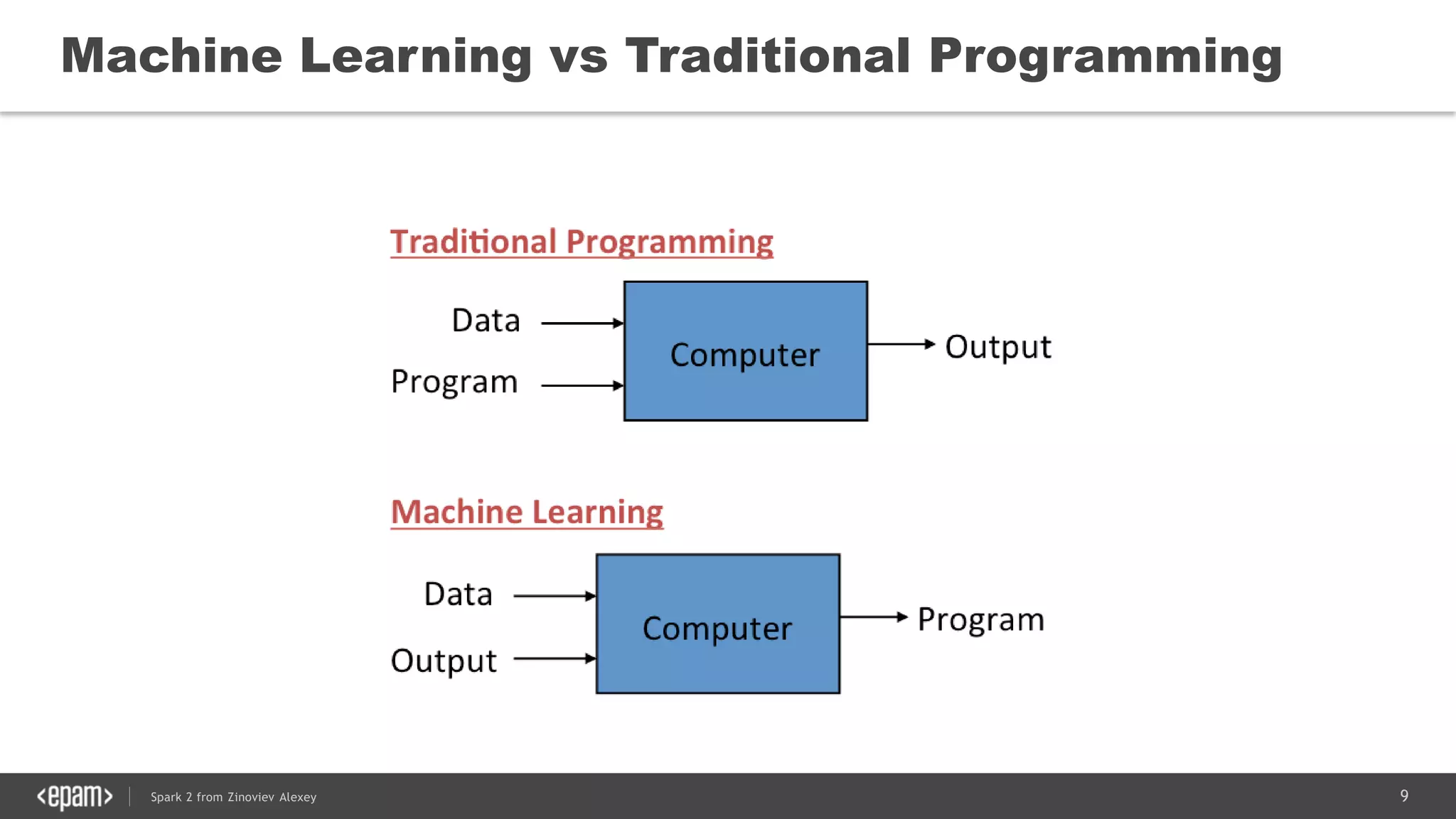
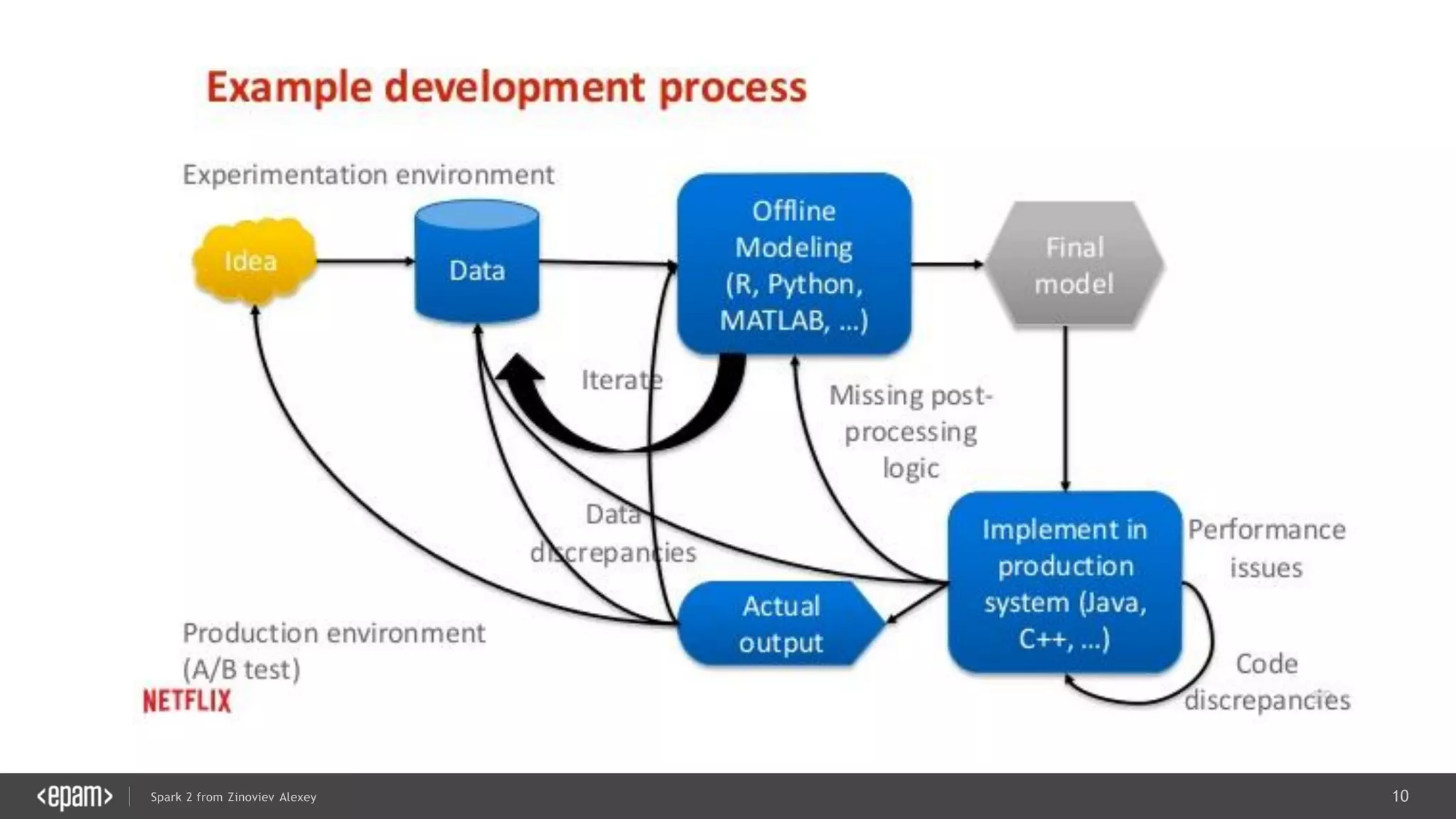
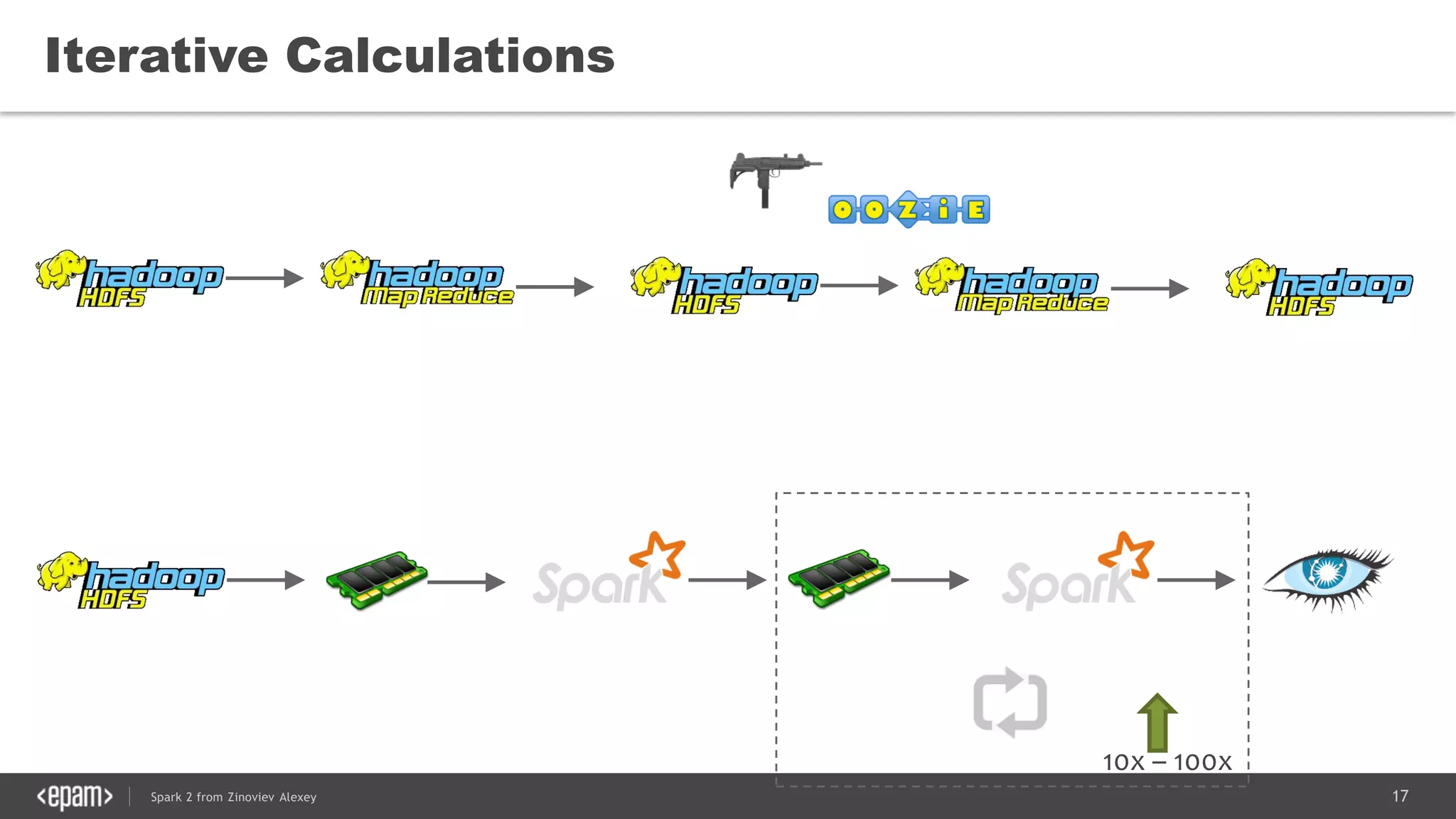
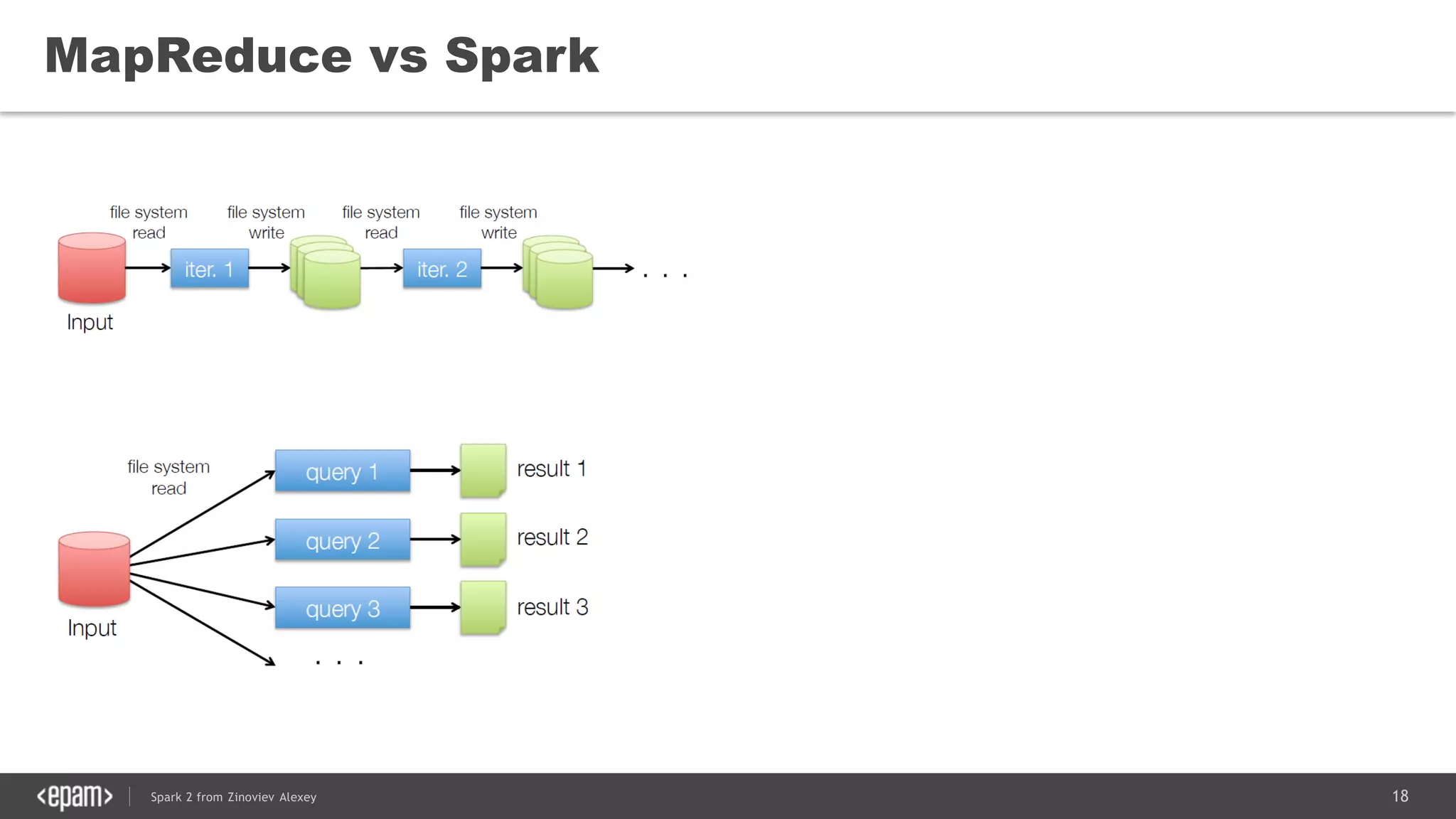
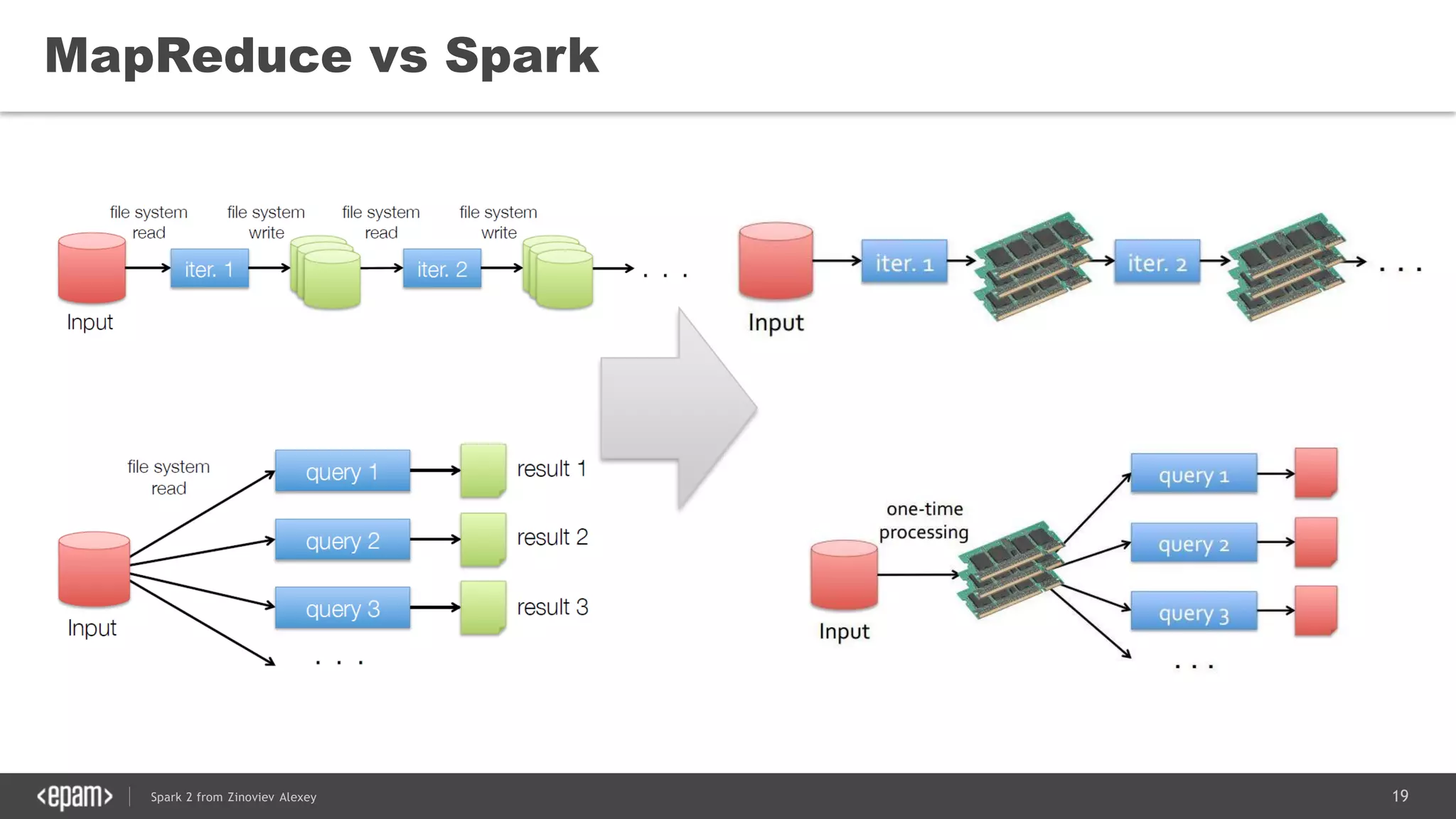
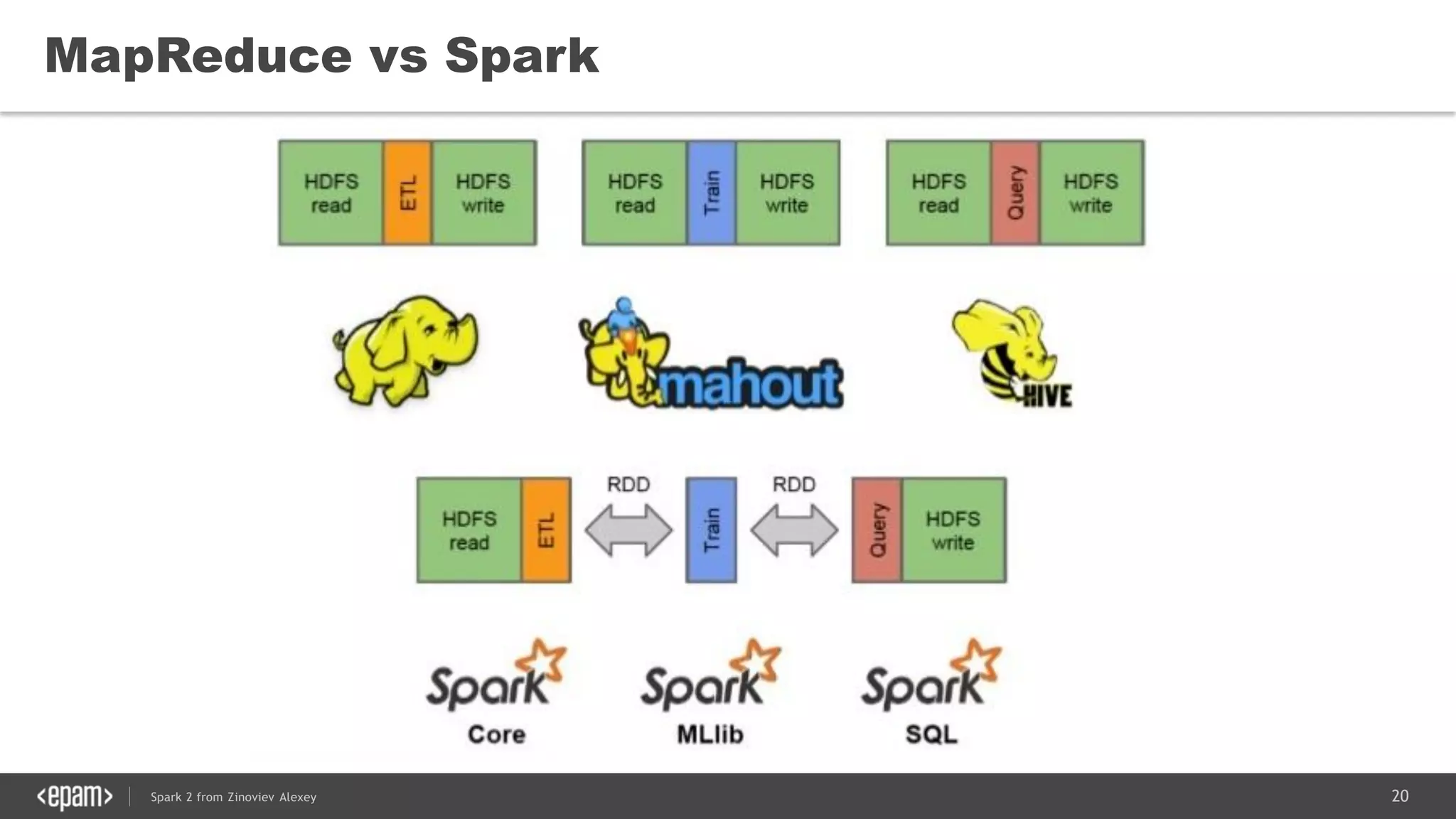
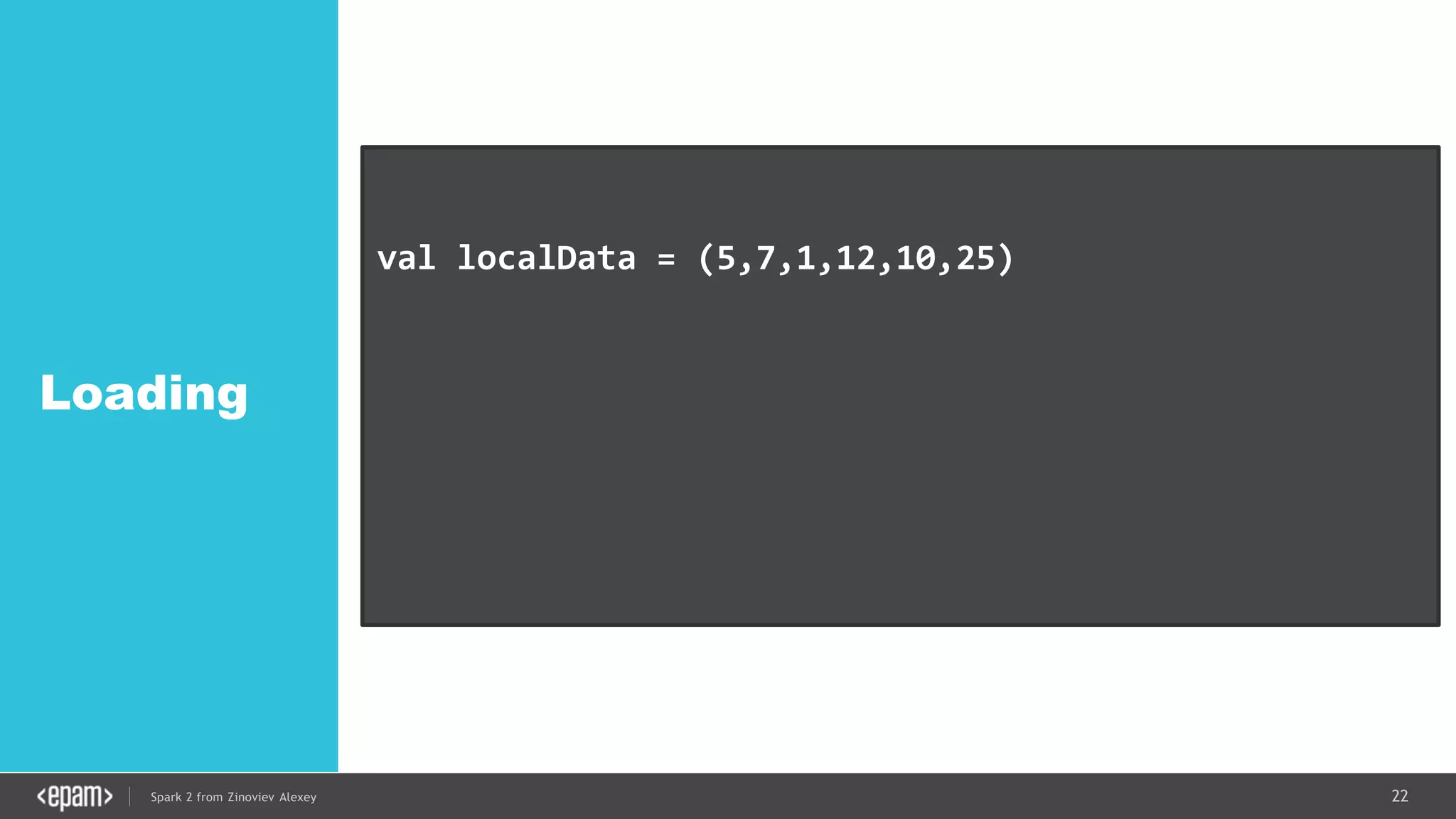
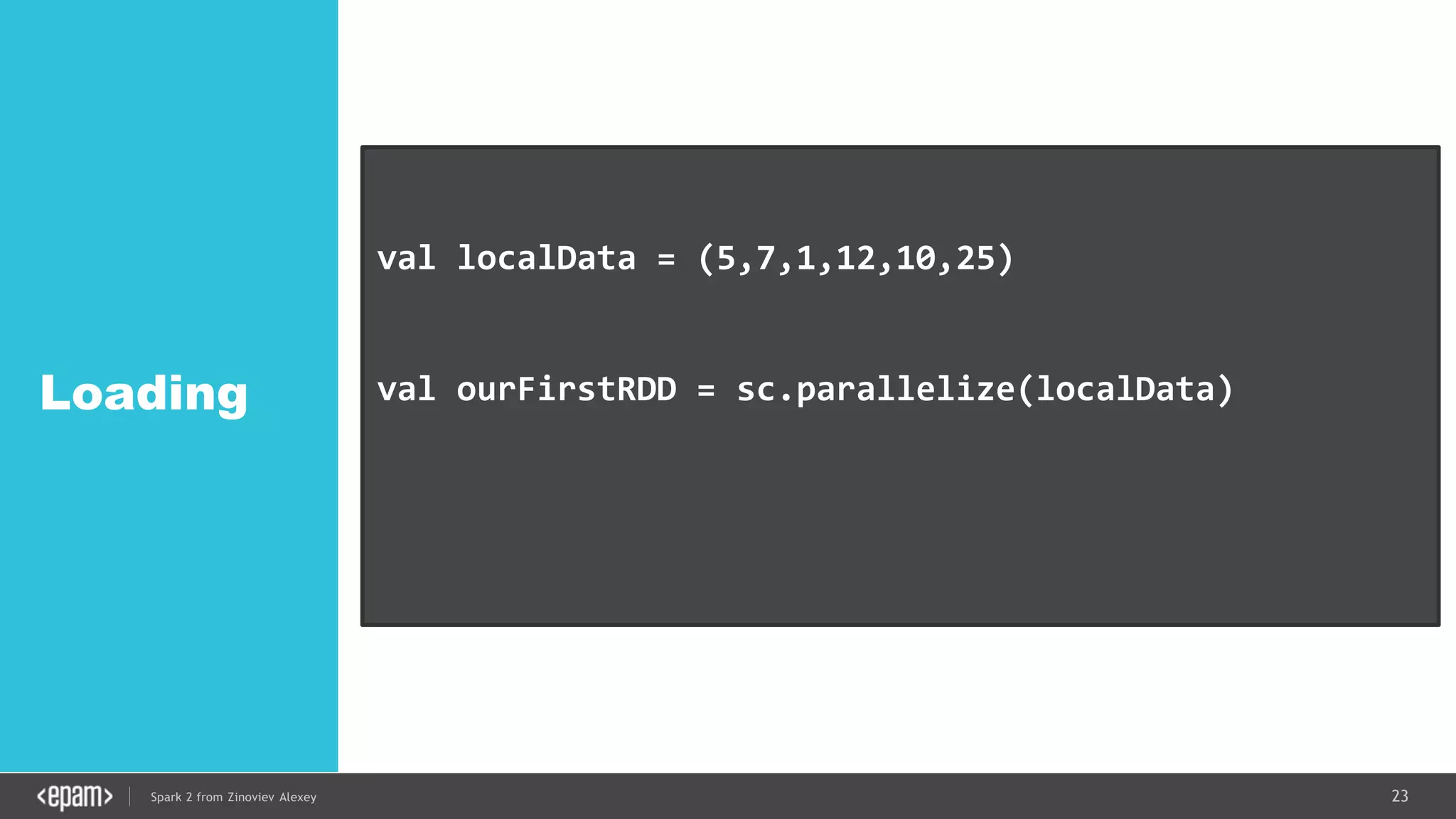
