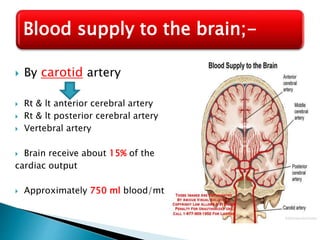
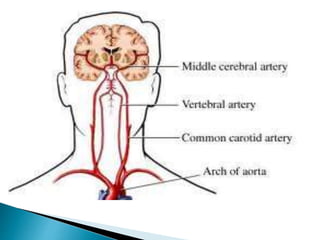
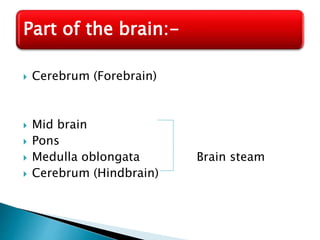
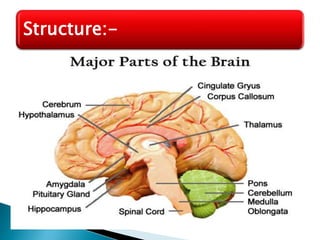
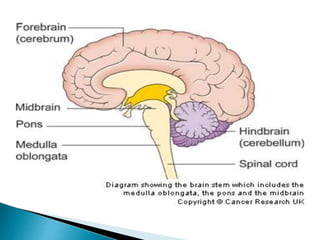
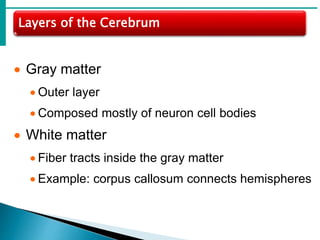
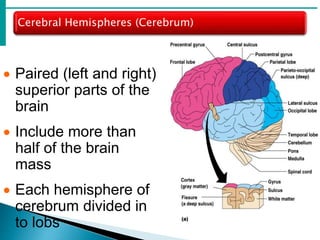
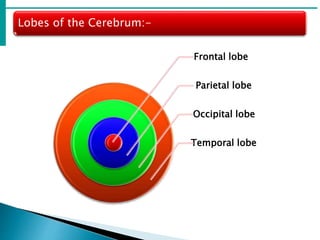
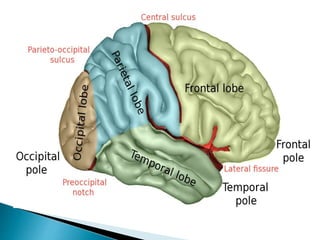
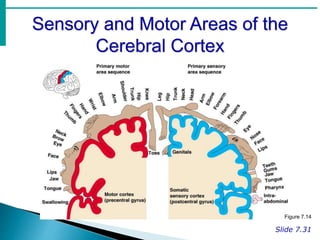
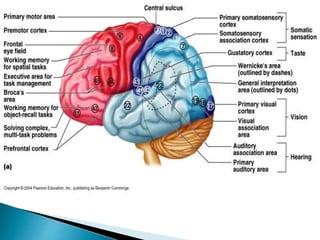
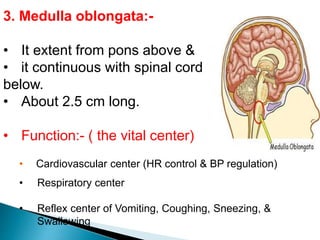
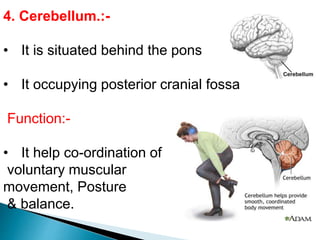
The brain is the largest mass of nervous tissue in the body and lies within the cranial cavity. It receives around 15% of cardiac output and weighs approximately 1380g in males and 1250g in females. The brain is made up of the cerebrum, brain stem, and cerebellum. The cerebrum is the largest part and is divided into four lobes - frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal - each serving different functions like reasoning, sensory processing, vision, and hearing/memory respectively. The brain stem connects the brain and spinal cord and contains the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata which are responsible for sensory/motor functions and vital activities like breathing and