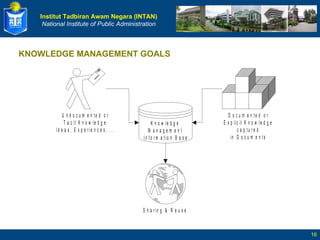
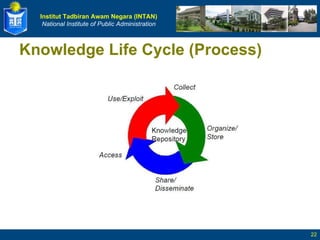
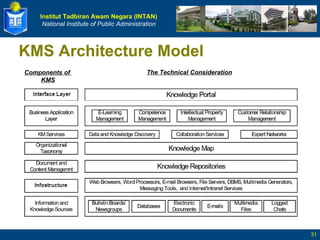
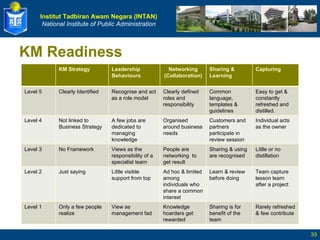
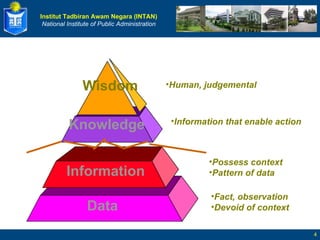
The document defines key terms related to knowledge management and discusses its implementation. It begins by defining data, information, knowledge, and wisdom. It then discusses tacit and explicit knowledge and the knowledge conversion process. The rest of the document outlines the definition and goals of knowledge management, its key elements and benefits, and a five stage roadmap for implementation.
![KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT Zakaria Deraman [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/km-ver1-0stud-100420232926-phpapp01/75/Km-ver-1-0-student-1-2048.jpg)





![Knowledge conversion – Tacit to Explicit Internalization [i&g&o] training mentoring tacit Socialization [i&i] brainstorming meeting Combination [g&o] repositories CoP tacit tacit tacit explicit explicit explicit explicit Externalization [ i&g] videotaping knowledge map](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/km-ver1-0stud-100420232926-phpapp01/85/Km-ver-1-0-student-8-320.jpg)