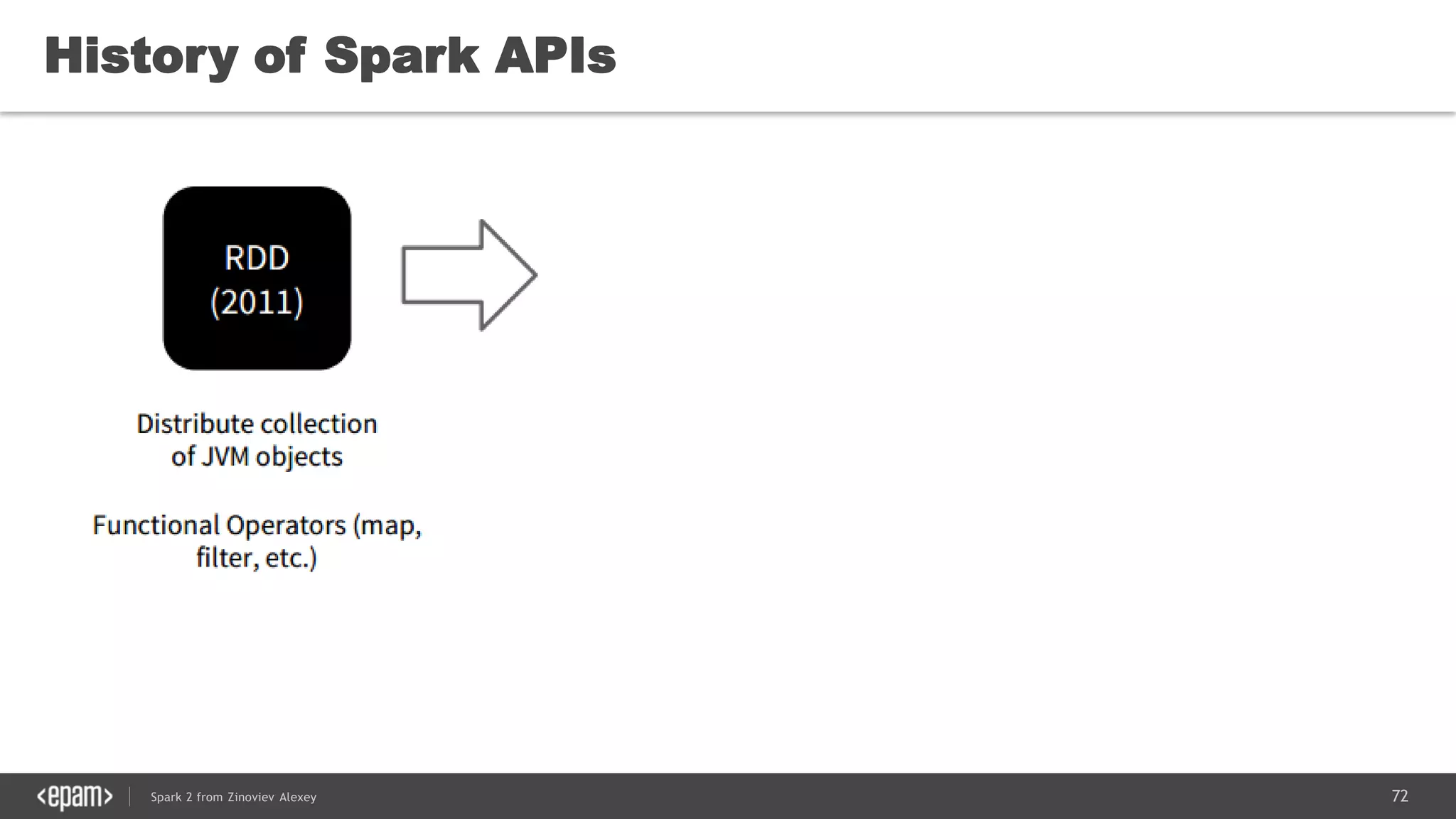
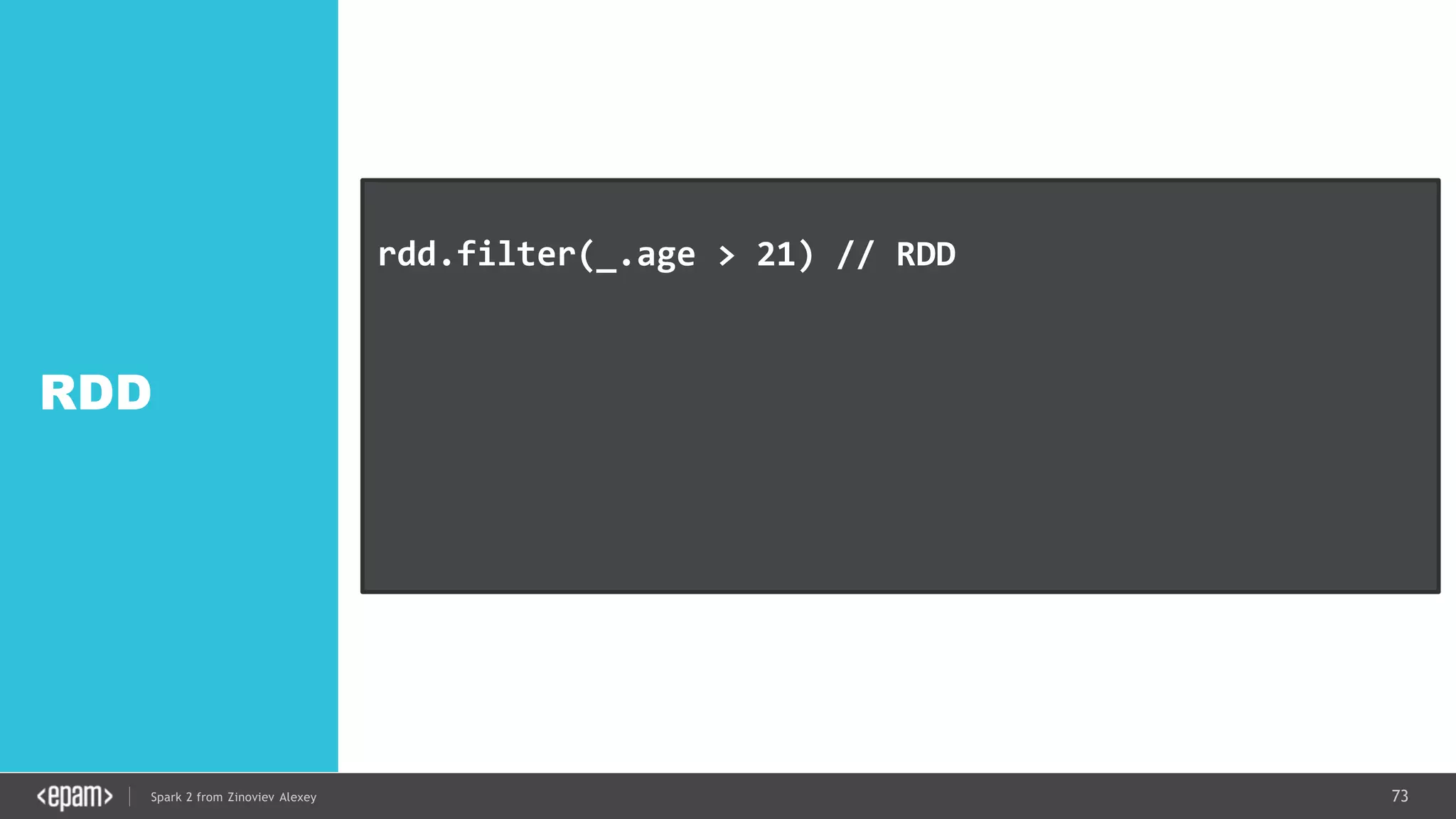
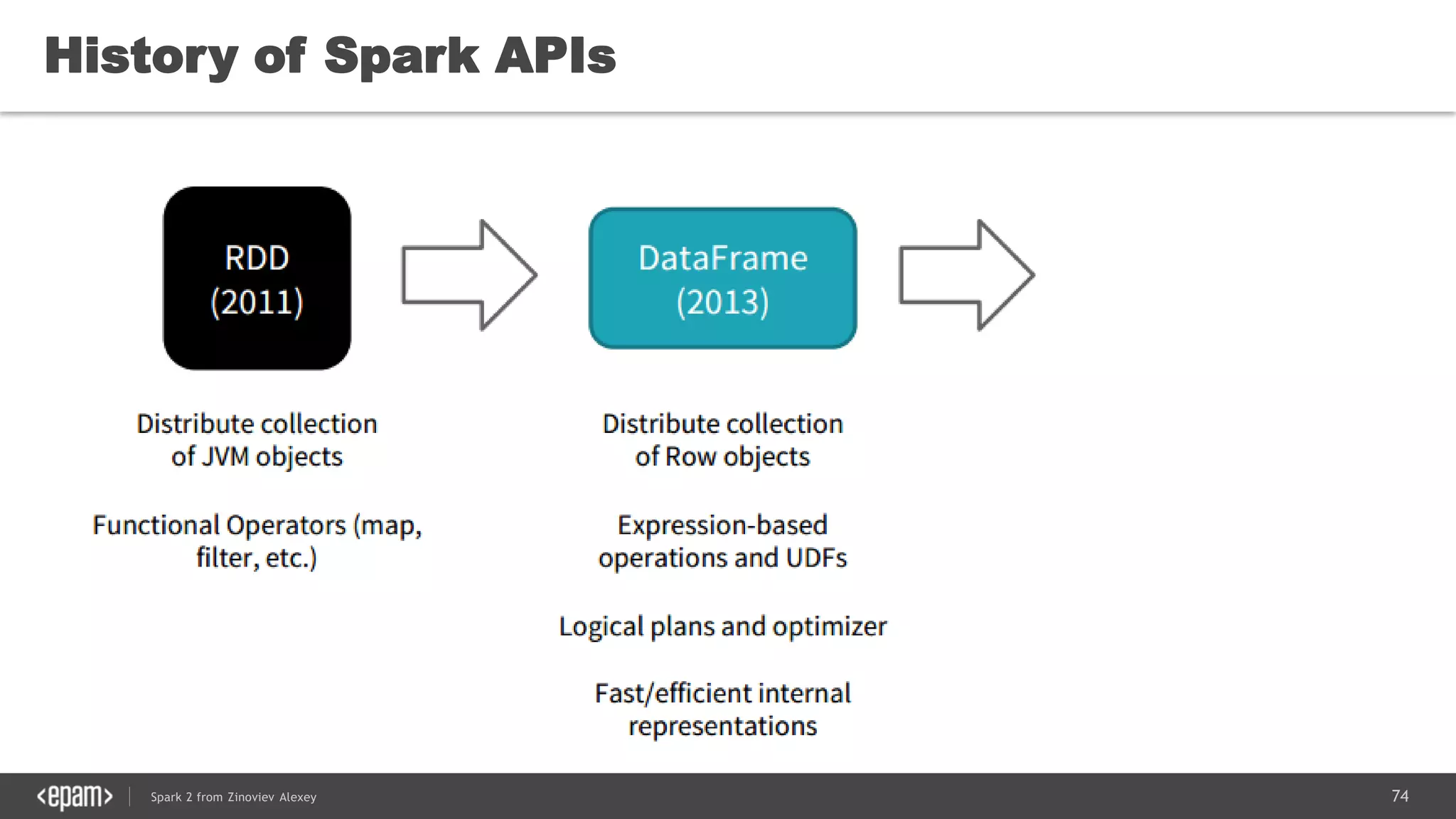
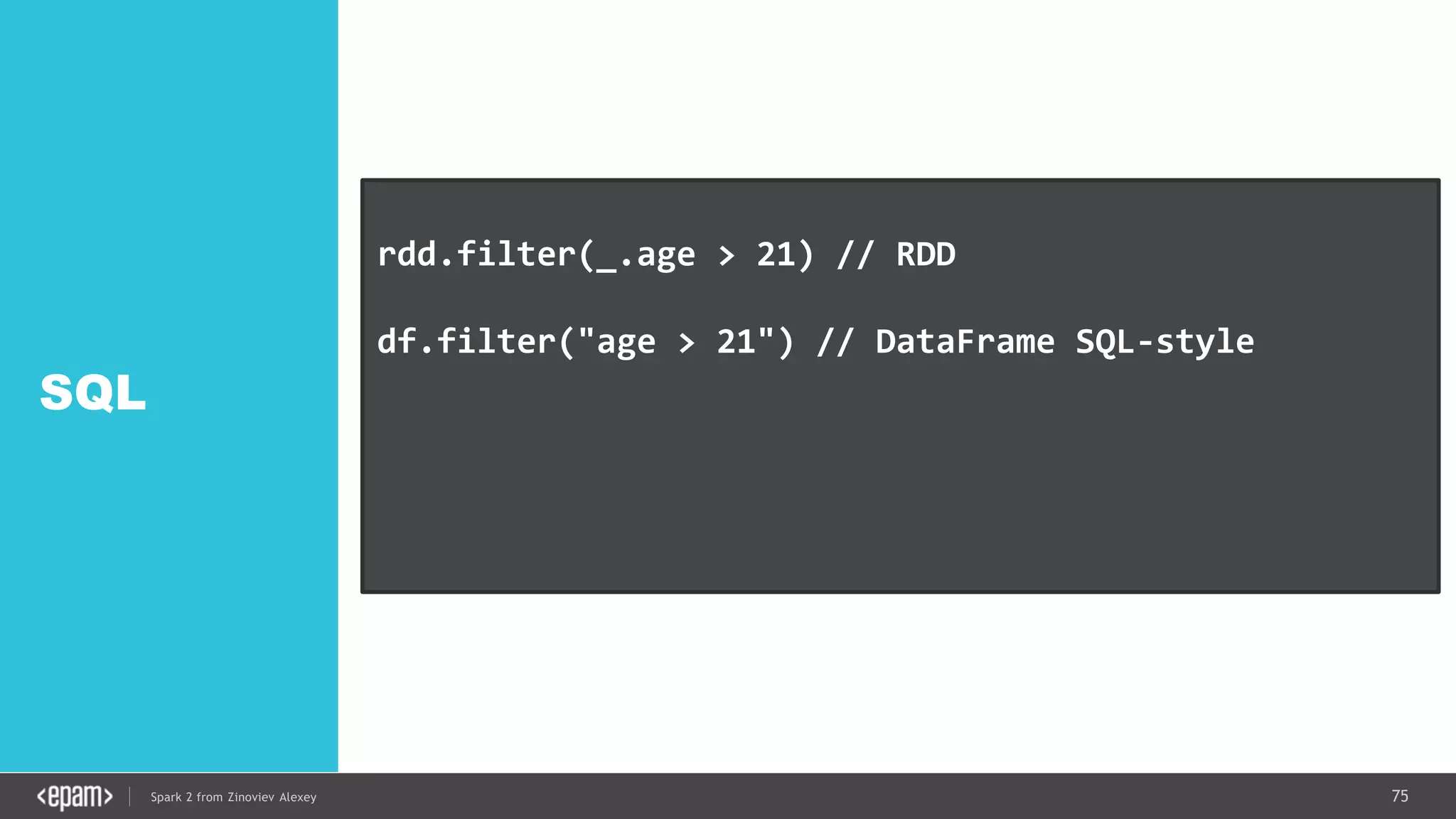
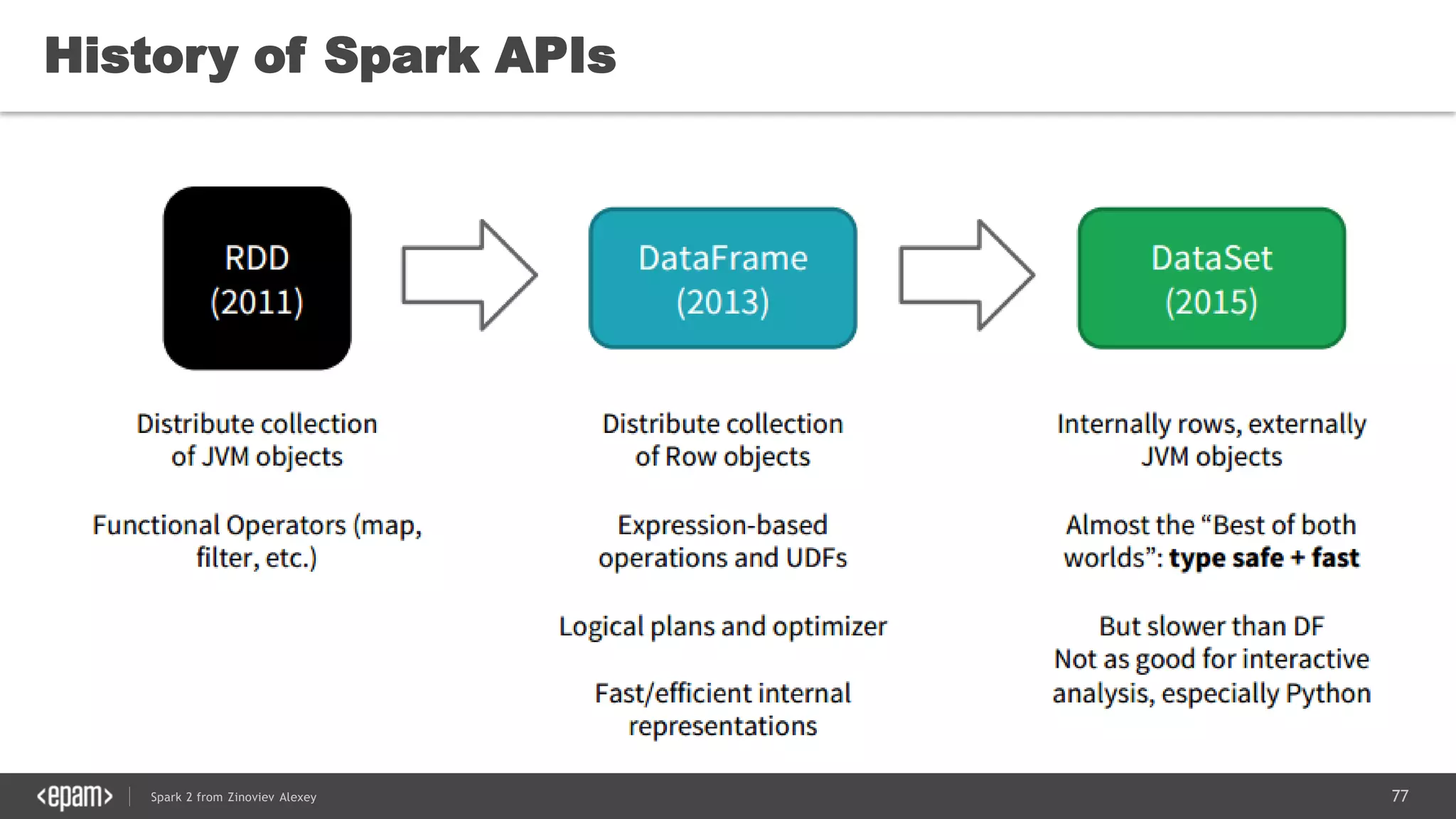
This document presents an overview of Spark 2 and its functionalities, including programmatic examples for loading data, using RDDs, and structured streaming. It discusses concepts such as map-reduce, machine learning, and differences between Spark and traditional Hadoop approaches. Additionally, it highlights the evolution of Spark APIs and the significance of Spark sessions in managing data frameworks.















