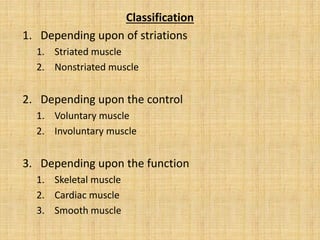
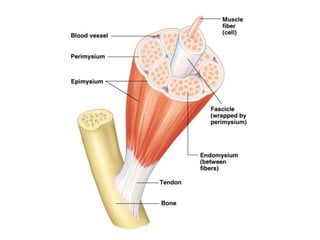
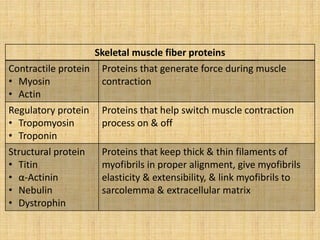
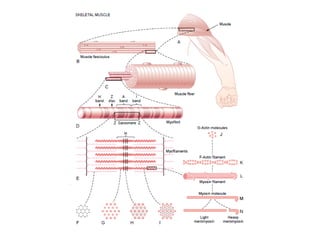
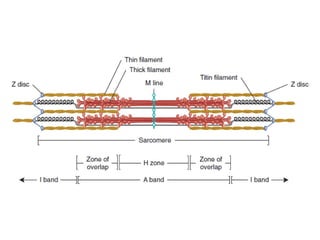
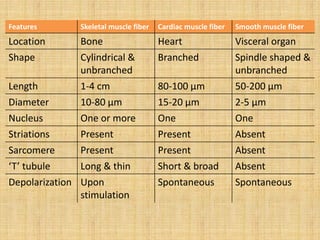
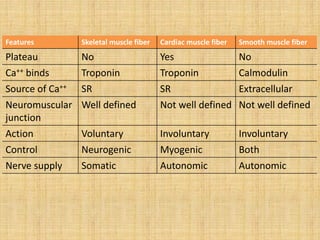
This document summarizes the key properties and functions of the three main types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. It describes their locations, structures, contraction mechanisms, and functions. Skeletal muscle is striated and voluntary, attaching to bones via tendons to enable movement. Cardiac muscle is also striated and pumps blood throughout the body. Smooth muscle is non-striated and involuntary, found in organs to enable processes like digestion. The document provides detailed descriptions of muscle fibers, sarcomeres, calcium handling, and more.