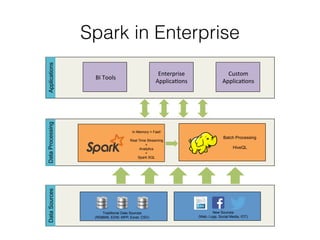
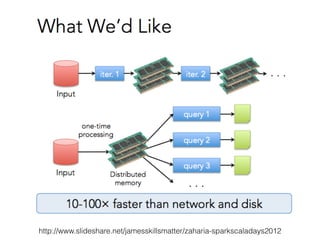
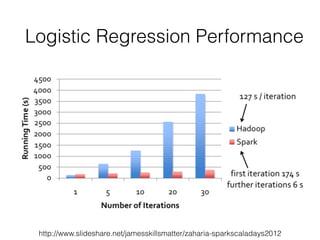
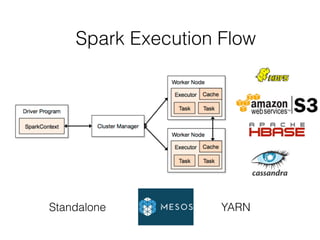
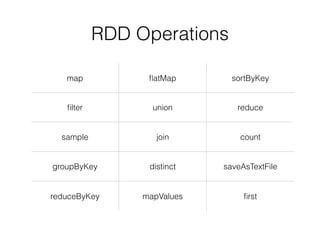
This document provides an introduction and overview of Apache Spark. It discusses why in-memory computing is important for speed, compares Spark and Ignite, describes what Spark is and how it works using Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDDs) and a directed acyclic graph (DAG) model. It also provides examples of Spark operations on RDDs and shows a word count example in Java, Scala and Python.








![RDDs Transformations Examples (1)
map(func)
! >>> myList = [1,2,3,4,5]!
! >>> myRDD = sc.parallelize(myList)!
! >>> myRDD.map(lambda x: x+1).collect()!
! [2, 3, 4, 5, 6]!
!
filter(func)
! >>> myRDD.filter(lambda x: x > 3).collect()!
! [4, 5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparkmeetup1introtospark-141126210613-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-Spark-20-320.jpg)
![RDDs Transformations Examples (2)
reduceByKey(func, [numTasks])
! >>> myList = [1,2,2,3,3,3,4,4,4,4,5,5,5,5,5]!
! >>> myRDD = sc.parallelize(myList)!
! >>> pairs = myRDD.map(lambda x: (x,1))!
! >>> pairs.collect()[:3]!
! [(1, 1), (2, 1), (2, 1)]!
! >>> counts = pairs.reduceByKey(lambda a, b: a + b)!
! >>> counts.collect()!
! [(1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (4, 4), (5, 5)]!
!
GroupByKey([numTasks])
! >>> for key, values in pairs.groupByKey().collect():!
! ... ! print "%s : %s" % (key, list(values))!
! 1 : [1]!
! 2 : [1, 1]!
! 3 : [1, 1, 1]!
!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparkmeetup1introtospark-141126210613-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-Spark-21-320.jpg)
![RDDs Actions Examples (1)
reduce(func)!
! >>> myList = [1,2,3,4,5]!
! >>> myRDD = sc.parallelize(myList)!
! >>> myRDD.reduce(lambda x,y: x+y)!
! 15!
!
collect()
! >>> myList = [1,2,3,4,5]
! >>> myRDD = sc.parallelize(myList)!
! >>> myRDD.collect()!
! [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparkmeetup1introtospark-141126210613-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-Spark-22-320.jpg)
![RDDs Actions Examples (2)
count()!
! >>> myList = [1,2,3,4,5]
! >>> myRDD = sc.parallelize(myList)!
! >>> myRDD.count()!
! 5!
!
take(3)!
! >>> myList = [1,2,3,4,5]
! >>> myRDD = sc.parallelize(myList)!
! >>> myRDD.take(3)!
! [1, 2, 3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparkmeetup1introtospark-141126210613-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-Spark-23-320.jpg)





![Wordcount Example (1)
Hadoop MapReduce Spark Scala
//package org.myorg;!
import java.io.IOException;!
i!mport java.util.*;!