![35Spark 2 from Zinoviev Alexey
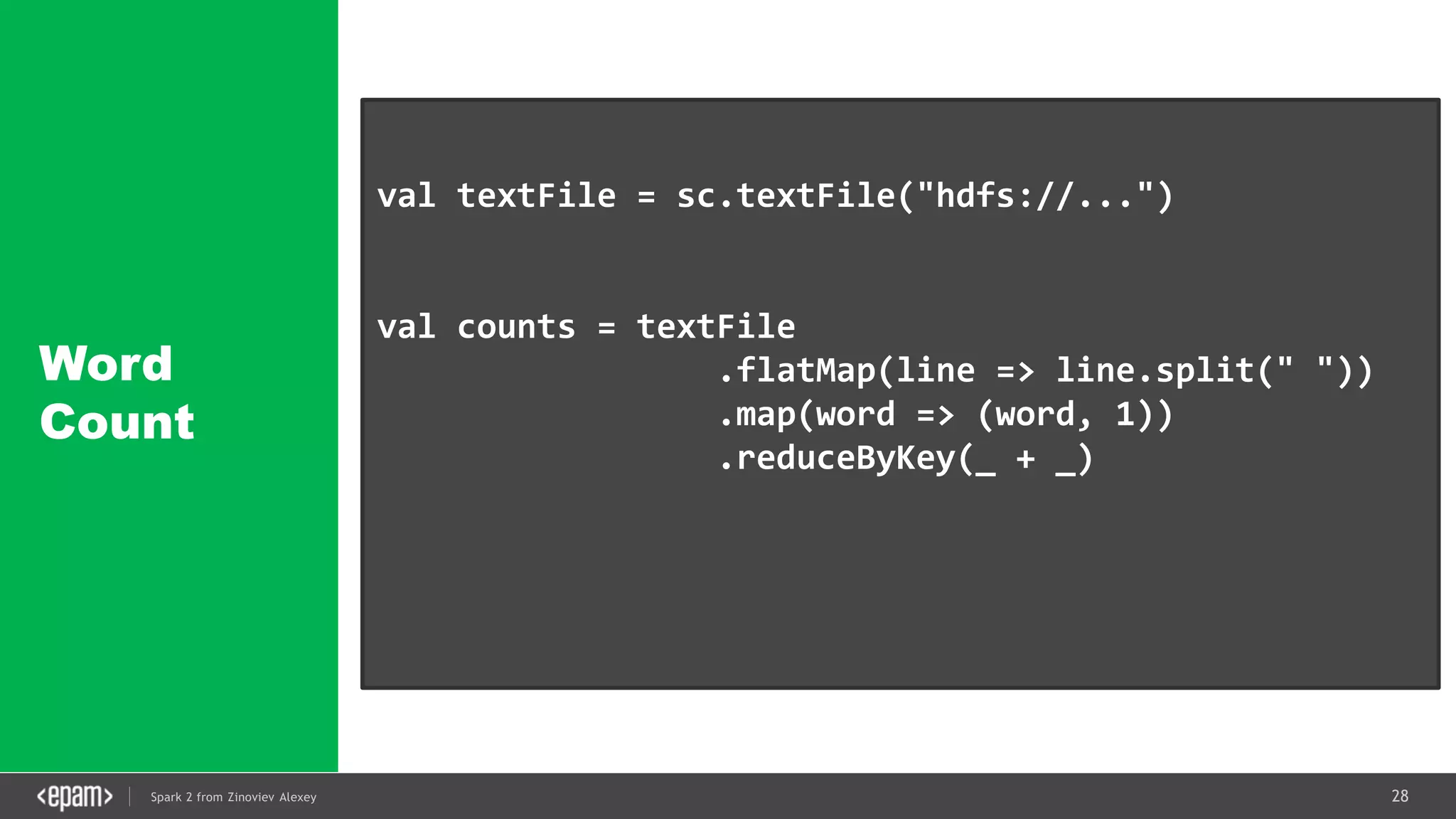
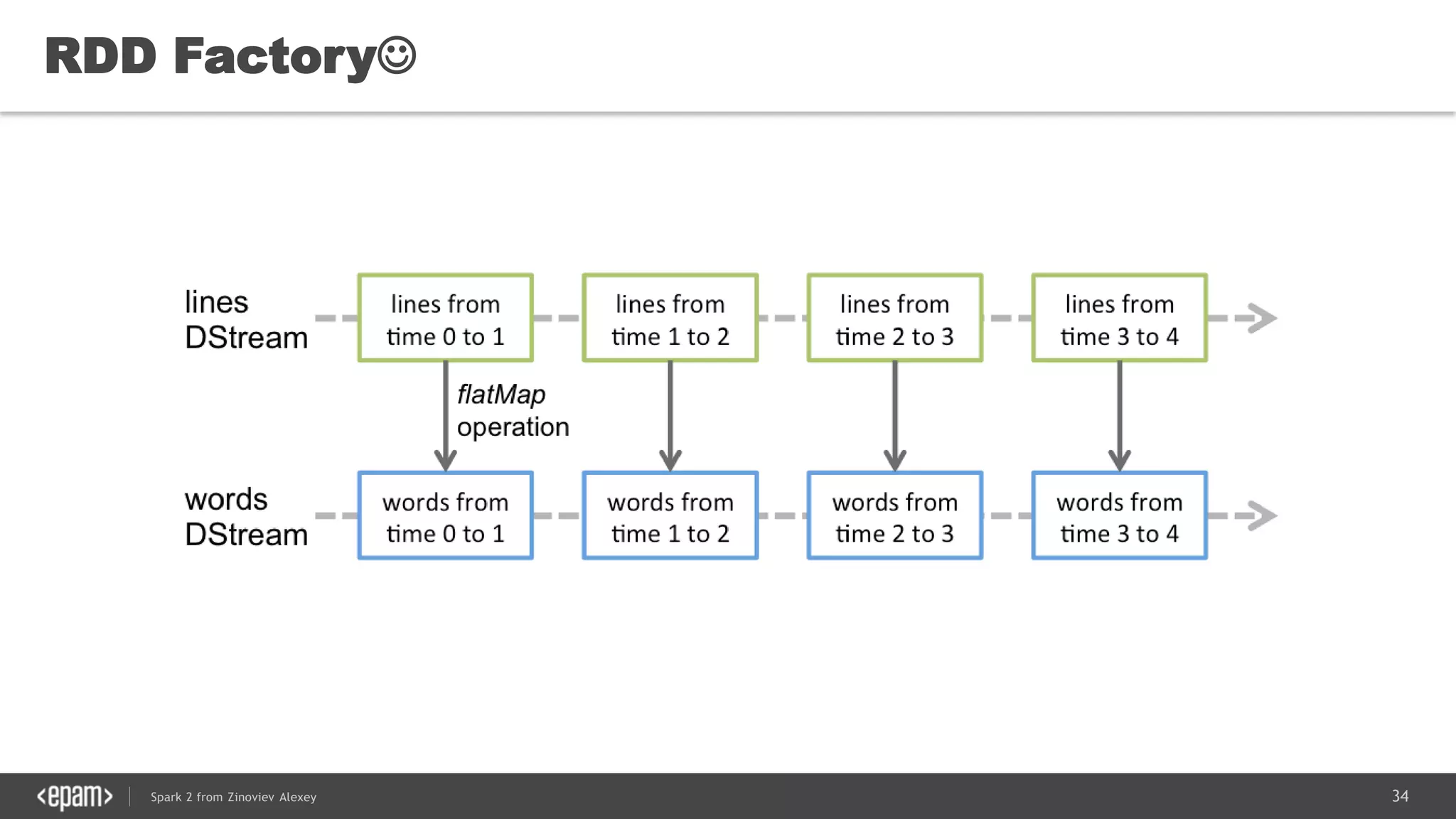
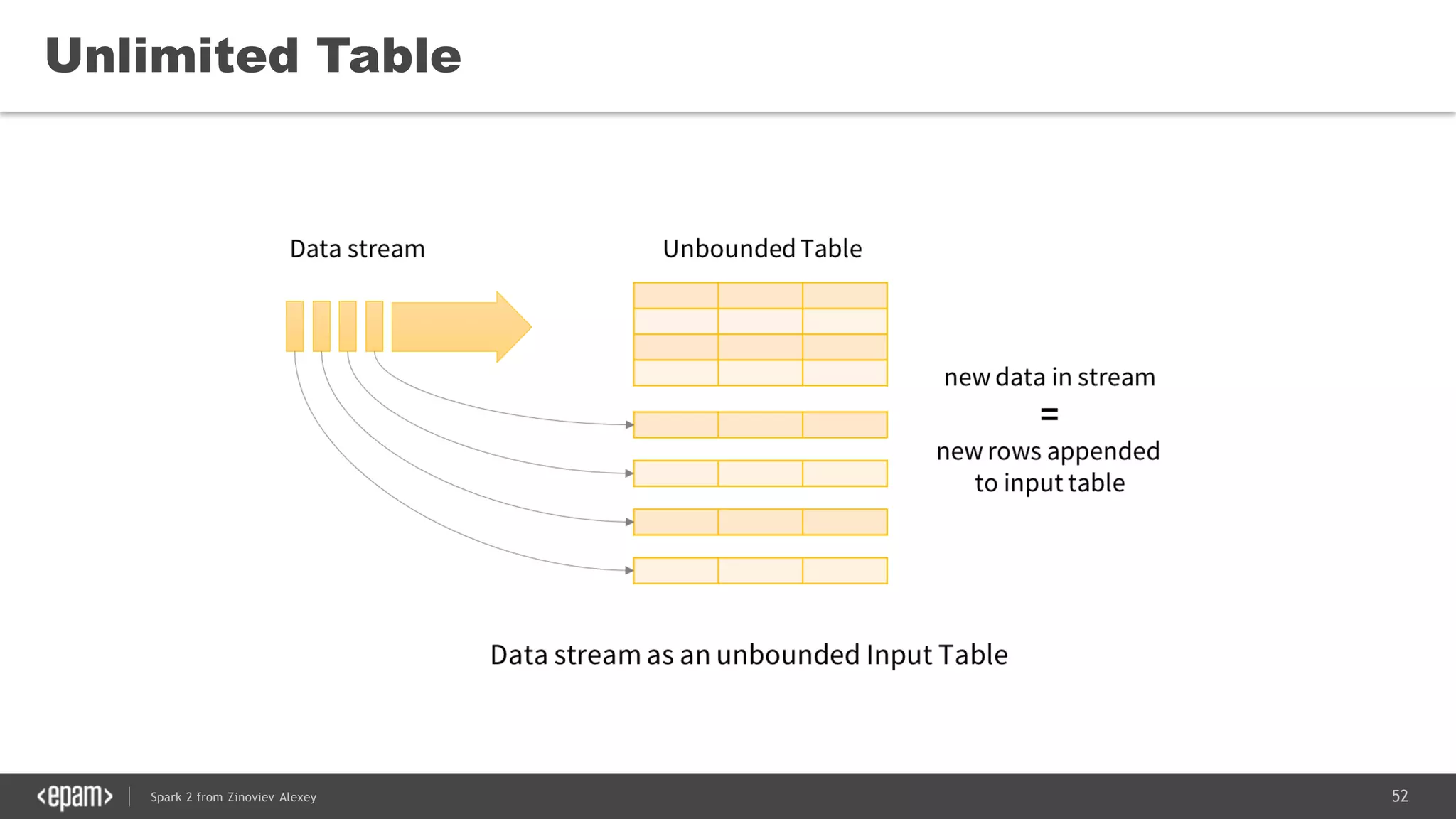
DStream
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[2]")
.setAppName("NetworkWordCount")
val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Seconds(1))
val lines = ssc.socketTextStream("localhost", 9999)
val words = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val pairs = words.map(word => (word, 1))
val wordCounts = pairs.reduceByKey(_ + _)
wordCounts.print()
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark2zinovievforit-subbotnik-161028213227/75/Joker-16-Spark-2-API-changes-Structured-Streaming-Encoders-35-2048.jpg)
![36Spark 2 from Zinoviev Alexey
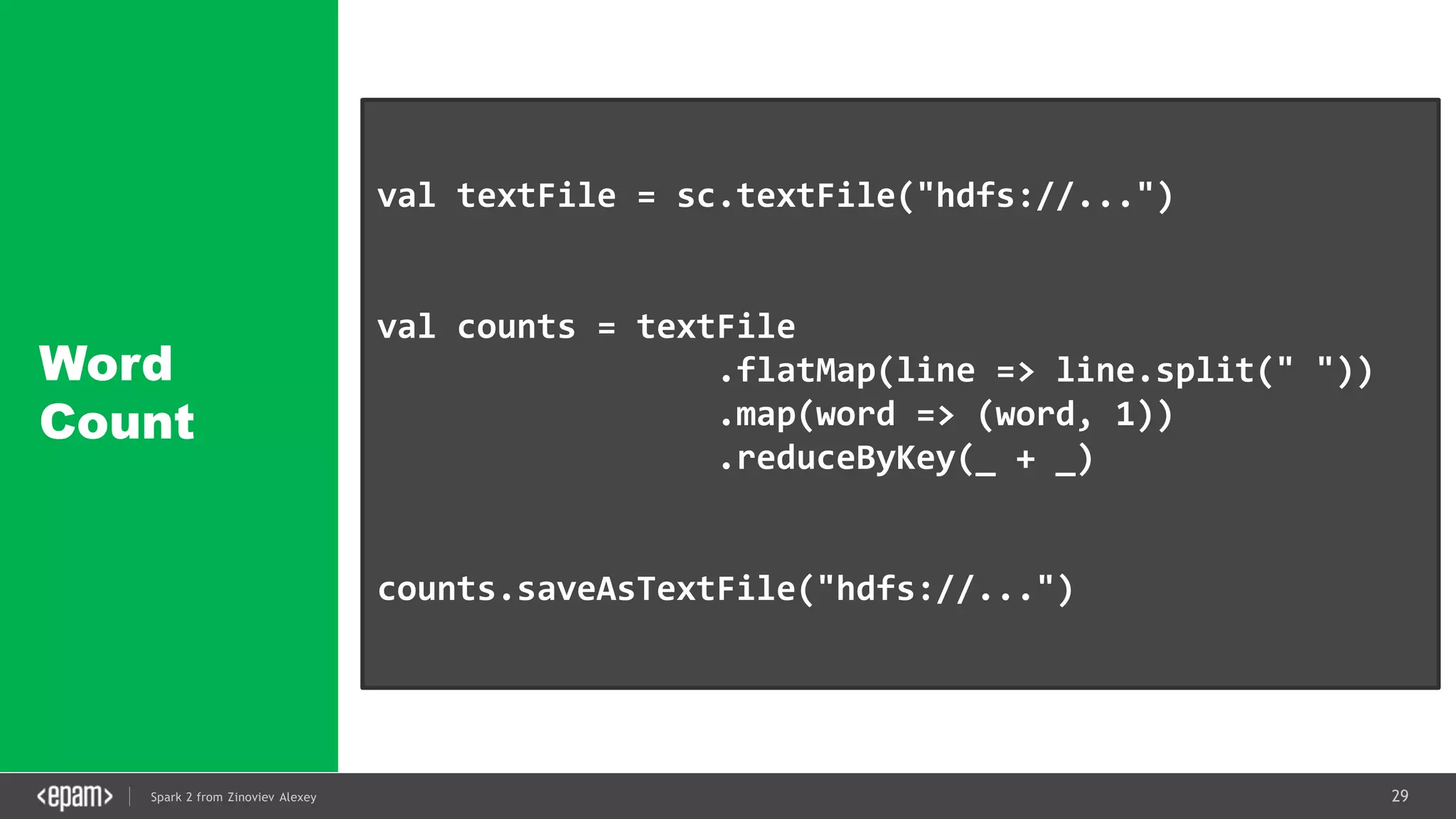
DStream
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[2]")
.setAppName("NetworkWordCount")
val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Seconds(1))
val lines = ssc.socketTextStream("localhost", 9999)
val words = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val pairs = words.map(word => (word, 1))
val wordCounts = pairs.reduceByKey(_ + _)
wordCounts.print()
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark2zinovievforit-subbotnik-161028213227/75/Joker-16-Spark-2-API-changes-Structured-Streaming-Encoders-36-2048.jpg)
![37Spark 2 from Zinoviev Alexey
DStream
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[2]")
.setAppName("NetworkWordCount")
val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Seconds(1))
val lines = ssc.socketTextStream("localhost", 9999)
val words = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val pairs = words.map(word => (word, 1))
val wordCounts = pairs.reduceByKey(_ + _)
wordCounts.print()
