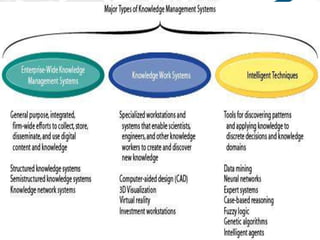
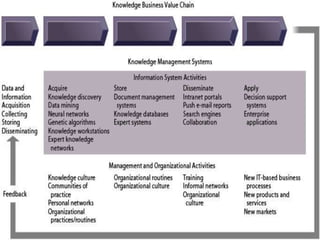
1) The document discusses knowledge management systems and knowledge-based expert systems. It describes key capabilities like leveraging existing knowledge and creating new knowledge to position companies favorably in markets.
2) Important reasons for actively managing knowledge are to facilitate decision-making, build learning organizations, and stimulate cultural change and innovation.
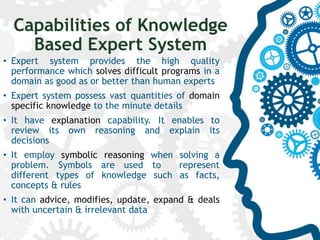
3) Expert systems provide high quality performance solving difficult problems like human experts through vast domain knowledge and explanation capabilities.