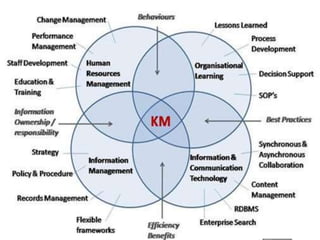
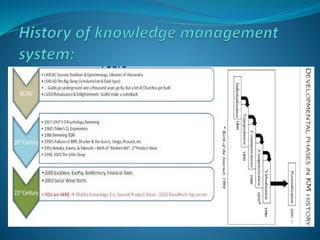
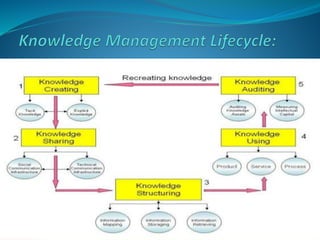
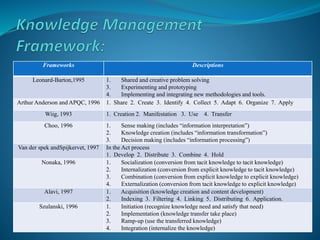
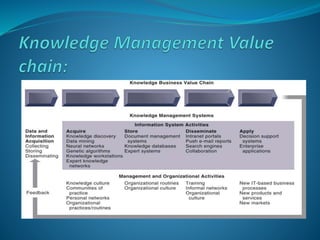
The presentation discusses the creation, distribution, and effective use of knowledge within organizations through various frameworks of knowledge management. It emphasizes the importance of both explicit and tacit knowledge and outlines methodologies for developing, sharing, and applying knowledge to enhance organizational effectiveness. Various scholars' contributions to knowledge processes are referenced, highlighting strategies for problem-solving, decision-making, and knowledge transfer.