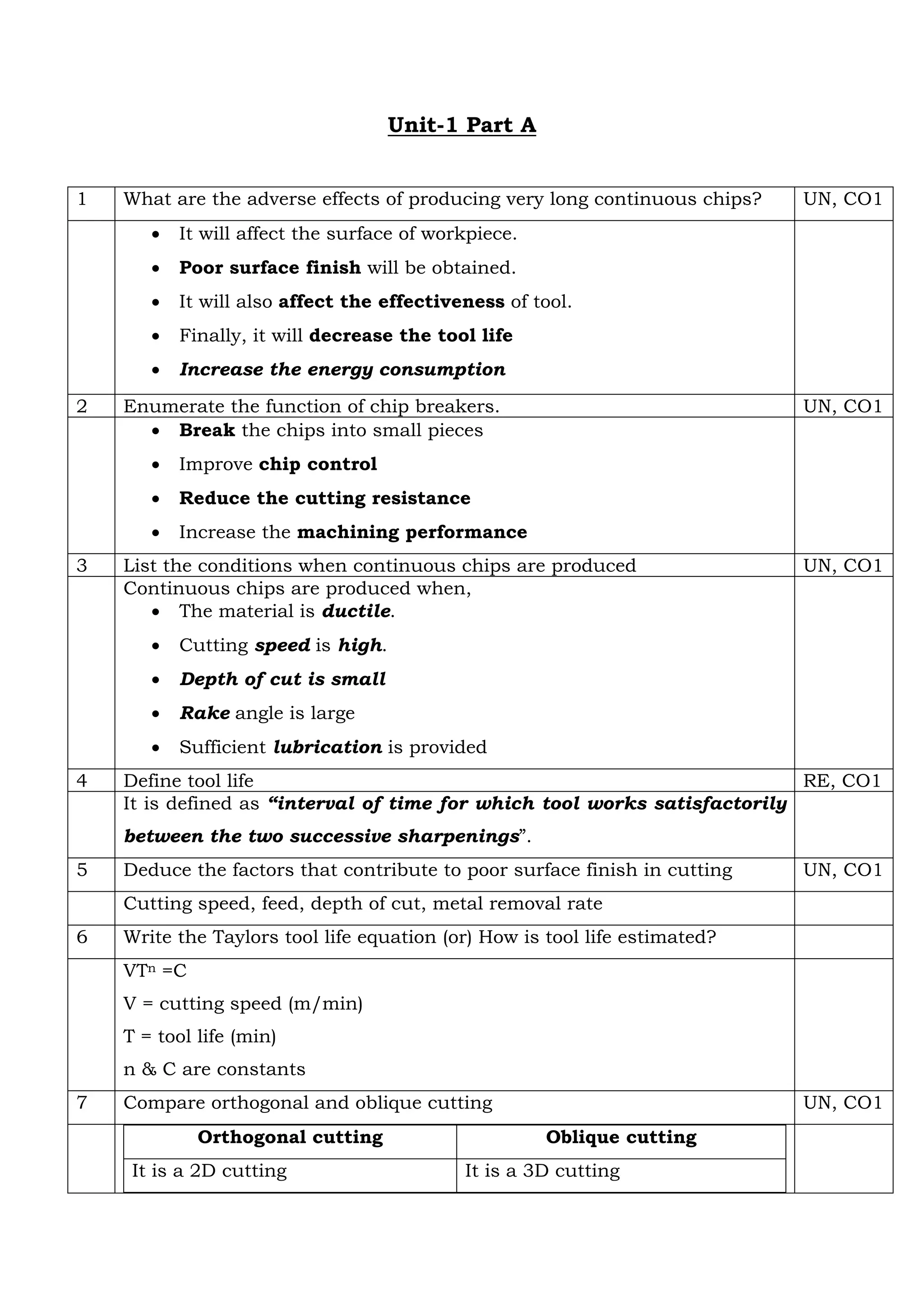
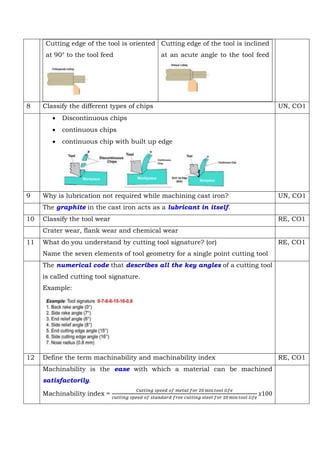
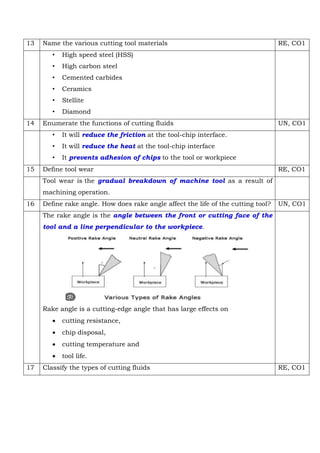
Producing very long continuous chips can adversely affect the workpiece surface finish and tool effectiveness, decrease tool life, and increase energy consumption. Chip breakers break chips into small pieces to improve chip control, reduce cutting resistance, and increase machining performance. Continuous chips are produced when the material is ductile, cutting speed is high, depth of cut is small, rake angle is large, and sufficient lubrication is provided. Tool life is defined as the interval of time for which a tool works satisfactorily between two successive sharpenings.