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark2zinovievforit-subbotnik-161028213227/75/Joker-16-Spark-2-API-changes-Structured-Streaming-Encoders-37-2048.jpg)
![38Spark 2 from Zinoviev Alexey
DStream
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[2]")
.setAppName("NetworkWordCount")
val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Seconds(1))
val lines = ssc.socketTextStream("localhost", 9999)
val words = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val pairs = words.map(word => (word, 1))
val wordCounts = pairs.reduceByKey(_ + _)
wordCounts.print()
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark2zinovievforit-subbotnik-161028213227/75/Joker-16-Spark-2-API-changes-Structured-Streaming-Encoders-38-2048.jpg)
![39Spark 2 from Zinoviev Alexey
DStream
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[2]")
.setAppName("NetworkWordCount")
val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Seconds(1))
val lines = ssc.socketTextStream("localhost", 9999)
val words = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
val pairs = words.map(word => (word, 1))
val wordCounts = pairs.reduceByKey(_ + _)
wordCounts.print()
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark2zinovievforit-subbotnik-161028213227/75/Joker-16-Spark-2-API-changes-Structured-Streaming-Encoders-39-2048.jpg)
(
vprog: (VertexID, VD, A) => VD,
sendMsg: EdgeTriplet[VD, ED] => Iterator[(VertexID,A)],
mergeMsg: (A, A) => A)
: Graph[VD, ED] = { <Your Pregel Computations> }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark2zinovievforit-subbotnik-161028213227/75/Joker-16-Spark-2-API-changes-Structured-Streaming-Encoders-40-2048.jpg)


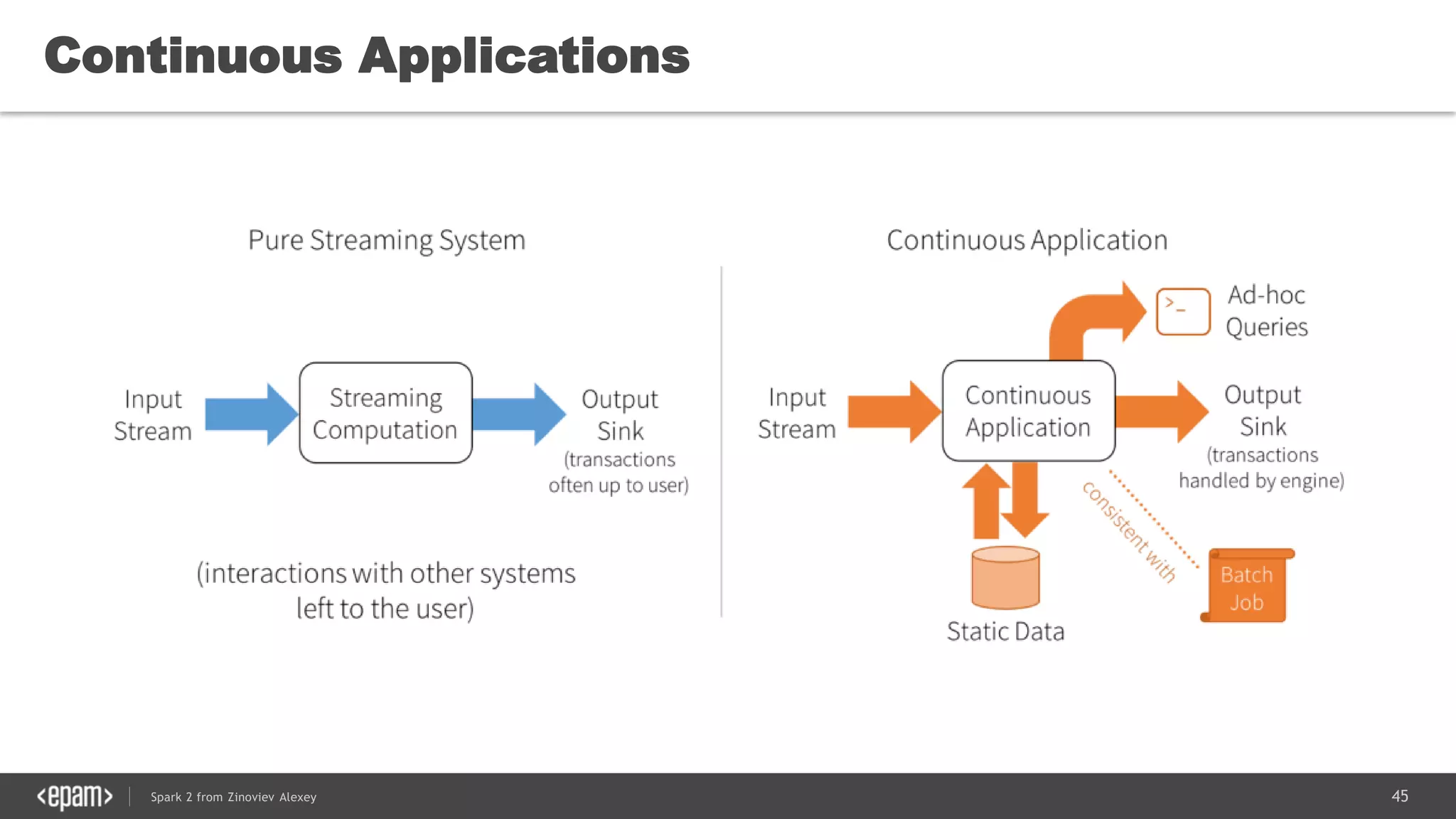
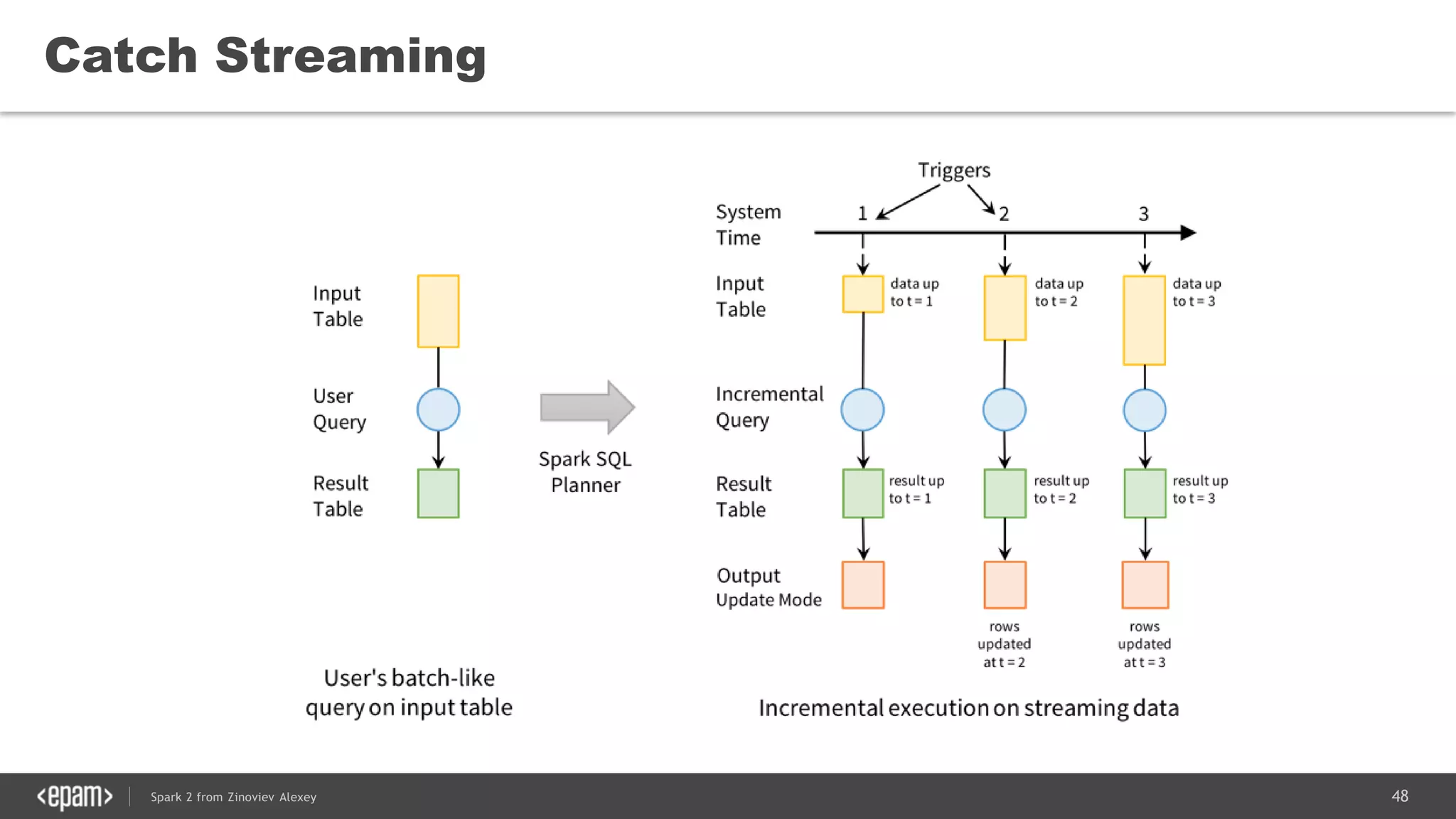


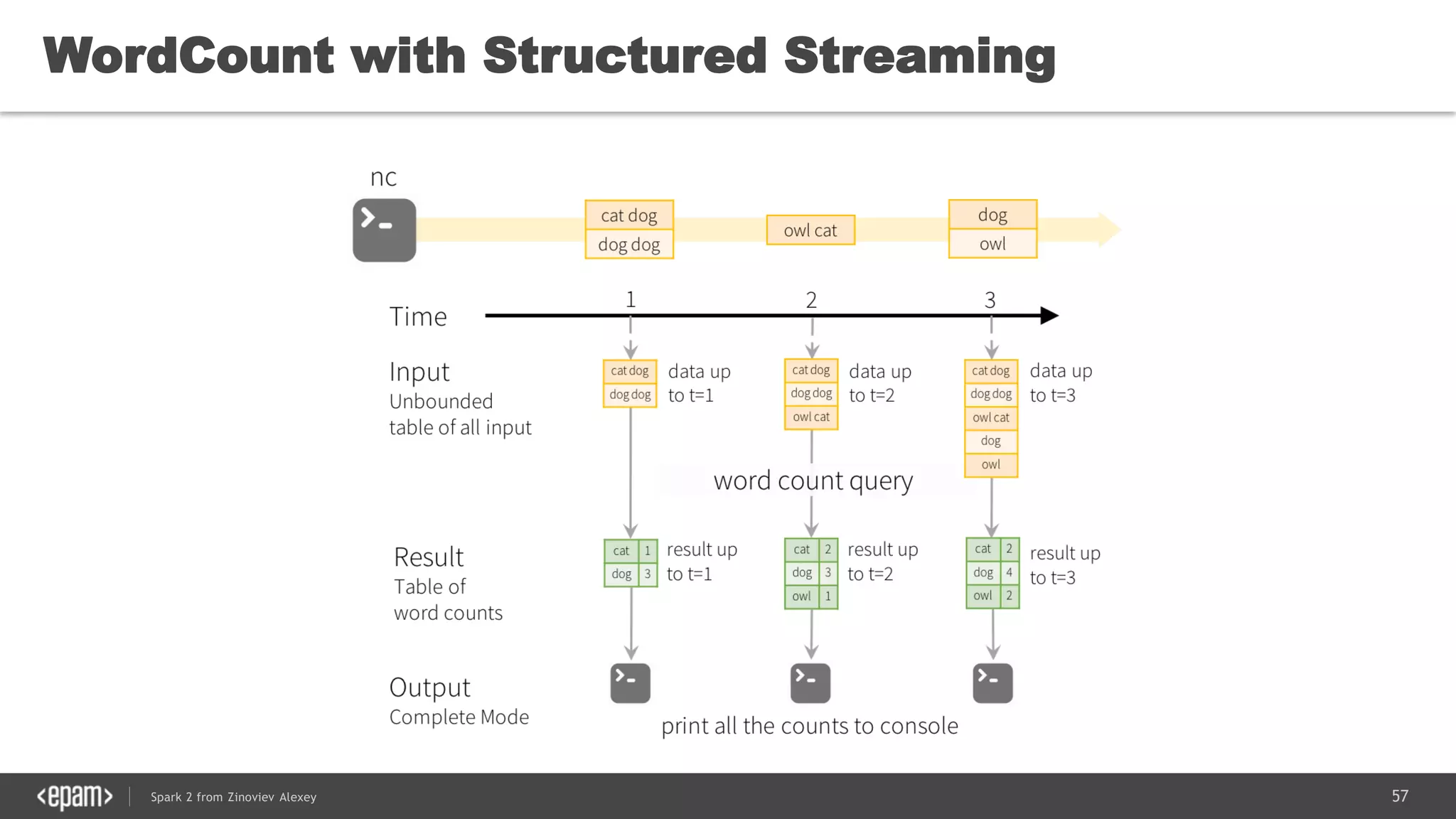
![53Spark 2 from Zinoviev Alexey
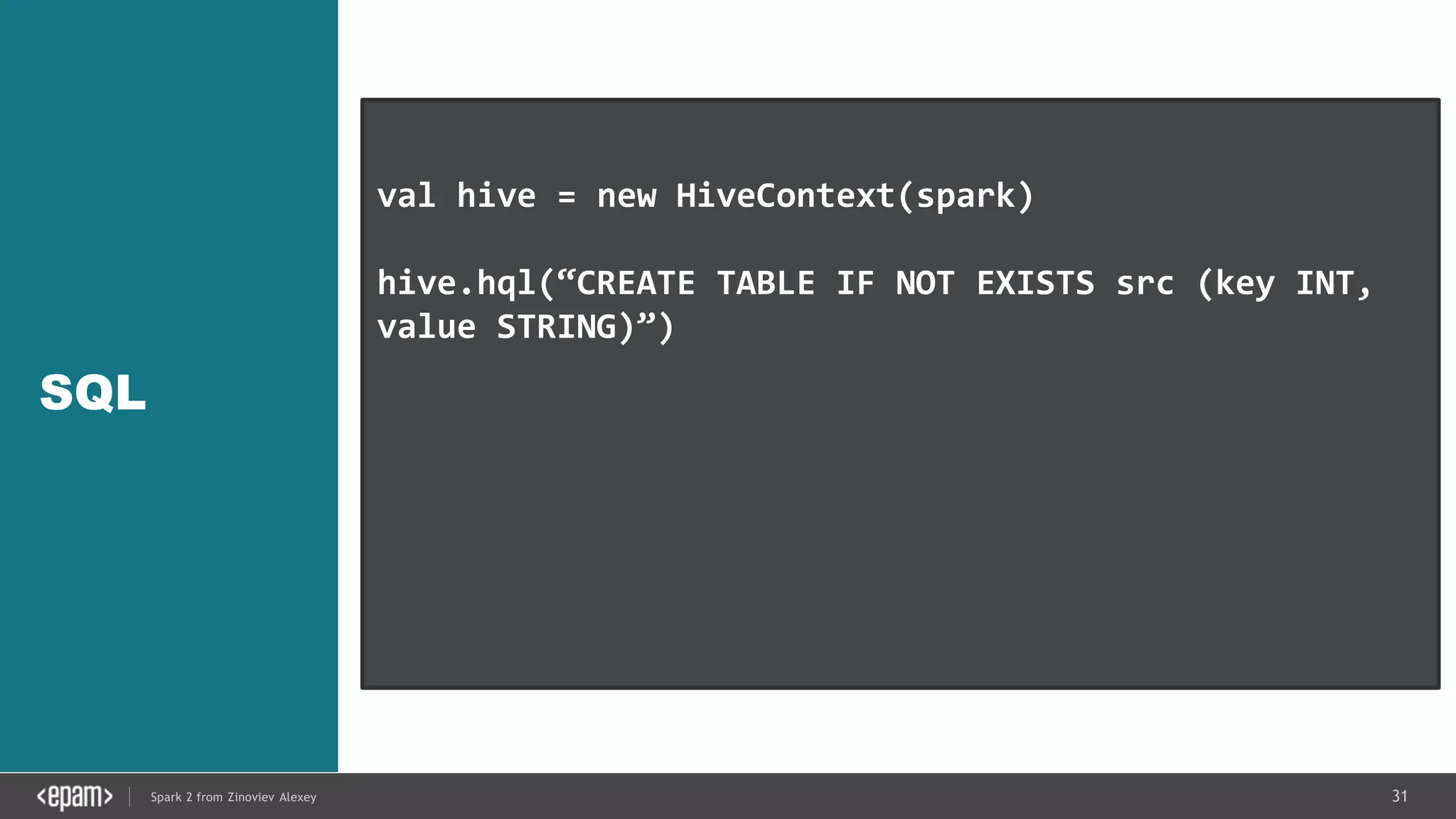
WordCount
from
Socket
val lines = spark.readStream