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;!
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.*;!
import org.apache.hadoop.io.*;!
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.*;!
i!mport org.apache.hadoop.util.*;!
public class WordCount {! !!
public static class Map extends MapReduceBase implements Mapper<LongWritable, Text,
Text, IntWritable> {!
! ! private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);!
!! ! private Text word = new Text();!
! ! public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, OutputCollector<Text,
IntWritable> output, Reporter reporter) throws IOException {!
! ! ! String line = value.toString();!
! ! ! StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(line);!
! ! ! while (tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {!
! ! ! ! word.set(tokenizer.nextToken());!
! ! ! ! output.collect(word, one);!
! ! ! }!
! ! }!
! }! !!
public static class Reduce extends MapReduceBase implements Reducer<Text,
IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {!
! ! public void reduce(Text key, Iterator<IntWritable> values,
OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output, Reporter reporter) throws IOException {!
! ! ! int sum = 0;!
! ! ! while (values.hasNext()) {!
! ! ! ! sum += values.next().get();!
! ! ! }!
! ! ! output.collect(key, new IntWritable(sum));!
! ! }!
! }! !!
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {!
! ! JobConf conf = new JobConf(WordCount.class);!
!! ! conf.setJobName("wordcount");!
! ! conf.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);!
!! ! conf.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);!
! ! conf.setMapperClass(Map.class);!
! ! //conf.setCombinerClass(Reduce.class);!
!! ! conf.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);!
! ! conf.setInputFormat(TextInputFormat.class);!
!! ! conf.setOutputFormat(TextOutputFormat.class);!
! ! FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(conf, new Path(args[0]));!
!! ! FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(conf, new Path(args[1]));!
! ! JobClient.runJob(conf);!
! }!
val file = spark.textFile("hdfs://...")val counts = file.flatMap(line => line..map(word => (word, .reduceByKey(_ + _)!
counts.saveAsTextFile("hdfs://...")
Spark Python
file = spark.textFile("hdfs://...")!
counts = file.flatMap(lambda line: line.split(" .map(lambda word: (word, 1)) !
.reduceByKey(lambda a, b: a + b)!
counts.saveAsTextFile("hdfs://...")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparkmeetup1introtospark-141126210613-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-Spark-30-320.jpg)
![Wordcount Example (2)
$ bin/pyspark --master local[2]
!
Welcome to
____ __
/ __/__ ___ _____/ /__
_ / _ / _ `/ __/ '_/
/__ / .__/_,_/_/ /_/_ version 1.1.0
/_/
!
Using Python version 2.7.3 (v2.7.3:70274d53c1dd, Apr 9 2012 20:52:43)
SparkContext available as sc.
>>>
--driver-memory MEM Memory for driver (e.g. 1000M, 2G) (Default: 512M).
--master MASTER_URL spark://host:port, mesos://host:port, yarn, or local.
--executor-memory MEM Memory per executor (e.g. 1000M, 2G) (Default: 1G).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparkmeetup1introtospark-141126210613-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-Spark-31-320.jpg)
![Wordcount Example (3)
>>> file = sc.textFile("file:///Users/ltsai/Downloads/spark-1.1.0-bin-hadoop2.4/README.md").cache()
14/11/25 15:33:14 INFO MemoryStore: ensureFreeSpace(163705) called with curMem=327410,
maxMem=278302556
14/11/25 15:33:14 INFO MemoryStore: Block broadcast_2 stored as values in memory (estimated size 159.9 KB,
free 264.9 MB)
!
>>> file.count()
14/11/25 15:33:34 INFO DAGScheduler: Stage 0 (count at <stdin>:1) finished in 2.185 s
14/11/25 15:33:34 INFO SparkContext: Job finished: count at <stdin>:1, took 2.301952 s
141
!
>>> counts = file.flatMap(lambda line: line.split())
... .map(lambda word: (word, 1))
... .reduceByKey(lambda a, b: a + b)
!
>>> counts.take(5)
[(u'email,', 1), (u'Contributing', 1), (u'webpage', 1), (u'when', 3), (u'<http://spark.apache.org/
documentation.html>.', 1)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparkmeetup1introtospark-141126210613-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-Spark-32-320.jpg)