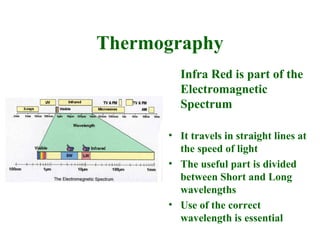
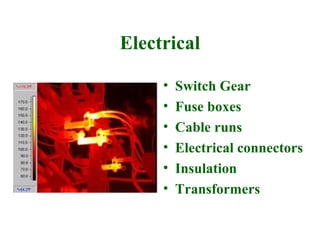
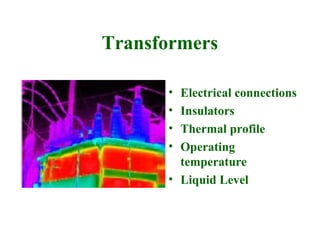
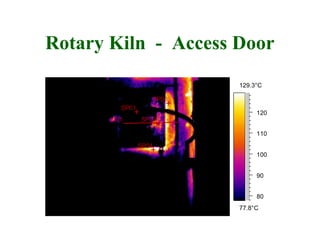
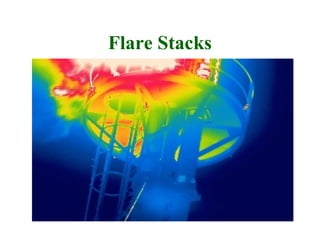
Thermographic testing uses infrared cameras to detect differences in surface temperatures that may indicate issues. It allows non-contact inspection of electrical equipment, buildings, industrial processes, and more. Key advantages are that it is non-destructive, fast, and can detect problems like loose connections, moisture ingress, insulation issues, and more from a distance. Operator experience is important to properly set up the infrared camera and interpret thermal images.