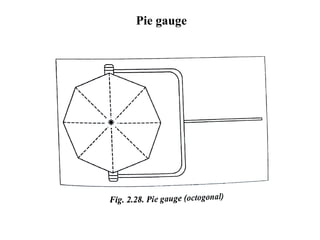
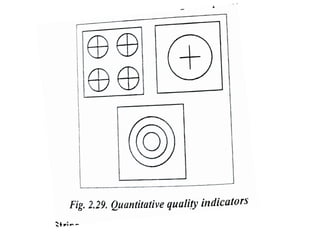
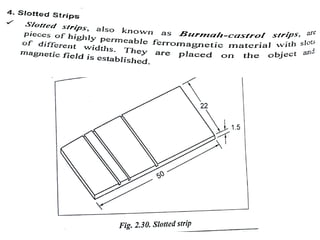
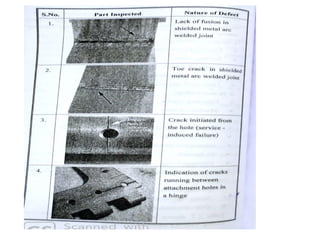
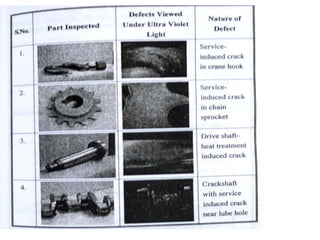
The document discusses liquid penetrant testing (LPT) and magnetic particle testing (MPT) as two surface non-destructive testing methods. It describes the basic principles, testing procedures, equipment, and applications of LPT and MPT. For LPT, it explains how penetrants are drawn into surface flaws using capillary action and developers are used to reveal the flaws. For MPT, it outlines how magnetizing a material causes magnetic particles to accumulate at flaws, making them visible. Both are effective for detecting surface-breaking defects in many materials.