1. The document proposes an efficient knowledge management model for Iran's agricultural sector that uses a systems approach to connect all relevant players and organizations.
2. It analyzes the current situation which includes illiteracy among farmers, lack of coordination between organizations, and disconnection between farmers and the agricultural system.
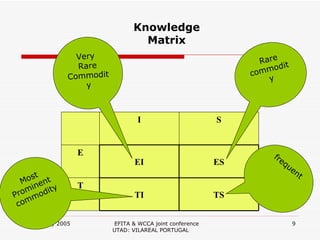
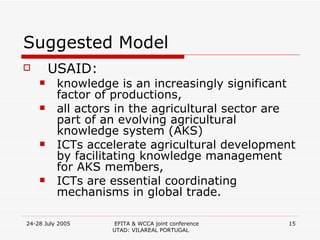
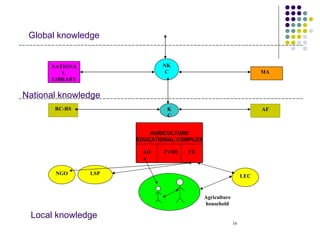
3. The suggested model aims to create connections between different levels of knowledge - from local to national to global - using organizations, libraries, and ICTs to facilitate knowledge sharing.