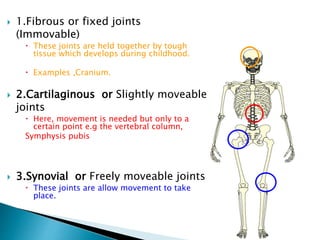
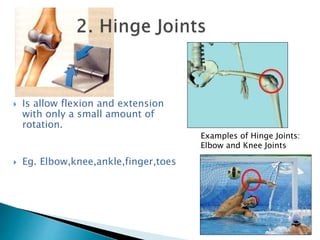
This document discusses the classification and types of joints in the human body. It defines a joint as the site where two or more bones articulate. There are three main types of joints: fibrous or fixed joints which are immovable; cartilaginous or slightly movable joints, such as those in the vertebral column; and synovial or freely movable joints which allow the greatest range of motion, such as the ball and socket shoulder and hip joints. Within synovial joints there are six classifications that differ in their motion: ball and socket, hinge, pivot, gliding, saddle, and condyloid.