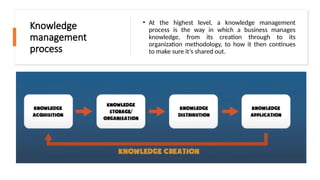
Knowledge management (KM) is crucial for organizing and sharing information within an organization, enhancing efficiency, productivity, and informed decision-making. It encompasses explicit, implicit, and tacit knowledge and utilizes systems such as document management and intranets to facilitate the process. Successful KM implementation requires a strategic approach, robust tools, and a culture that prioritizes knowledge sharing to thrive in a competitive environment.