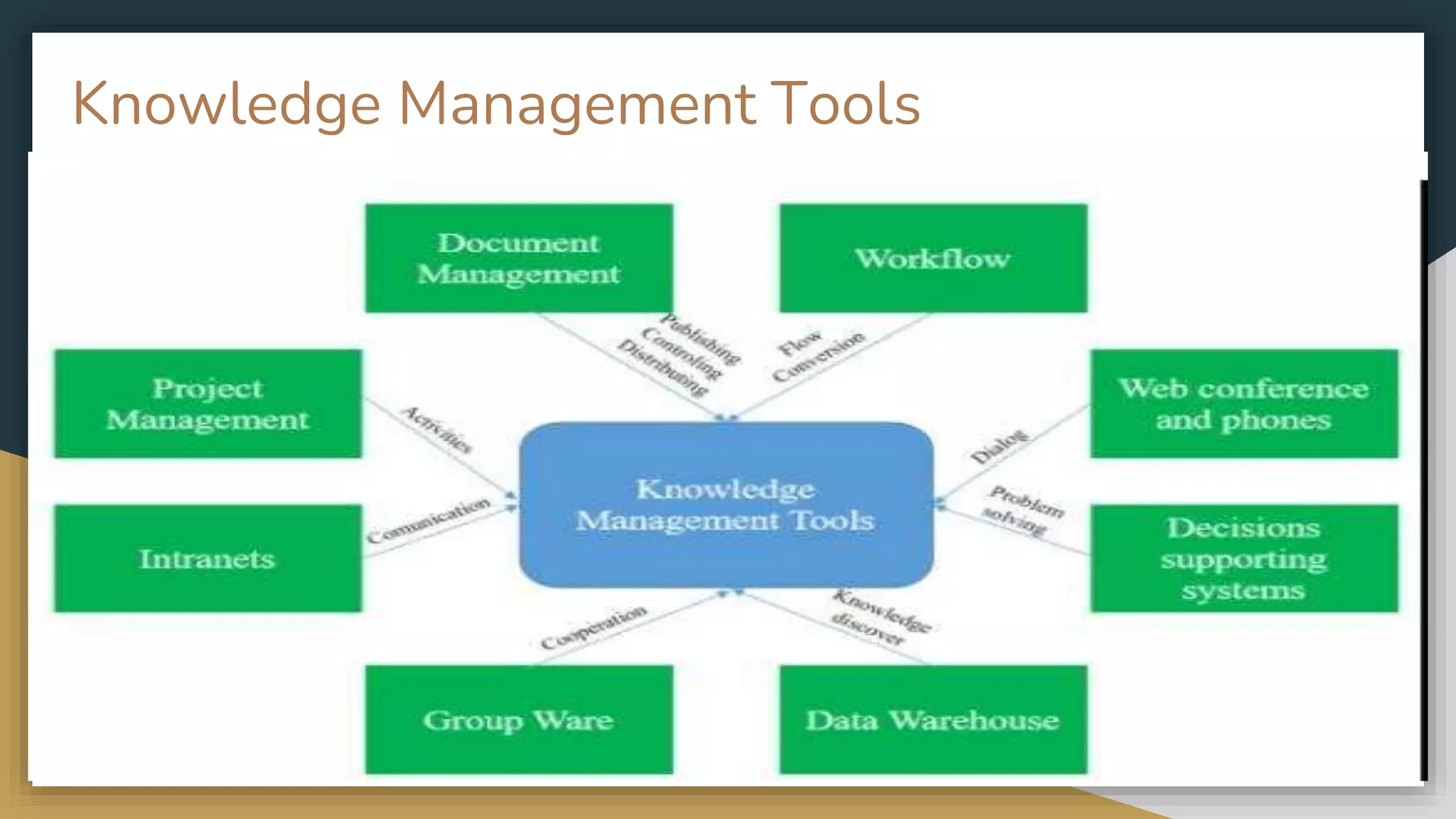
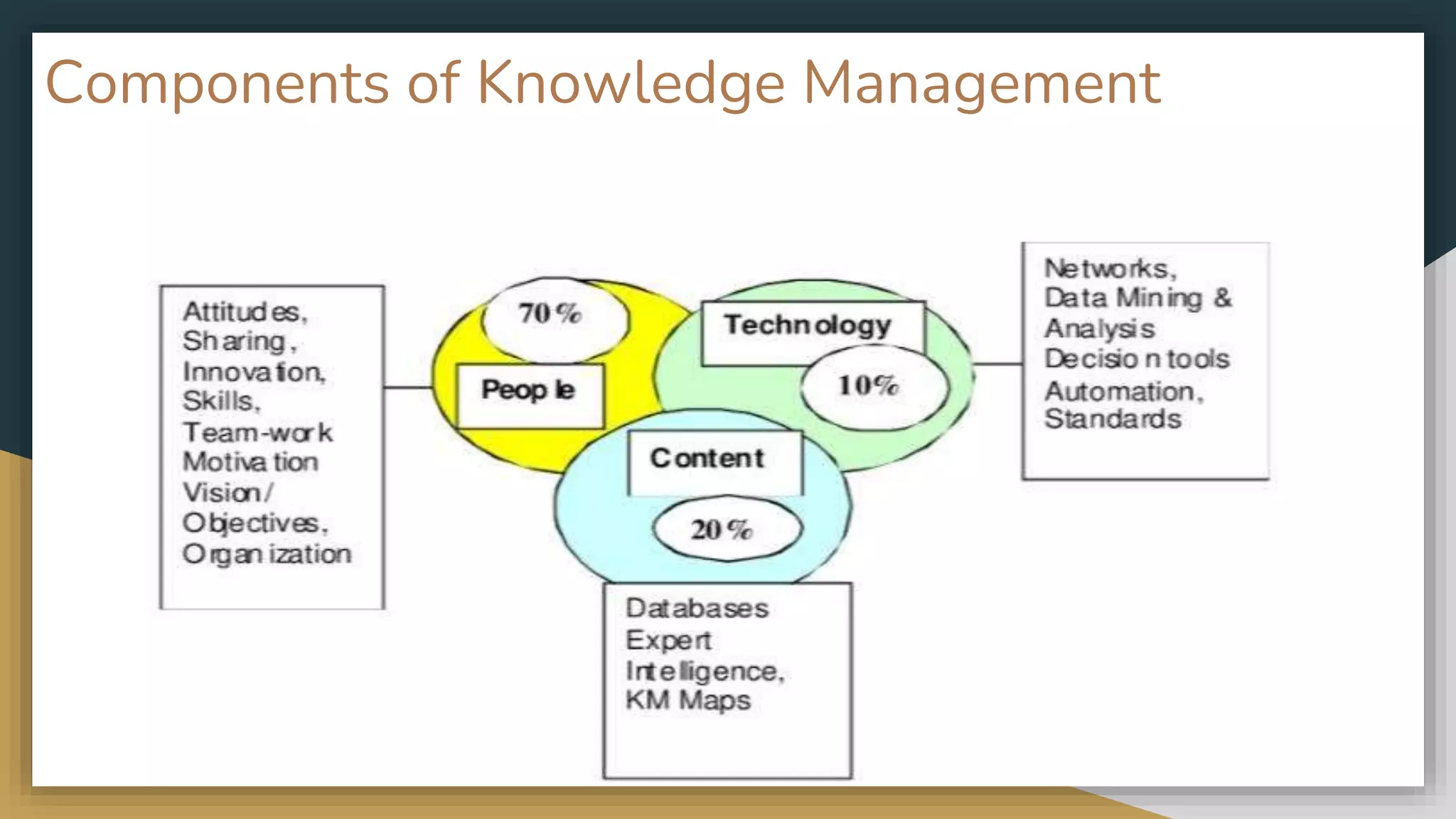
The document discusses knowledge management (KM) and its significance in libraries, outlining types of knowledge, objectives, challenges, and benefits of KM. It emphasizes the importance of both tacit and explicit knowledge in enhancing organizational learning and improving library services through effective sharing and utilization of knowledge. The changing landscape of libraries due to technology and globalization highlights the need for integrating KM practices to meet user expectations and drive innovation.