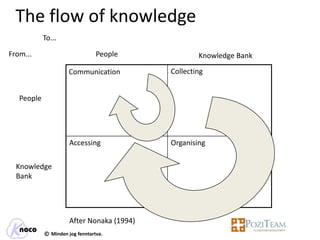
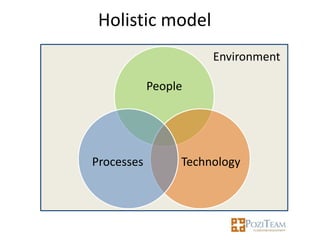
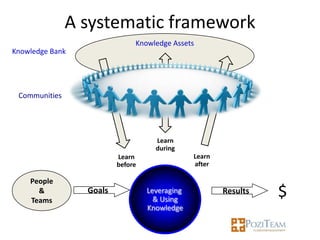
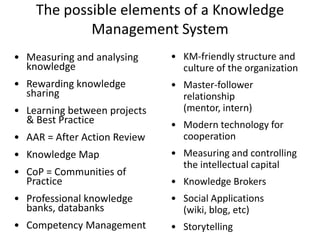
The document outlines the importance of knowledge management (KM) for the success of clusters, citing the experience of Tibor Gyulai, an expert in organizational development and KM. It discusses the benefits of KM in fostering innovation, enhancing decision-making, and cultivating a knowledge-sharing culture among member companies within clusters. Additionally, it emphasizes the role of cluster management in integrating KM processes and the need for collaboration and shared resources to optimize knowledge capital.