.format("socket")
.option("host", "localhost")
.option("port", 9999)
.load()
val words = lines.as[String].flatMap(_.split(" "))
val wordCounts = words.groupBy("value").count()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark2zinovievforit-subbotnik-161028213227/75/Joker-16-Spark-2-API-changes-Structured-Streaming-Encoders-53-2048.jpg)
![54Spark 2 from Zinoviev Alexey
WordCount
from
Socket
val lines = spark.readStream
.format("socket")
.option("host", "localhost")
.option("port", 9999)
.load()
val words = lines.as[String].flatMap(_.split(" "))
val wordCounts = words.groupBy("value").count()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark2zinovievforit-subbotnik-161028213227/75/Joker-16-Spark-2-API-changes-Structured-Streaming-Encoders-54-2048.jpg)
![55Spark 2 from Zinoviev Alexey
WordCount
from
Socket
val lines = spark.readStream
.format("socket")
.option("host", "localhost")
.option("port", 9999)
.load()
val words = lines.as[String].flatMap(_.split(" "))
val wordCounts = words.groupBy("value").count()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark2zinovievforit-subbotnik-161028213227/75/Joker-16-Spark-2-API-changes-Structured-Streaming-Encoders-55-2048.jpg)
![56Spark 2 from Zinoviev Alexey
WordCount
from
Socket
val lines = spark.readStream
.format("socket")
.option("host", "localhost")
.option("port", 9999)
.load()
val words = lines.as[String].flatMap(_.split(" "))
val wordCounts = words.groupBy("value").count()
Don’t forget
to start
Streaming](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark2zinovievforit-subbotnik-161028213227/75/Joker-16-Spark-2-API-changes-Structured-Streaming-Encoders-56-2048.jpg)




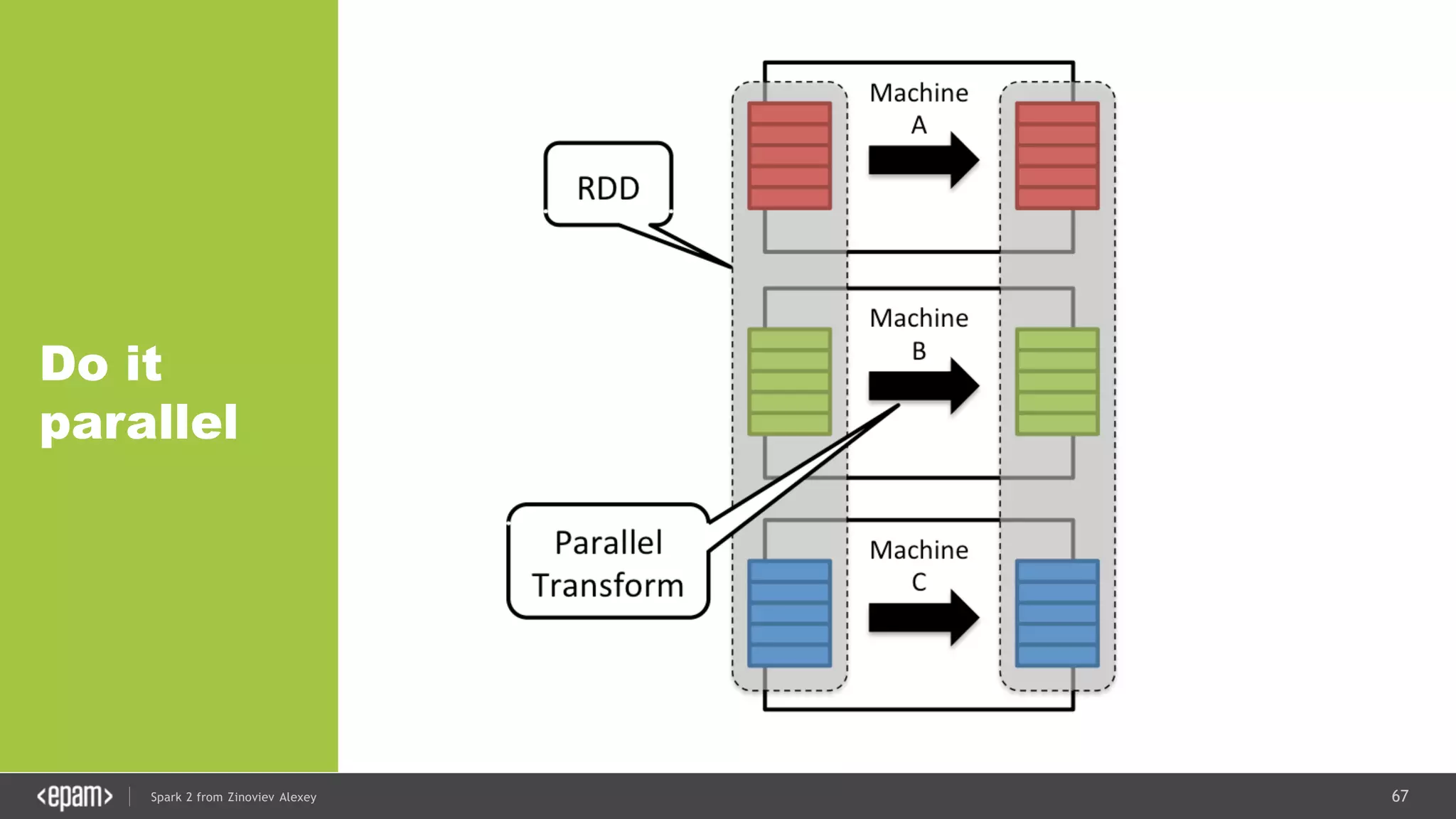
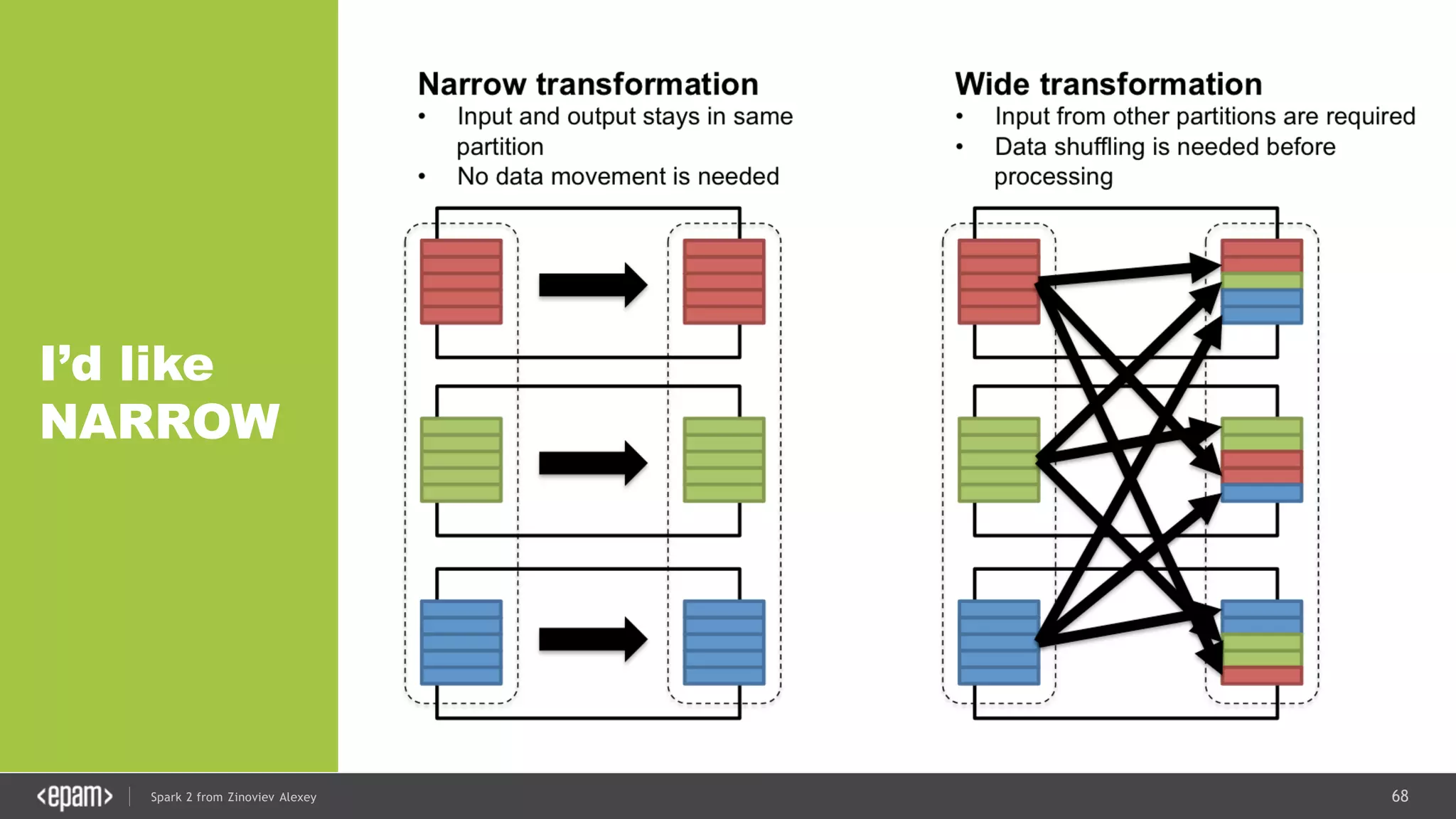
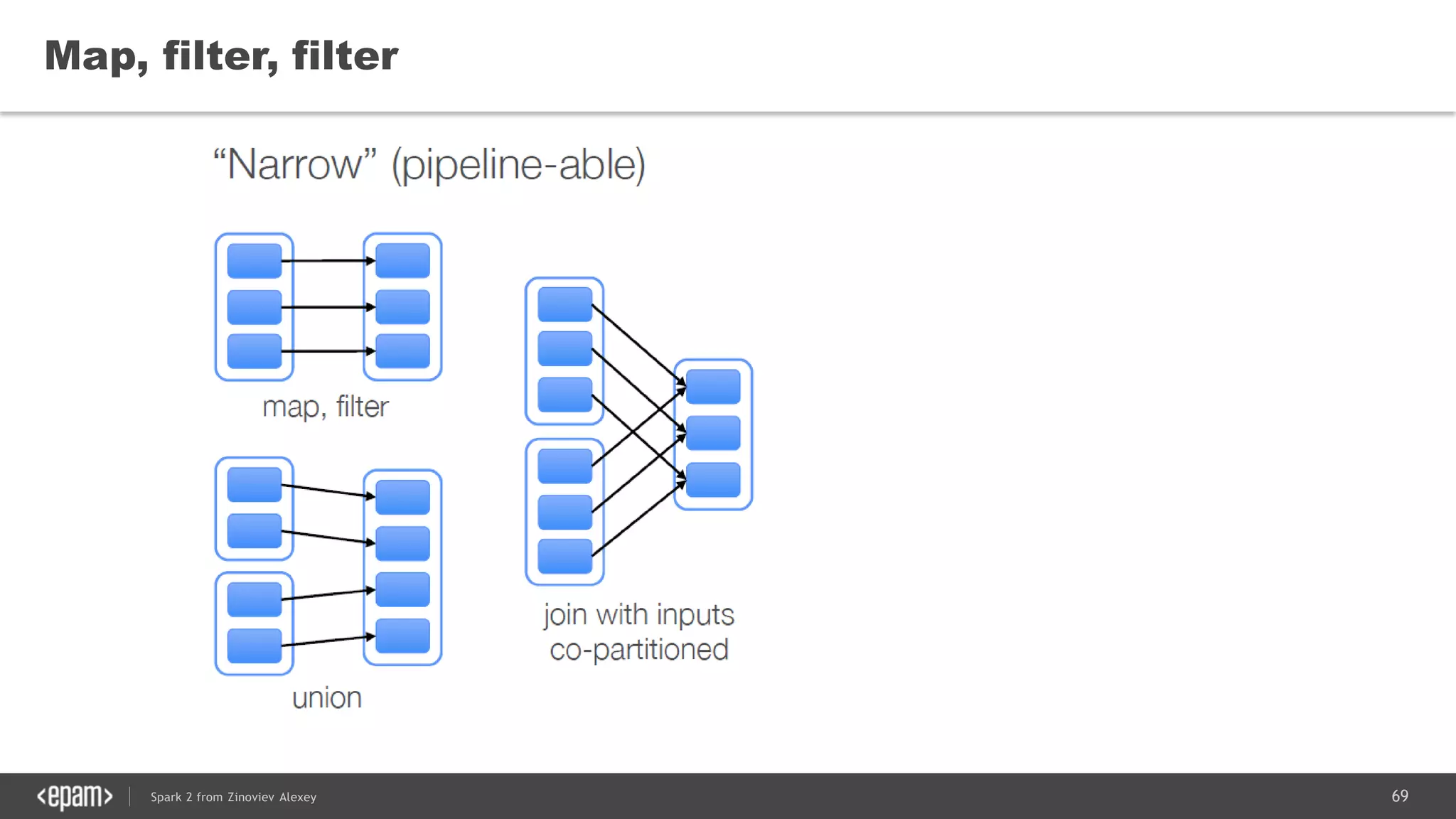
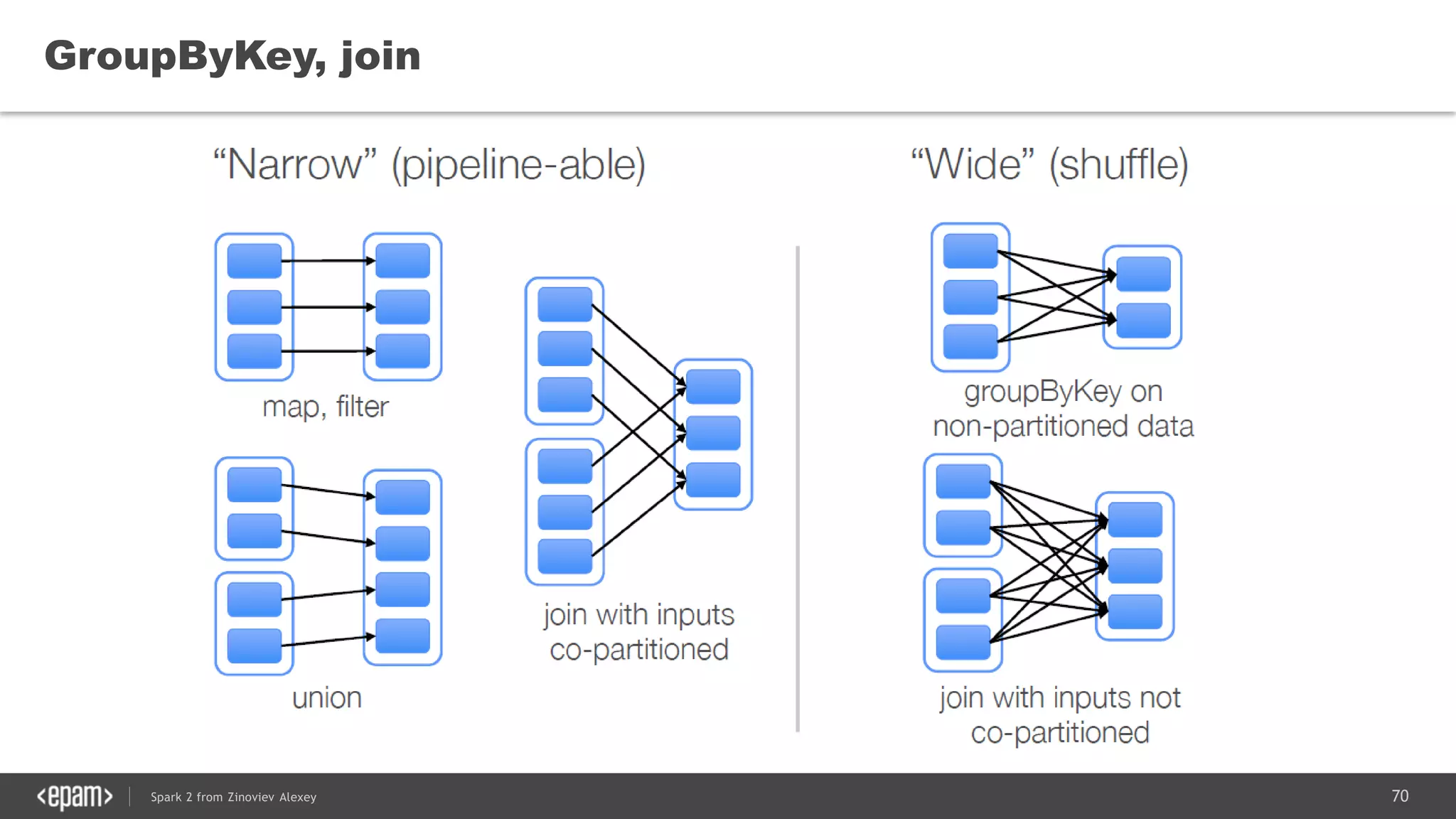

