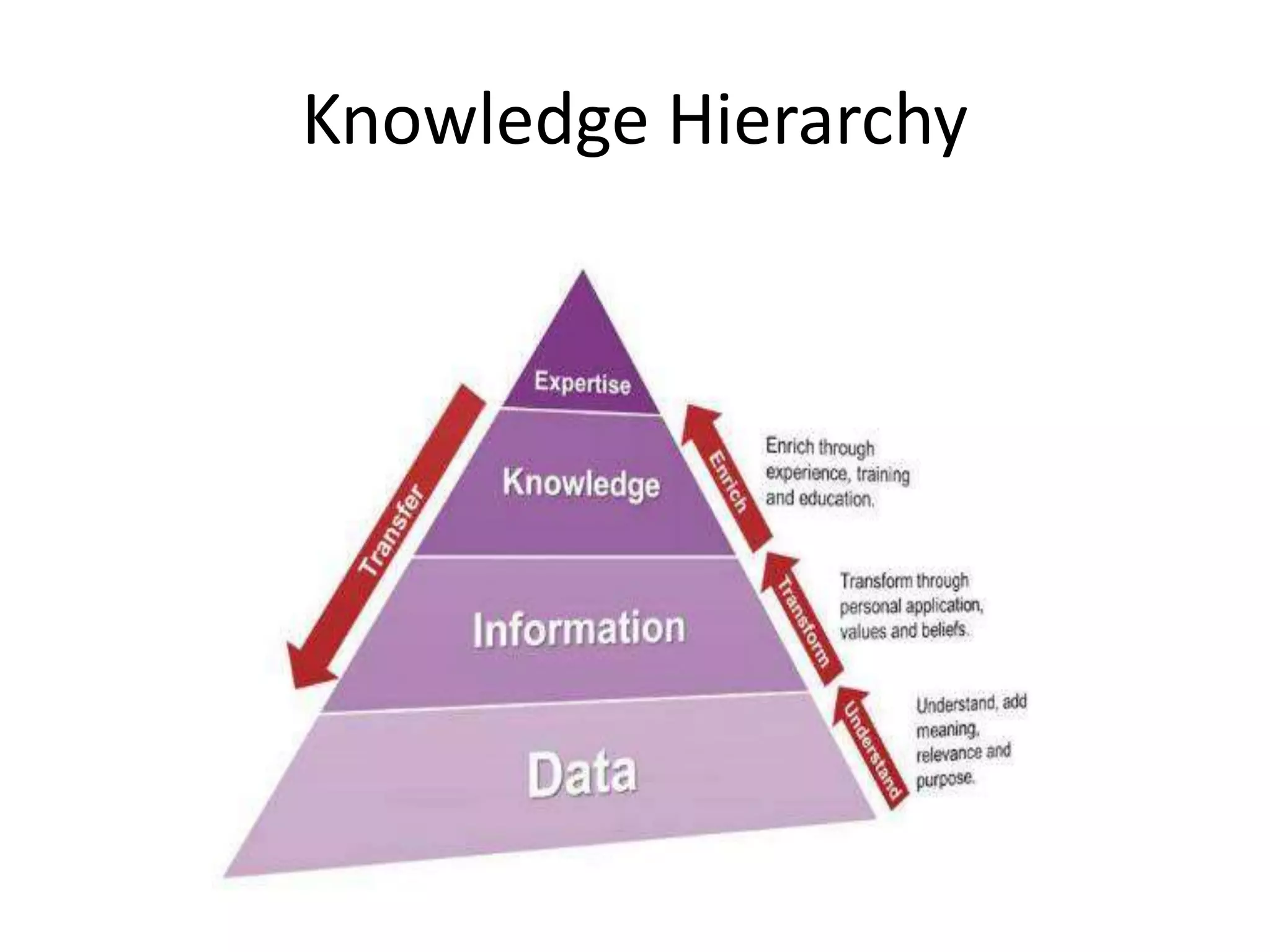
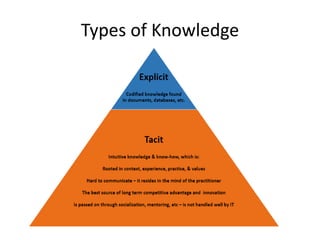
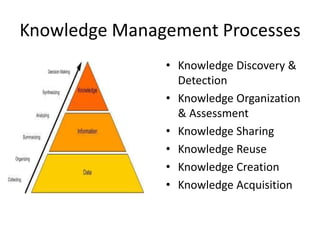
A knowledge management system is an information system designed to assist in sharing and integrating knowledge within an organization. It facilitates key knowledge management processes like knowledge discovery, organization, sharing, reuse, and creation. Benefits of a KM system include giving all employees access to management and business knowledge, making it easier to adopt new technologies, and improving staff engagement. Examples of KM systems include feedback databases that share customer and employee feedback, shared project files that allow collaborative work, and research databases containing market information.