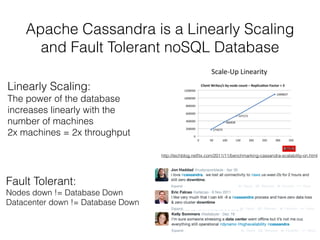
- Apache Cassandra is a linearly scalable and fault tolerant NoSQL database that increases throughput linearly with additional machines
- It is an AP system that is eventually consistent according to the CAP theorem, sacrificing consistency in favor of availability and partition tolerance
- Cassandra uses replication and consistency levels to control fault tolerance at the server and client levels respectively
- Its data model and use of SSTables allows for fast writes and queries along clustering columns