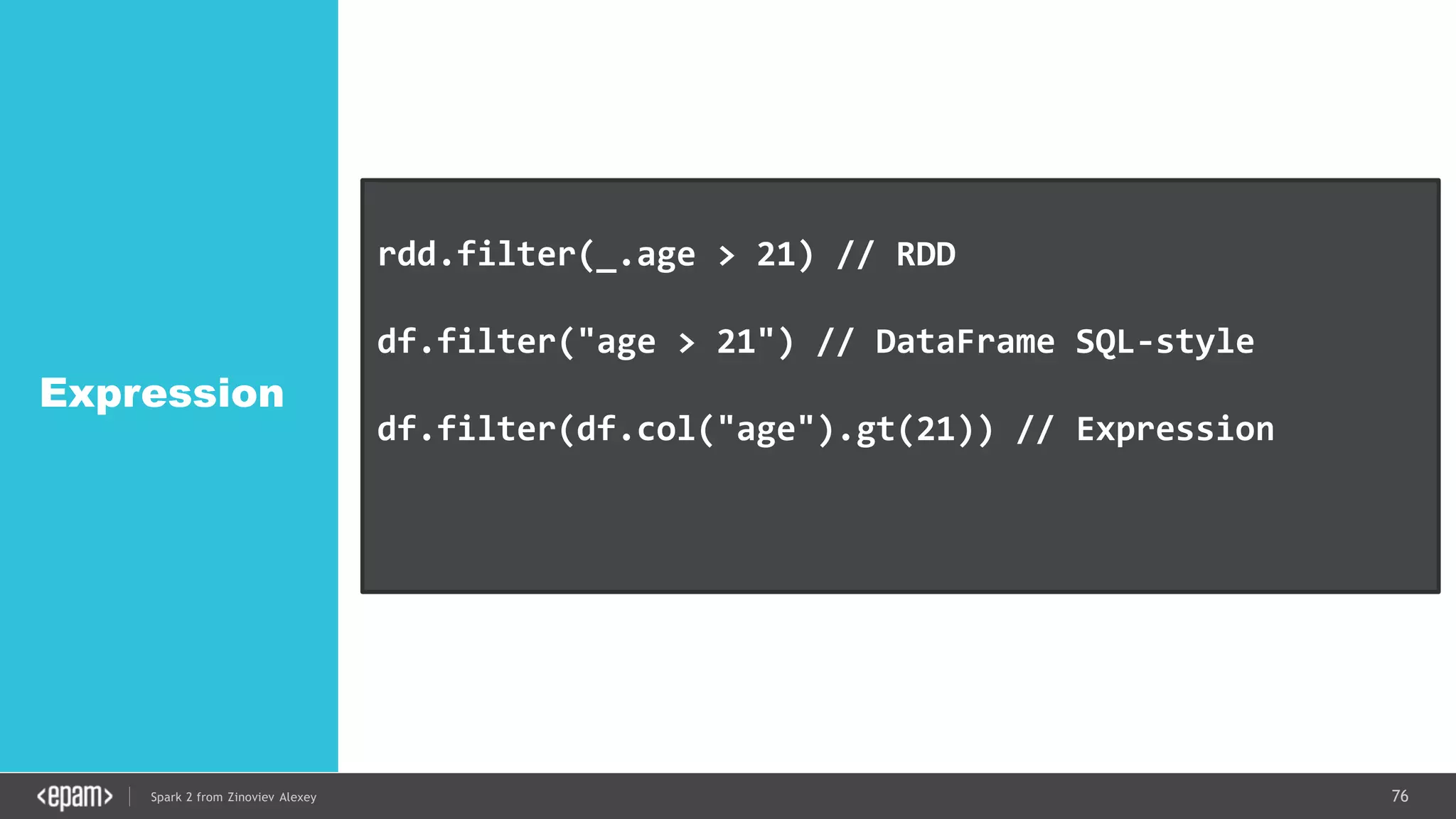

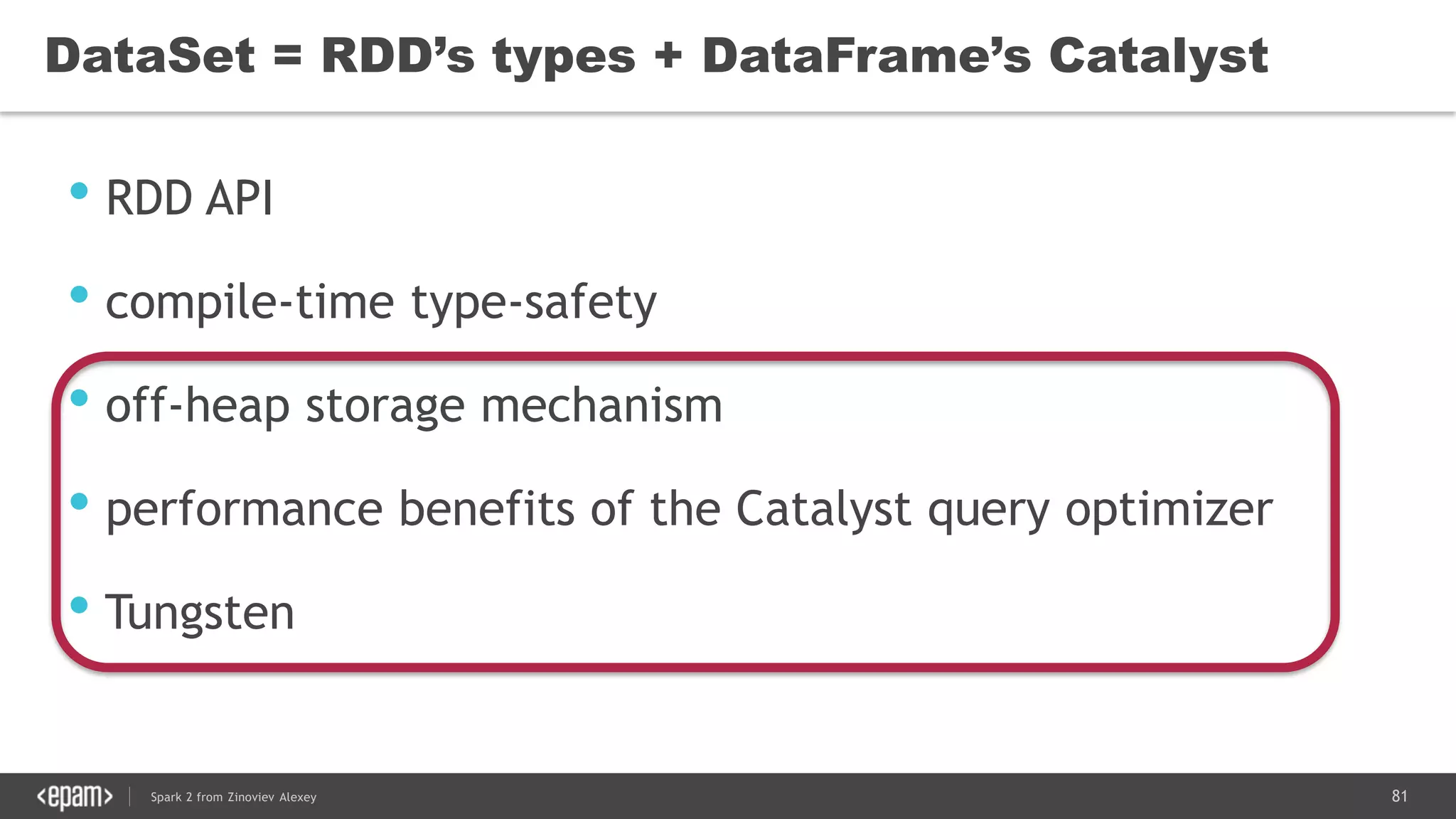
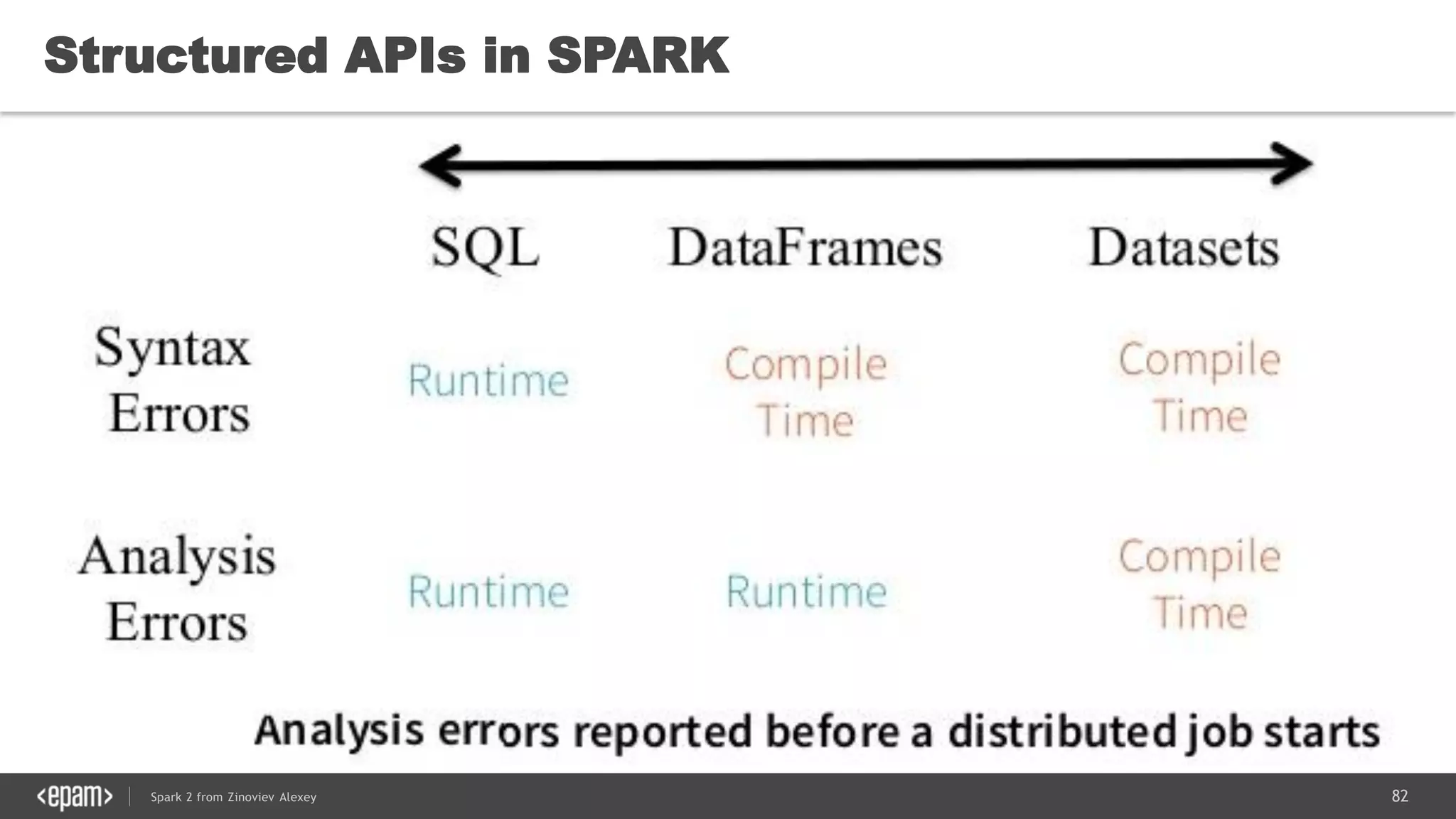
![83Spark 2 from Zinoviev Alexey
Unified API in Spark 2.0
DataFrame = Dataset[Row]
Dataframe is a schemaless (untyped) Dataset now](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark2zinovievforit-subbotnik-161028213227/75/Joker-16-Spark-2-API-changes-Structured-Streaming-Encoders-83-2048.jpg)
![84Spark 2 from Zinoviev Alexey
Define
case class
case class User(email: String, footSize: Long, name: String)
// DataFrame -> DataSet with Users
val userDS =
spark.read.json("/home/tmp/datasets/users.json").as[User]
userDS.map(_.name).collect()
userDS.filter(_.footSize > 38).collect()
ds.rdd // IF YOU REALLY WANT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark2zinovievforit-subbotnik-161028213227/75/Joker-16-Spark-2-API-changes-Structured-Streaming-Encoders-84-2048.jpg)
![85Spark 2 from Zinoviev Alexey
Read JSON
case class User(email: String, footSize: Long, name: String)
// DataFrame -> DataSet with Users
val userDS =
spark.read.json("/home/tmp/datasets/users.json").as[User]
userDS.map(_.name).collect()
userDS.filter(_.footSize > 38).collect()
ds.rdd // IF YOU REALLY WANT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark2zinovievforit-subbotnik-161028213227/75/Joker-16-Spark-2-API-changes-Structured-Streaming-Encoders-85-2048.jpg)
![86Spark 2 from Zinoviev Alexey
Filter by
Field
case class User(email: String, footSize: Long, name: String)
// DataFrame -> DataSet with Users
val userDS =
spark.read.json("/home/tmp/datasets/users.json").as[User]
userDS.map(_.name).collect()
userDS.filter(_.footSize > 38).collect()
ds.rdd // IF YOU REALLY WANT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark2zinovievforit-subbotnik-161028213227/75/Joker-16-Spark-2-API-changes-Structured-Streaming-Encoders-86-2048.jpg)




