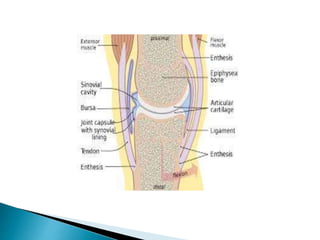
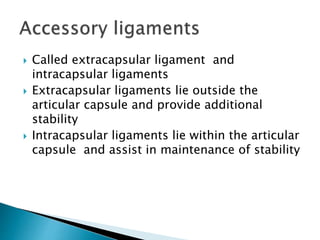
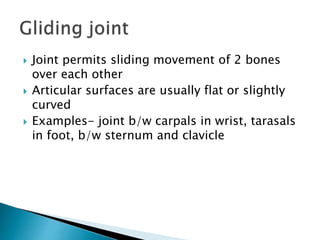
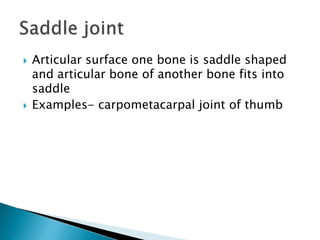
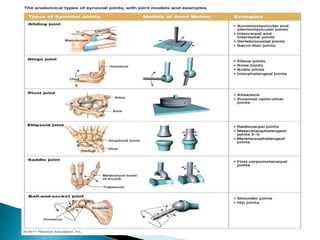
This document discusses the classification and structure of joints in the human body. It describes three types of joints: fibrous joints, cartilaginous joints, and synovial joints. Synovial joints are the most common and include ball-and-socket joints, hinge joints, pivot joints, gliding joints, condyloid joints, and saddle joints. These joints are characterized by an articular capsule containing synovial fluid that lubricates and nourishes the joint structures to allow movement.