![92Spark 2 from Zinoviev Alexey
RDD?
case class User(email: String, footSize: Long, name: String)
// DataFrame -> DataSet with Users
val userDS =
spark.read.json("/home/tmp/datasets/users.json").as[User]
userDS.map(_.name).collect()
userDS.filter(_.footSize > 38).collect()
ds.rdd // IF YOU REALLY WANT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark2zinovievforit-subbotnik-161028213227/75/Joker-16-Spark-2-API-changes-Structured-Streaming-Encoders-92-2048.jpg)




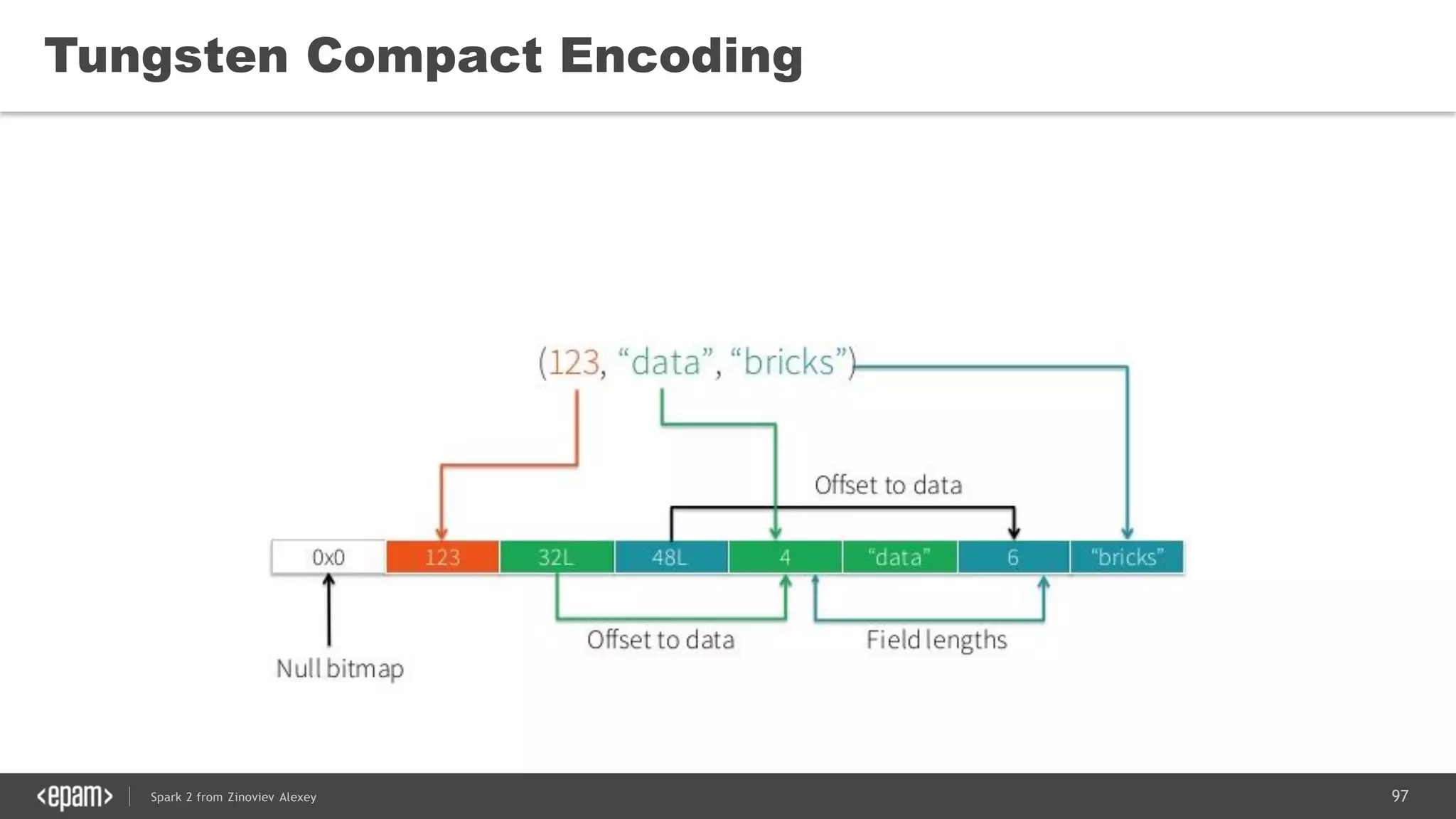










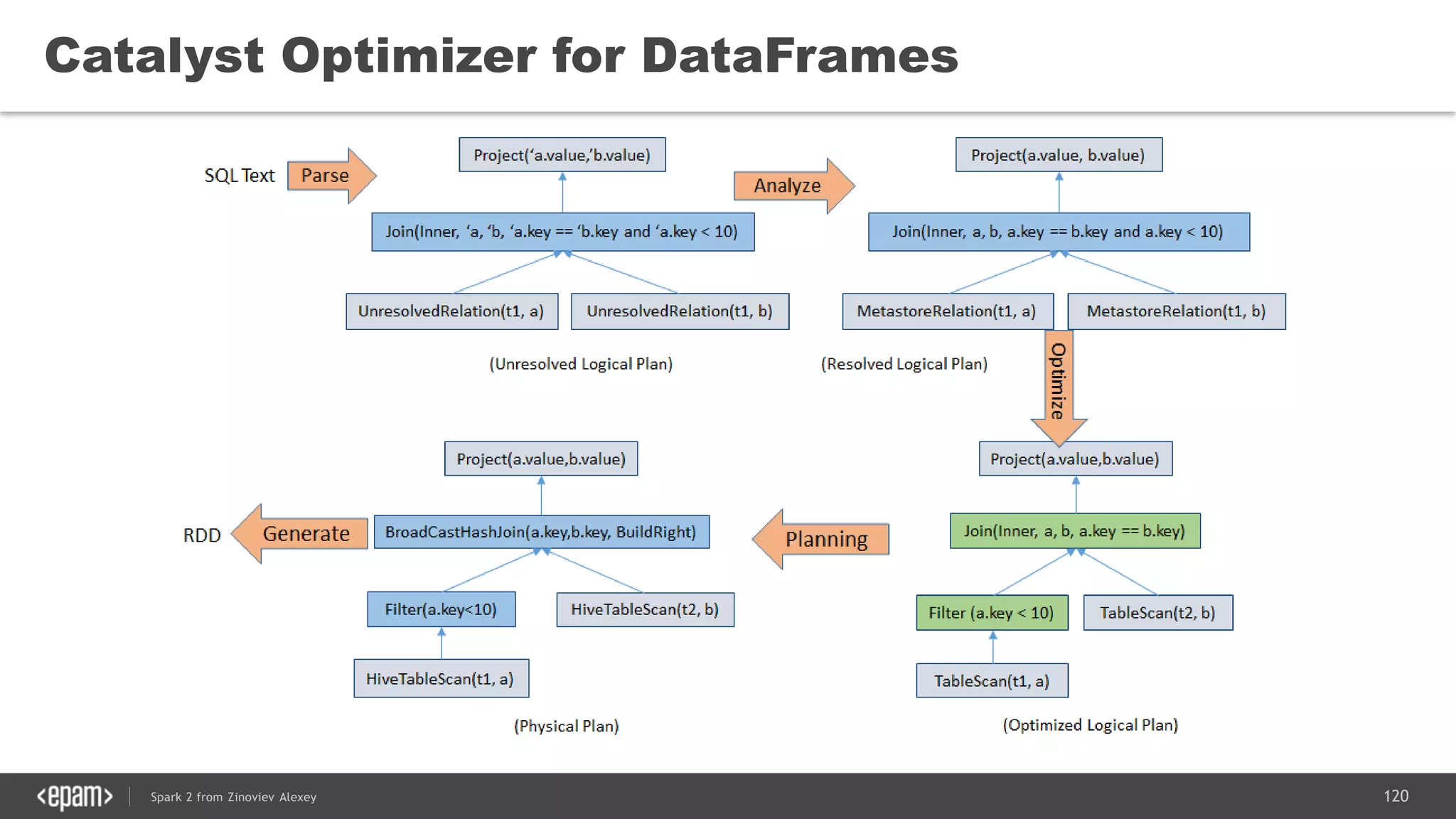
![121Spark 2 from Zinoviev Alexey
Unified Logical Plan
DataFrame = Dataset[Row]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark2zinovievforit-subbotnik-161028213227/75/Joker-16-Spark-2-API-changes-Structured-Streaming-Encoders-121-2048.jpg)

![123Spark 2 from Zinoviev Alexey
DataSet.explain()
== Physical Plan ==
Project [avg(price)#43,carat#45]
+- SortMergeJoin [color#21], [color#47]
:- Sort [color#21 ASC], false, 0
: +- TungstenExchange hashpartitioning(color#21,200), None
: +- Project [avg(price)#43,color#21]
: +- TungstenAggregate(key=[cut#20,color#21], functions=[(avg(cast(price#25 as
bigint)),mode=Final,isDistinct=false)], output=[color#21,avg(price)#43])
: +- TungstenExchange hashpartitioning(cut#20,color#21,200), None
: +- TungstenAggregate(key=[cut#20,color#21],
functions=[(avg(cast(price#25 as bigint)),mode=Partial,isDistinct=false)],
output=[cut#20,color#21,sum#58,count#59L])
: +- Scan CsvRelation(-----)
+- Sort [color#47 ASC], false, 0
+- TungstenExchange hashpartitioning(color#47,200), None
+- ConvertToUnsafe
+- Scan CsvRelation(----)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spark2zinovievforit-subbotnik-161028213227/75/Joker-16-Spark-2-API-changes-Structured-Streaming-Encoders-123-2048.jpg)